PreAssessment - Boone County Schools
... DNA of the offspring is identical to that of the parent Some plants reproduce this way Requires two different parent (sex) cells. DNA of the offspring is different than that of both parents. Each time offspring are formed, a new combination of traits is passed. Advantage- variation among offspring a ...
... DNA of the offspring is identical to that of the parent Some plants reproduce this way Requires two different parent (sex) cells. DNA of the offspring is different than that of both parents. Each time offspring are formed, a new combination of traits is passed. Advantage- variation among offspring a ...
Part 1: Motivation, Basic Concepts, Algorithms
... • Crossover was originally based on the premise that highly fit individuals often share certain traits, called building blocks, in common. • For fixed-length vector individuals, a building block was often defined as a collection of genes set to certain values. • For example, perhaps parameters and n ...
... • Crossover was originally based on the premise that highly fit individuals often share certain traits, called building blocks, in common. • For fixed-length vector individuals, a building block was often defined as a collection of genes set to certain values. • For example, perhaps parameters and n ...
Chapter 4: The Period of Pregnancy and Prenatal Development
... • Two thirds of infant deaths occur during the first month after birth • What accounts for the fact that the United States is behind so many other industrialized countries in the rate of infant mortality? ...
... • Two thirds of infant deaths occur during the first month after birth • What accounts for the fact that the United States is behind so many other industrialized countries in the rate of infant mortality? ...
Psychology 30 Unit 2: Prenatal Review Questions 1. Based on the
... Define gamete (sex cells/sperm or ova), gene (basic unit of genetic info, have about 30,000), DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid, the substance that genes are made of, it determines the nature of every cell in the body and how it will function), and chromosome (rod shaped portions of DNA organized in 23 pair ...
... Define gamete (sex cells/sperm or ova), gene (basic unit of genetic info, have about 30,000), DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid, the substance that genes are made of, it determines the nature of every cell in the body and how it will function), and chromosome (rod shaped portions of DNA organized in 23 pair ...
lecture 3
... Actively reorganise gene organisation by creating, shuffling or modifying existing ...
... Actively reorganise gene organisation by creating, shuffling or modifying existing ...
Genetics - Biology Junction
... 3. Another word for a heterozygous genotype 4. Shows a 3:1 ratio of phenotypes 5. Occurs whenever both alleles for a gene are expressed 6. Generation of all hybrids produced by crossing two pure organisms 7. Plant studied by Gregor Mendel 10. Study of how characteristics are transmitted from parents ...
... 3. Another word for a heterozygous genotype 4. Shows a 3:1 ratio of phenotypes 5. Occurs whenever both alleles for a gene are expressed 6. Generation of all hybrids produced by crossing two pure organisms 7. Plant studied by Gregor Mendel 10. Study of how characteristics are transmitted from parents ...
I. The Emerging Role of Genetics and Genomics in Medicine
... 3. The gene responsible for being male is ________________________________ C. Sex Chromosomes and Their Genes 1. The X chromosome has ______________________________________ genes. 2. The Y chromosome has ______________________________________ genes. 3. The three groups of Y-linked genes are _______ ...
... 3. The gene responsible for being male is ________________________________ C. Sex Chromosomes and Their Genes 1. The X chromosome has ______________________________________ genes. 2. The Y chromosome has ______________________________________ genes. 3. The three groups of Y-linked genes are _______ ...
1.5MB - Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
... Blue trees = tall, Red trees = short In the F2 generation, short trees tend to carry “red” chromosomes where the height genes are located, taller trees tend to carry “blue” chromosomes QTL mapping use statistical methods to find these regions ...
... Blue trees = tall, Red trees = short In the F2 generation, short trees tend to carry “red” chromosomes where the height genes are located, taller trees tend to carry “blue” chromosomes QTL mapping use statistical methods to find these regions ...
Using mouse genetics to understand human disease
... Blue trees = tall, Red trees = short In the F2 generation, short trees tend to carry “red” chromosomes where the height genes are located, taller trees tend to carry “blue” chromosomes QTL mapping use statistical methods to find these regions ...
... Blue trees = tall, Red trees = short In the F2 generation, short trees tend to carry “red” chromosomes where the height genes are located, taller trees tend to carry “blue” chromosomes QTL mapping use statistical methods to find these regions ...
Problems in Prenatal Development Human Development March 12
... Hereditary Causes: Genetic blueprint has _____________________ of genes. Each person has 5 or 6 recessive genes that are _____________________ but have no effect on development. If each parent has the same imperfect gene or it’s a _______________________ gene, it may cause a birth defect. Some only ...
... Hereditary Causes: Genetic blueprint has _____________________ of genes. Each person has 5 or 6 recessive genes that are _____________________ but have no effect on development. If each parent has the same imperfect gene or it’s a _______________________ gene, it may cause a birth defect. Some only ...
course outline
... contain only two allelic variants (Aa), within the population there may be may different variants (A, a, A1, A2, A3 etc.) 2. Allelic variation can be detected through a number of means: a. electrophoresis (protein level) b. nucleic acid analysis (DNA level) ...
... contain only two allelic variants (Aa), within the population there may be may different variants (A, a, A1, A2, A3 etc.) 2. Allelic variation can be detected through a number of means: a. electrophoresis (protein level) b. nucleic acid analysis (DNA level) ...
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... into a sequence of amino acids Takes place in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm When mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, ribosomes attach to it like clothespins on a ...
... into a sequence of amino acids Takes place in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm When mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, ribosomes attach to it like clothespins on a ...
4th Quarter test
... The meadow rose (Rosa blanda), cherry tree (Prunus avium), apple tree (Malus pumila), and moss rose (Rosa centifolia) all belong to the Rosaceae Family. The 2 plants that belong to the same genus are the ___. a. b. c. d. ...
... The meadow rose (Rosa blanda), cherry tree (Prunus avium), apple tree (Malus pumila), and moss rose (Rosa centifolia) all belong to the Rosaceae Family. The 2 plants that belong to the same genus are the ___. a. b. c. d. ...
4th Quarter test A
... #24 The meadow rose (Rosa blanda), cherry tree (Prunus avium), apple tree (Malus pumila), and moss rose (Rosa centifolia) all belong to the Rosaceae Family. The 2 plants that belong to the same genus are the ___. a. b. c. d. ...
... #24 The meadow rose (Rosa blanda), cherry tree (Prunus avium), apple tree (Malus pumila), and moss rose (Rosa centifolia) all belong to the Rosaceae Family. The 2 plants that belong to the same genus are the ___. a. b. c. d. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Gene Linkage and Genetic Mapping
... Copy-number variations (CNVs) • A substantial portion of the human genome can be duplicated or deleted in much larger but still submicroscopic chunks ranging from 1 kb to 1 Mb. • This type of variation is known as copy-number variation (CNV). • The extra or missing copies of the genome in CNVs can ...
... Copy-number variations (CNVs) • A substantial portion of the human genome can be duplicated or deleted in much larger but still submicroscopic chunks ranging from 1 kb to 1 Mb. • This type of variation is known as copy-number variation (CNV). • The extra or missing copies of the genome in CNVs can ...
Review ch 11 Patterns of Inheritance
... also called X-inactivation. Example: Calico cats can only be female ...
... also called X-inactivation. Example: Calico cats can only be female ...
03 Beyond Mendel
... Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each gene has only 2 alleles, 1 of which is completely dominant to the other ...
... Mendel worked with a simple system peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each gene has only 2 alleles, 1 of which is completely dominant to the other ...
THE MID YEAR EXAM GRADE WILL BE DIVIDED 90 % FROM
... Make sure you know the following: Relate several inferences about the history of life that are supported by evidence from fossils and rocks. Explain how biogeography provides evidence that species evolve adaptations to their environments. Explain how the anatomy and development of organisms provide ...
... Make sure you know the following: Relate several inferences about the history of life that are supported by evidence from fossils and rocks. Explain how biogeography provides evidence that species evolve adaptations to their environments. Explain how the anatomy and development of organisms provide ...
chapter17_part2
... • Reproductive isolating mechanisms prevent interbreeding among species • Heritable aspects of body form, function, or behavior that arise as populations diverge • Prezygotic isolating mechanisms prevent pollination or mating • Postzygotic isolating mechanisms result in weak or infertile hybrids ...
... • Reproductive isolating mechanisms prevent interbreeding among species • Heritable aspects of body form, function, or behavior that arise as populations diverge • Prezygotic isolating mechanisms prevent pollination or mating • Postzygotic isolating mechanisms result in weak or infertile hybrids ...
Simulating Population Genetics
... [email protected] adapted from Dannie Durand [email protected] ...
... [email protected] adapted from Dannie Durand [email protected] ...
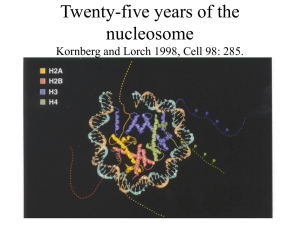
Twenty-five years of the nucleosome Kornberg and Lorch 1998, Cell
... Important point• P289- Although acetylation of histone tails may counteract condensation of nucleosomes in chromatin fibers, it is unlikely to disrupt the structure of the core particle for transcription • Why? Tails are outside of the core, make little contribution to overall structure • Chromatin ...
... Important point• P289- Although acetylation of histone tails may counteract condensation of nucleosomes in chromatin fibers, it is unlikely to disrupt the structure of the core particle for transcription • Why? Tails are outside of the core, make little contribution to overall structure • Chromatin ...
Lesson Overview
... To see human chromosomes clearly, cell biologists photograph cells in mitosis, when the chromosomes are fully condensed and easy to view Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the photographs and arrange them in a picture known as a karyotype. It shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes g ...
... To see human chromosomes clearly, cell biologists photograph cells in mitosis, when the chromosomes are fully condensed and easy to view Scientists then cut out the chromosomes from the photographs and arrange them in a picture known as a karyotype. It shows the complete diploid set of chromosomes g ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.