Gene Mapping - manasquanschools
... • Genes on same chromosome may be inherited together – “linked” – patterns remain similar to parental types – ***The further apart genes are, the more they act like they are on separate chromosomes*** ...
... • Genes on same chromosome may be inherited together – “linked” – patterns remain similar to parental types – ***The further apart genes are, the more they act like they are on separate chromosomes*** ...
Name: Biology I: Chapter 14 Guided Reading Chapter 12.4 When
... Disorders that happen among sex-chromosomes can also occur. In females nondisjunction can lead to _____________________________. A female with this disorder usually inherits only _______ X chromosome. These women are ____________ which means that they are unable to _________________. Their sex organ ...
... Disorders that happen among sex-chromosomes can also occur. In females nondisjunction can lead to _____________________________. A female with this disorder usually inherits only _______ X chromosome. These women are ____________ which means that they are unable to _________________. Their sex organ ...
NAME: ______ ASSIGNMENT 1. and 2. DUE:_Monday, January 14
... Replication of all the chromosomal DNA occurs _____. (p. 239) whenever a cell makes protein to repair gene damage caused by mutation before a cell divides whenever a cell needs RNA in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell ...
... Replication of all the chromosomal DNA occurs _____. (p. 239) whenever a cell makes protein to repair gene damage caused by mutation before a cell divides whenever a cell needs RNA in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell ...
Karyotypes
... All living organisms store their genetic instruction manual in molecules of DNA. Although the specific sequence of bases may differ from species to species, the structure of DNA is consistent among all living organisms. The DNA is arranged in long molecules that are called chromosomes. Your chromoso ...
... All living organisms store their genetic instruction manual in molecules of DNA. Although the specific sequence of bases may differ from species to species, the structure of DNA is consistent among all living organisms. The DNA is arranged in long molecules that are called chromosomes. Your chromoso ...
Biology Final Review Sheet
... What percentage of all species that lived on Earth is estimated to be extinct? What is fitness? What is adaptation? According to Darwin’s principle of common descent, species have descended from a commo ...
... What percentage of all species that lived on Earth is estimated to be extinct? What is fitness? What is adaptation? According to Darwin’s principle of common descent, species have descended from a commo ...
Exam V Study Guide
... plants at an abbey? The archetype, or type specimen, the organism made up of the most common forms of traits found in nature, is also referred to as the? When a gene for a given trait comes in alternative versions that specify different forms of the trait (for example, purple flower and white flower ...
... plants at an abbey? The archetype, or type specimen, the organism made up of the most common forms of traits found in nature, is also referred to as the? When a gene for a given trait comes in alternative versions that specify different forms of the trait (for example, purple flower and white flower ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... a) F1 generation i. All plants had purple flowers ii. Heterozygous – both traits b) F2 – Some purple, some white ...
... a) F1 generation i. All plants had purple flowers ii. Heterozygous – both traits b) F2 – Some purple, some white ...
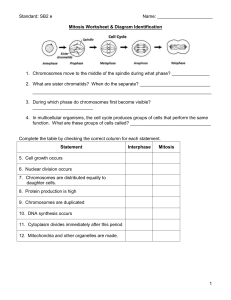
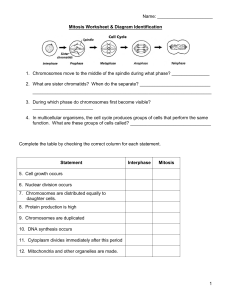
Mitosis Diagram Worksheet
... 18. What two main changes are taking place in cell B? ____________________________ 19. Sequence the six diagrams in order from first to last. ___________________________ 20. What is the end product of mitosis? ________________________________________ 21. What is the main difference between cytokines ...
... 18. What two main changes are taking place in cell B? ____________________________ 19. Sequence the six diagrams in order from first to last. ___________________________ 20. What is the end product of mitosis? ________________________________________ 21. What is the main difference between cytokines ...
Meiosis - Down the Rabbit Hole
... Reproduction where the genetic material combined is called sexual reproduction Two cells, a sperm and an egg, unite to form a zygote, the single cell from which the organism develops Meiosis is the process of producing sperm and eggs (gametes) – the number of chromosomes are halved ...
... Reproduction where the genetic material combined is called sexual reproduction Two cells, a sperm and an egg, unite to form a zygote, the single cell from which the organism develops Meiosis is the process of producing sperm and eggs (gametes) – the number of chromosomes are halved ...
Reproduction of Organisms
... chromosomes are formed. Meiosis results in egg and sperm cells (sex cells—gametes) in plants and animals and spores in some plant cells. Meiosis is very much like mitosis except the cell divides twice resulting in haploid daughter cells (they have half as much genetic material as the parent cell ...
... chromosomes are formed. Meiosis results in egg and sperm cells (sex cells—gametes) in plants and animals and spores in some plant cells. Meiosis is very much like mitosis except the cell divides twice resulting in haploid daughter cells (they have half as much genetic material as the parent cell ...
Study = Practice with your BRAIN!
... A cell containing a complete set of homologous chromosomes pairs. ...
... A cell containing a complete set of homologous chromosomes pairs. ...
Recombination is the principal source of variation in asexually
... 75. An example of complementary base pairing in the DNA double helix is a) A with T. b) T with C. c) 3’ hydroxyl with 5’ phosphate. d) free basing. 76. A chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule complexed with proteins. a) T b) F 77. If an organism is 2n = 2x = 20 and the haploid genome size is ...
... 75. An example of complementary base pairing in the DNA double helix is a) A with T. b) T with C. c) 3’ hydroxyl with 5’ phosphate. d) free basing. 76. A chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule complexed with proteins. a) T b) F 77. If an organism is 2n = 2x = 20 and the haploid genome size is ...
Mitosis/meiosis study guide
... 8. Describe how cancer and tumors happen. 9. What is the p53 gene? 10. What are the daughter cells that come from meiosis called? How do the amounts and sizes differ between males and females? 11. During sexual reproduction, the male and female sex cells combine to form what cell? 12. What is the di ...
... 8. Describe how cancer and tumors happen. 9. What is the p53 gene? 10. What are the daughter cells that come from meiosis called? How do the amounts and sizes differ between males and females? 11. During sexual reproduction, the male and female sex cells combine to form what cell? 12. What is the di ...
BIO101 Unit 4
... union of the sperm nucleus and the egg nucleus which creates the zygote with a diploid number of chromosomes. gamete a haploid sex cell; the egg or sperm which contain one-half the normal number of chromosomes; the egg unites with a sperm to form the zygote during fertilization. gastrula an early cl ...
... union of the sperm nucleus and the egg nucleus which creates the zygote with a diploid number of chromosomes. gamete a haploid sex cell; the egg or sperm which contain one-half the normal number of chromosomes; the egg unites with a sperm to form the zygote during fertilization. gastrula an early cl ...
Evolution- Speciation (Zygotic) Barriers PPT Lecture
... Species that breed at different times of the day, different seasons, or different years cannot mix their ...
... Species that breed at different times of the day, different seasons, or different years cannot mix their ...
4.1 Le Noyau
... • Everything that occurs within a cell is the result of how the bases on the DNA molecule are arranged. • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
... • Everything that occurs within a cell is the result of how the bases on the DNA molecule are arranged. • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
Mitosis Worksheet
... 3. During which phase do chromosomes first become visible? ________________________ 4. In multicellular organisms, the cell cycle produces groups of cells that perform the same function. What are these groups of cells called? ________________________________ ...
... 3. During which phase do chromosomes first become visible? ________________________ 4. In multicellular organisms, the cell cycle produces groups of cells that perform the same function. What are these groups of cells called? ________________________________ ...
Variation and Evolution notes
... •Evolution can only take place if there is variability in a population. •There are two ways this can happen. ...
... •Evolution can only take place if there is variability in a population. •There are two ways this can happen. ...
1 •Mitosis •Meiosis •Sex and Genetic Variability •Cloning
... • Reduced VARIABILITY • Reduced ADAPTABILITY • No Need for TWO different sexes! ...
... • Reduced VARIABILITY • Reduced ADAPTABILITY • No Need for TWO different sexes! ...
ch 10 notes - Redlands High School
... For humans there are 23 pairs of chromosomes Since any possible male gamete can fertilize any possible female gamete, then the possible combinations are (x) X = more than 70 trillion (without considering the effects of crossing over) ...
... For humans there are 23 pairs of chromosomes Since any possible male gamete can fertilize any possible female gamete, then the possible combinations are (x) X = more than 70 trillion (without considering the effects of crossing over) ...
Name
... the genotype________________. We show it by using __CAPITOL__ letters. Recessive gene – The trait that will show up only when _it is the only allele present (no dominant allele to “take over). We show it by using _lowercase_letters. Answer: Where do an organism’s traits come from? Directly from _par ...
... the genotype________________. We show it by using __CAPITOL__ letters. Recessive gene – The trait that will show up only when _it is the only allele present (no dominant allele to “take over). We show it by using _lowercase_letters. Answer: Where do an organism’s traits come from? Directly from _par ...
Mitosis
... Bell Work RHLT1: I can explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the passing of information from parent to offspring. 1. Why do you think it is important for your body cells to reproduce? Answer with at least 2 sentences. ...
... Bell Work RHLT1: I can explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the passing of information from parent to offspring. 1. Why do you think it is important for your body cells to reproduce? Answer with at least 2 sentences. ...
userfiles/1290/Genetics Review Sheet - Answer Key
... the genotype________________. We show it by using __CAPITAL__ letters. Recessive gene – The trait that will show up only when _it is the only allele present (no dominant allele to “take over). We show it by using _lowercase_letters. Answer: Where do an organism’s traits come from? Directly from _par ...
... the genotype________________. We show it by using __CAPITAL__ letters. Recessive gene – The trait that will show up only when _it is the only allele present (no dominant allele to “take over). We show it by using _lowercase_letters. Answer: Where do an organism’s traits come from? Directly from _par ...
History of Genetics
... • ___________ contains all the genetic instructions to create all the cells in your body. • What Does DNA stand For? ...
... • ___________ contains all the genetic instructions to create all the cells in your body. • What Does DNA stand For? ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.