Chapter 2
... Week 12- Circulatory system begins to function, heart has been beating almost two months Week 16- Movement felt by the mother Week 22-28- Age of viability ...
... Week 12- Circulatory system begins to function, heart has been beating almost two months Week 16- Movement felt by the mother Week 22-28- Age of viability ...
Keystone Review Question
... plants that resist insect pests and bacterial and fungal infections. Which outcome would most likely be a reason why some scientists recommend caution in planting genetically modified plants? ...
... plants that resist insect pests and bacterial and fungal infections. Which outcome would most likely be a reason why some scientists recommend caution in planting genetically modified plants? ...
Name
... In the Inquiry Warm-Up, you investigated how many chromosomes there are in each cell of a person who has Down syndrome. Using what you learned from that activity, answer the questions below. ...
... In the Inquiry Warm-Up, you investigated how many chromosomes there are in each cell of a person who has Down syndrome. Using what you learned from that activity, answer the questions below. ...
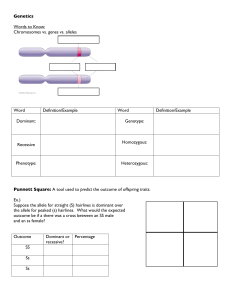
Practice with Punnett Squares
... CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus of a cell. It consists of DNA and proteins. A chromosome contains smaller segments called GENES. GENE- A segment of a chromosome that determines a particular trait of an organism by coding for specific proteins. GAMETE- Egg and sperm cells (sex cells). T ...
... CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus of a cell. It consists of DNA and proteins. A chromosome contains smaller segments called GENES. GENE- A segment of a chromosome that determines a particular trait of an organism by coding for specific proteins. GAMETE- Egg and sperm cells (sex cells). T ...
Name: Class: Date: Asexual Reproduction Section Quiz Choose the
... a. Chromosome assortment during meiosis is not random. b. Linked genes are located on the same chromosome. c. The physical distance between genes can be determined. d. Genes recombine independently during mitosis. _____ 2. Which observation of Morgan’s is evidence that crossing over occurs? a. Linke ...
... a. Chromosome assortment during meiosis is not random. b. Linked genes are located on the same chromosome. c. The physical distance between genes can be determined. d. Genes recombine independently during mitosis. _____ 2. Which observation of Morgan’s is evidence that crossing over occurs? a. Linke ...
LG and SC 2017 10 genetics
... SC22 I can explain the processes involved in natural selection including variation, isolation, adaptation and selection. SC23 I can recognise that biodiversity is a result of evolutionary processes. SC24 I can investigate changes caused by natural selection in a particular population as a result of ...
... SC22 I can explain the processes involved in natural selection including variation, isolation, adaptation and selection. SC23 I can recognise that biodiversity is a result of evolutionary processes. SC24 I can investigate changes caused by natural selection in a particular population as a result of ...
CHAPTER 15
... As a consequence, females consist of a mosaic of two types of cells, some with an active paternal X chromosome, others with an active maternal X chromosome. After an X chromosome is inactivated in a particular cell, all mitotic descendants of that cell will have the same inactive X. If a female ...
... As a consequence, females consist of a mosaic of two types of cells, some with an active paternal X chromosome, others with an active maternal X chromosome. After an X chromosome is inactivated in a particular cell, all mitotic descendants of that cell will have the same inactive X. If a female ...
Klinefelter Syndrome - Western States Genetics Services Collaborative
... chromosomes means that the baby will be born with both male and female sex organs (ambiguous genitalia), or that their child will be homosexual. These conditions are no more likely to happen in a child with a change in the sex chromosomes than in someone with the typical sex chromosomes. For some pe ...
... chromosomes means that the baby will be born with both male and female sex organs (ambiguous genitalia), or that their child will be homosexual. These conditions are no more likely to happen in a child with a change in the sex chromosomes than in someone with the typical sex chromosomes. For some pe ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... “Chromosomes have attracted many microscopists not only because these sausage-like bodies represent vehicles of genetic material (and hence, are biologically important) but also because they are hypnotically beautiful objects” (Hsu 1979). The first cytologist who described chromosome behavior during ...
... “Chromosomes have attracted many microscopists not only because these sausage-like bodies represent vehicles of genetic material (and hence, are biologically important) but also because they are hypnotically beautiful objects” (Hsu 1979). The first cytologist who described chromosome behavior during ...
PDF of PPT
... • Speciation occurs along two main pathways: geographic separation ( allopatric s peciation) and through mechanisms that occur within a shared h abitat ( sympatric speciation). Both p athways force reproductive isolation b ...
... • Speciation occurs along two main pathways: geographic separation ( allopatric s peciation) and through mechanisms that occur within a shared h abitat ( sympatric speciation). Both p athways force reproductive isolation b ...
Biology B Final Review ANSWERS
... A. They pass on to their offspring new characteristics they acquired during their lifetimes. B. They are better adapted to exist in their environment than others. C. They do not pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes. D. They tend to produce fewer of ...
... A. They pass on to their offspring new characteristics they acquired during their lifetimes. B. They are better adapted to exist in their environment than others. C. They do not pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes. D. They tend to produce fewer of ...
Biology B Final Review ANSWERS
... Proteins are chains of amino acids bonded together. Which is the correct sequence for making proteins? A. Information in DNA is formed into protein directly. B. Information in RNA uses thermal energy to make protein. C. Information in RNA mutates into DNA and then is made into protein. D. Informatio ...
... Proteins are chains of amino acids bonded together. Which is the correct sequence for making proteins? A. Information in DNA is formed into protein directly. B. Information in RNA uses thermal energy to make protein. C. Information in RNA mutates into DNA and then is made into protein. D. Informatio ...
The F plasmid and conjugation
... A few chromosomal genes will always be transferred as part of the F’ plasmid Can create partial diploids Merozygotes – partial diploids in which two gene copies are identical Heterogenotes – partial dipoids carrying different alleles of the same gene ...
... A few chromosomal genes will always be transferred as part of the F’ plasmid Can create partial diploids Merozygotes – partial diploids in which two gene copies are identical Heterogenotes – partial dipoids carrying different alleles of the same gene ...
LINKAGE - TYPES OF LINKAGE AND ESTIMATION OF LINKAGE
... 3. The distance between the linked genes determines the degree of strength of linkage. Closely located genes show stronger linkage that the widely located genes. 4. Linked genes do not always stay together, but are often exchanged reciprocally by cross over. Complete Linkage The genes closely locate ...
... 3. The distance between the linked genes determines the degree of strength of linkage. Closely located genes show stronger linkage that the widely located genes. 4. Linked genes do not always stay together, but are often exchanged reciprocally by cross over. Complete Linkage The genes closely locate ...
Chapter 3
... the 20 types of amino acids needed for development into a human being. The codes for each particular gene can vary, although usually they do not. Some genes have alternate versions of base pairs, with transpositions, deletions, or repetitions of base pairs not found in other versions of the same gen ...
... the 20 types of amino acids needed for development into a human being. The codes for each particular gene can vary, although usually they do not. Some genes have alternate versions of base pairs, with transpositions, deletions, or repetitions of base pairs not found in other versions of the same gen ...
12.2 Complex patterns of inheritance
... chromosomes Each gene may have more than one allele Trait usually expressed in a continuous range of variability ...
... chromosomes Each gene may have more than one allele Trait usually expressed in a continuous range of variability ...
xCh 20 genetics W11b
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
xCh 20 genetics W11
... mucus which interferes with breathing Symptoms usually appear shortly after birth. ...
... mucus which interferes with breathing Symptoms usually appear shortly after birth. ...
Name - Madison Public Schools
... the longest part of the Cell Cycle, where the cell grows it its full size, DNA replicates (doubles), and the cell prepares for division; for cells that divide, they spend 90% of the Cell Cycle in Interphase the division of the nucleus; broken into 4 parts: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophas ...
... the longest part of the Cell Cycle, where the cell grows it its full size, DNA replicates (doubles), and the cell prepares for division; for cells that divide, they spend 90% of the Cell Cycle in Interphase the division of the nucleus; broken into 4 parts: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophas ...
What is the genetic basis of complex traits? One of the most
... The statistical study of the alleles that occur in a locus and the phenotypes (traits) that they produce ...
... The statistical study of the alleles that occur in a locus and the phenotypes (traits) that they produce ...
Edexcel Core Biology - Science Website
... Animals and plants produce too many offspring. Think about how many tadpoles you see at the start of spring, and how few frogs you see at the end of spring. A lot of them die, because there is not enough food to go around. Of course they all try their best to get all the food they need, so they have ...
... Animals and plants produce too many offspring. Think about how many tadpoles you see at the start of spring, and how few frogs you see at the end of spring. A lot of them die, because there is not enough food to go around. Of course they all try their best to get all the food they need, so they have ...
Genetics Notes - Metcalfe County Schools
... • Many insects produce pheromones (chemical signals) to facilitate mating and reproduction. Scientists have discovered that pheromones, if given at a certain time in an insect’s life cycle, can confuse male insects and disrupt the mating process. Crop growers want to use this knowledge to help cont ...
... • Many insects produce pheromones (chemical signals) to facilitate mating and reproduction. Scientists have discovered that pheromones, if given at a certain time in an insect’s life cycle, can confuse male insects and disrupt the mating process. Crop growers want to use this knowledge to help cont ...
BIO 170 General Biology I
... e. They are all acceptable 9) Which is true about a population a. They can be dispersed over several continents b. They may be composed of numerous species c. They are alive at the same time d. All of the above 10) Which of the following lends evidence for evolution a. Fossils b. Homology c. Biogeog ...
... e. They are all acceptable 9) Which is true about a population a. They can be dispersed over several continents b. They may be composed of numerous species c. They are alive at the same time d. All of the above 10) Which of the following lends evidence for evolution a. Fossils b. Homology c. Biogeog ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.