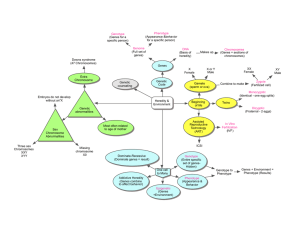
Traits: The Puppeteering of Genetics
... Example include height, weight, and skin color, cancer risk, or any trait in which multiple factors come into play (generally quantitative values) ...
... Example include height, weight, and skin color, cancer risk, or any trait in which multiple factors come into play (generally quantitative values) ...
Chromosome vs. Gene Mutations
... • Are due to a change in a single gene. • Can involve changes in several nucleotides ...
... • Are due to a change in a single gene. • Can involve changes in several nucleotides ...
Congenital And Genetic Disorders
... Sperm are either X or Y Fertilization of an egg by sperm reestablishes the diploid number of 46 and XX (female) or XY (male) sex determination. ...
... Sperm are either X or Y Fertilization of an egg by sperm reestablishes the diploid number of 46 and XX (female) or XY (male) sex determination. ...
Related Document
... children, how many of these children would most likely have extra fingers or toes? ...
... children, how many of these children would most likely have extra fingers or toes? ...
Chromosomes and Diseases - Faculty of Science at Bilkent
... • Observation: Chimps, gorillas, and orangutans have 24 pairs of chromosomes, whereas humans have 23 pairs. • Hypothesis: Common ancestor of all great apes had 24 pairs of chromosomes and that the fusion of two of the ancestor's chromosomes (chromosomes 2p and 2q) created chromosome 2 in humans ...
... • Observation: Chimps, gorillas, and orangutans have 24 pairs of chromosomes, whereas humans have 23 pairs. • Hypothesis: Common ancestor of all great apes had 24 pairs of chromosomes and that the fusion of two of the ancestor's chromosomes (chromosomes 2p and 2q) created chromosome 2 in humans ...
I. sex determination
... A. Sex chromosomes in humans are the X and Y chromosomes 1. Females are XX and males are XY a) Females are said to be homogametic (as all their gametes will have an X chromosome) and males heterogametic (producing gametes with either an X or Y chromosome) 2. All factors being equal, there is a 50% c ...
... A. Sex chromosomes in humans are the X and Y chromosomes 1. Females are XX and males are XY a) Females are said to be homogametic (as all their gametes will have an X chromosome) and males heterogametic (producing gametes with either an X or Y chromosome) 2. All factors being equal, there is a 50% c ...
Human Chromosomes Section 14–2
... human chromosomes. It also describes genetic disorders that are sex-linked, as well as disorders caused by nondisjunction. ...
... human chromosomes. It also describes genetic disorders that are sex-linked, as well as disorders caused by nondisjunction. ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide - Maples Elementary School
... The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are called ______________. What is a mutation? There are two main types of mutations? What are they? What kind of mutation is caused by a piece of DNA breaking away from its chromosome and becoming attached to a nonhomologous chromosome? What kind of mutation is cau ...
... The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are called ______________. What is a mutation? There are two main types of mutations? What are they? What kind of mutation is caused by a piece of DNA breaking away from its chromosome and becoming attached to a nonhomologous chromosome? What kind of mutation is cau ...
BY 123 SI Session #9 Chapter 15 Siby123.yolasite.com Terms to
... a. The genes are on the same chromosome, but they are more than 50 map units (50%) apart. b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of the ...
... a. The genes are on the same chromosome, but they are more than 50 map units (50%) apart. b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of the ...
Ch. 12 .1 12.2 Human Genetics Notes
... Nondisjunction in meiosis I results in all the gametes having abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Nondisjunction in meiosis II results in two normal gametes and two abnormal gametes. (Note that for simplicity only two pairs of homologous chromosomes are shown rather than all 23 pairs.) ...
... Nondisjunction in meiosis I results in all the gametes having abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Nondisjunction in meiosis II results in two normal gametes and two abnormal gametes. (Note that for simplicity only two pairs of homologous chromosomes are shown rather than all 23 pairs.) ...
Chromosome Theory of Inheritance -States that genes or alleles
... -The less often a gene crosses over with another one, the closer it must be to it, so if the frequency is low, the distance between the two must be small ...
... -The less often a gene crosses over with another one, the closer it must be to it, so if the frequency is low, the distance between the two must be small ...
The Chromosomal Basis for Inheritance Thomas Hunt Morgan Early
... Let b+ = gray body and b = black body. Let vg+ = normal wings and vg = vestigial wings What is the expected phenotype ratios if a fly heterozygous for both traits is crossed with one that is homozygous recessive for both traits? ...
... Let b+ = gray body and b = black body. Let vg+ = normal wings and vg = vestigial wings What is the expected phenotype ratios if a fly heterozygous for both traits is crossed with one that is homozygous recessive for both traits? ...
Mutations - Kaikoura High School
... immediately and properly repaired. • If they occur in somatic cells then they are non-inheritable, if in gametes then can be passed on to offspring. • Can be due to mistakes in DNA replication (spontaneous) or caused by mutagenic agents e.g. UV light, ionising radiation, Xrays, chemicals, viruses ...
... immediately and properly repaired. • If they occur in somatic cells then they are non-inheritable, if in gametes then can be passed on to offspring. • Can be due to mistakes in DNA replication (spontaneous) or caused by mutagenic agents e.g. UV light, ionising radiation, Xrays, chemicals, viruses ...
View Ch. 13 PowerPoint here.
... • Human genetic disorders show sex linkage when the relevant gene is on the X chromosome. • An example is hemophilia - Disease that affects a single protein in a cascade of proteins involved in the formation of blood clots • Form of hemophilia is caused by an X-linked recessive allele – Heterozygous ...
... • Human genetic disorders show sex linkage when the relevant gene is on the X chromosome. • An example is hemophilia - Disease that affects a single protein in a cascade of proteins involved in the formation of blood clots • Form of hemophilia is caused by an X-linked recessive allele – Heterozygous ...
aneuploidy
... Chromosome Mutations on page 308. You may not trace! It must be on PLAIN white paper!! It needs to be as large as the paper…not too small!! ...
... Chromosome Mutations on page 308. You may not trace! It must be on PLAIN white paper!! It needs to be as large as the paper…not too small!! ...
Sex-Linked Inheritance Student Notes • Sex linked inheritance
... Sex linked inheritance varies the Mendel number of __________________by having males a 50/50 percent chance of inheriting the characteristic on the X chromosome only. ...
... Sex linked inheritance varies the Mendel number of __________________by having males a 50/50 percent chance of inheriting the characteristic on the X chromosome only. ...
Human Genetic Variation - Mediapolis Community School
... What is a gene? • A gene is a functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be ...
... What is a gene? • A gene is a functional and physical unit of heredity passed from parent to offspring. • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be ...
Chap. 13 Sex Linked Inheiritance_2
... Nondisjunction of Autosomes • “Failure of homologues or sister chromatids to separate properly during meiosis” • Aneuploidy – gain or loss of a chromosome – Monosomy – loss of a chromosome – Trisomy – gain of a chromosome ...
... Nondisjunction of Autosomes • “Failure of homologues or sister chromatids to separate properly during meiosis” • Aneuploidy – gain or loss of a chromosome – Monosomy – loss of a chromosome – Trisomy – gain of a chromosome ...
Primary School Presentation - Unique The Rare Chromosome
... Every cell in the human body normally contains 23 PAIRS of chromosomes, making 46 chromosomes in total Of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in each of these cells, one member of each pair is normally inherited from the father and the other member is normally inherited from the mother. ...
... Every cell in the human body normally contains 23 PAIRS of chromosomes, making 46 chromosomes in total Of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in each of these cells, one member of each pair is normally inherited from the father and the other member is normally inherited from the mother. ...
X-linked Inheritance - Great Ormond Street Hospital
... Sometimes these altered genes are passed from a parent to a child; sometimes they develop within an individual as a result of a copying mistake when cells divide. In the laboratory we are not yet able to test very many genes though the number of available tests is growing fast. Genes are arranged al ...
... Sometimes these altered genes are passed from a parent to a child; sometimes they develop within an individual as a result of a copying mistake when cells divide. In the laboratory we are not yet able to test very many genes though the number of available tests is growing fast. Genes are arranged al ...
The DNA molecule exits for most of the cell cycle as
... Homologous chromosomes - contrasting chromosomes of same type, one from each parent. Chromatid - one half of the "X" chromosome shape. The two halves are sister chromatids and exact copies of each other. They will go to separate daughter cells during meiosis. Centromere - protein band that joins the ...
... Homologous chromosomes - contrasting chromosomes of same type, one from each parent. Chromatid - one half of the "X" chromosome shape. The two halves are sister chromatids and exact copies of each other. They will go to separate daughter cells during meiosis. Centromere - protein band that joins the ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)