Chapter 9 - Advanced Biology
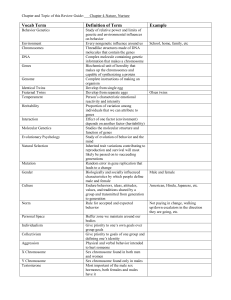
... If a cell has a complete set with pairs matched up = diploid number (2n) Gamete with ½ of each pair = haploid number (n) ...
... If a cell has a complete set with pairs matched up = diploid number (2n) Gamete with ½ of each pair = haploid number (n) ...
Human Genetics and Pedigrees
... There are several sex-linked genetic disorders. Colorblindness Hemophilia Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy ...
... There are several sex-linked genetic disorders. Colorblindness Hemophilia Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy ...
Y Chromosome: Unraveling the Mystery and Exploring
... Q2: What does the Y do? A2: The Y codes for male anatomical features, sperm production, and regulation of some autosomal genes Q3: What can we learn from the Y chromosome? ...
... Q2: What does the Y do? A2: The Y codes for male anatomical features, sperm production, and regulation of some autosomal genes Q3: What can we learn from the Y chromosome? ...
Chapter 15~ The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance ______
... – Duchenne muscular dystropy (MD) – hemophilia X-inactivation: 2nd X chromosome in females condenses into a Barr body ...
... – Duchenne muscular dystropy (MD) – hemophilia X-inactivation: 2nd X chromosome in females condenses into a Barr body ...
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis–Inheritance Connection
... • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Ensures an equal expression of genes from the sex chromosomes even though females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
... • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Ensures an equal expression of genes from the sex chromosomes even though females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
The end of the male gene pool?
... Y chromosome was bound for oblivion. Hope may be at hand, though. Writing in the latest issue of Nature, Jennifer Hughes and her colleagues at the Whitehead lnstitute for Biomedical Research at MIT come out in support of the Y chromosome's chances of survival. "We can confidently say that the decay ...
... Y chromosome was bound for oblivion. Hope may be at hand, though. Writing in the latest issue of Nature, Jennifer Hughes and her colleagues at the Whitehead lnstitute for Biomedical Research at MIT come out in support of the Y chromosome's chances of survival. "We can confidently say that the decay ...
Clicker review
... C incomplete dominance D Both A and B E Both B and C 3 Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, pancreas, digestive system, and other organs resulting in symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to recurrent infections. This is an example of______________. A epistasis B pleiotropy C multiple alleles D ...
... C incomplete dominance D Both A and B E Both B and C 3 Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, pancreas, digestive system, and other organs resulting in symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to recurrent infections. This is an example of______________. A epistasis B pleiotropy C multiple alleles D ...
chapter 6 vocabulary card sort
... chromosomes not directly involved in determining the sex (gender) of an individual ...
... chromosomes not directly involved in determining the sex (gender) of an individual ...
Karyotyping
... abnormalities from malformation or disease. It examines the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a certain sample of cells. Extra, missing, or abnormal positions of chromosome pieces can cause problems with a person’s growth, development, and body functions. A few of the abnormalities that can ...
... abnormalities from malformation or disease. It examines the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a certain sample of cells. Extra, missing, or abnormal positions of chromosome pieces can cause problems with a person’s growth, development, and body functions. A few of the abnormalities that can ...
Ch 3 Sec3
... during the formation of sex cells – Discovered that grasshopper’s sex cells have half the number of chromosomes as their regular body cells. – One chromosome in each pair came from each parent. ...
... during the formation of sex cells – Discovered that grasshopper’s sex cells have half the number of chromosomes as their regular body cells. – One chromosome in each pair came from each parent. ...
Chapter 11 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - An
... Not all genes on X chromosome are involved in sex determination (Fig 15.9). Genes on sex chromosomes are said to be sex-linked (X-linked or Y-linked) Examples of Recessive X-linked disorders: o 1. Hemophilia defined by lack of a protein involved in blood clotting. plagued much of royal families ...
... Not all genes on X chromosome are involved in sex determination (Fig 15.9). Genes on sex chromosomes are said to be sex-linked (X-linked or Y-linked) Examples of Recessive X-linked disorders: o 1. Hemophilia defined by lack of a protein involved in blood clotting. plagued much of royal families ...
File
... deleted. Known disorders in humans include WolfHirschhorn syndrome, which is caused by partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 4; Cri du chat syndrome is due to a partial deletion of the short are of chromosome number 5. ...
... deleted. Known disorders in humans include WolfHirschhorn syndrome, which is caused by partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 4; Cri du chat syndrome is due to a partial deletion of the short are of chromosome number 5. ...
Sex Linked Traits
... • One pair of chromosomes is related to the sex of an individual , these chromosomes are called sex chromosomes ...
... • One pair of chromosomes is related to the sex of an individual , these chromosomes are called sex chromosomes ...
Faithful meiotic chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
... Meiosis is the specialized cell division that is essential for the generation of haploid germ cells. It not only compensates for the doubling of chromosome number after fertilization but also generates genetic diversity by reciprocal exchange of paternal and maternal chromosome portions. Defects in ...
... Meiosis is the specialized cell division that is essential for the generation of haploid germ cells. It not only compensates for the doubling of chromosome number after fertilization but also generates genetic diversity by reciprocal exchange of paternal and maternal chromosome portions. Defects in ...
Chapter 4 - Nature v. Nurture and Evolution
... Complex molecule containing genetic information that makes a chromosome Biochemical unit of heredity that makes up the chromosomes and capable of synthesizing a protein Complete instructions of making an organism Develop from single egg Develop from separate eggs Person’s characteristic emotional re ...
... Complex molecule containing genetic information that makes a chromosome Biochemical unit of heredity that makes up the chromosomes and capable of synthesizing a protein Complete instructions of making an organism Develop from single egg Develop from separate eggs Person’s characteristic emotional re ...
File
... Fathers pass X-linked alleles to only and all of their daughters. Males receive their X chromosome only from their mothers. Therefore, fathers cannot pass sex-linked traits to their sons. Mothers can pass sex-linked alleles to both sons and daughters. Females receive two X chromosomes, one from ...
... Fathers pass X-linked alleles to only and all of their daughters. Males receive their X chromosome only from their mothers. Therefore, fathers cannot pass sex-linked traits to their sons. Mothers can pass sex-linked alleles to both sons and daughters. Females receive two X chromosomes, one from ...
Genetics Lecture Part 2
... Different chromosomal systems for sex discrimination A. Inheritance of sex linked genes (on X or Y) a. Color blindness b. Hemophilia: missing one or more blood clotting protein c. Duchene muscular dystrophy : weakening of the muscles and loss of coordination due to the absence of a key muscle protei ...
... Different chromosomal systems for sex discrimination A. Inheritance of sex linked genes (on X or Y) a. Color blindness b. Hemophilia: missing one or more blood clotting protein c. Duchene muscular dystrophy : weakening of the muscles and loss of coordination due to the absence of a key muscle protei ...
LEQ: How do the events of meiosis account for Mendel`s laws?
... Easy to care for Lots of offspring Quick generation time ...
... Easy to care for Lots of offspring Quick generation time ...
4.3.5 Sex Chromosomes and Sex Linkage Questions
... Each person normally has one pair of sex chromosomes in each cell. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. The X chromosome contains about 1000 genes, including the genes for haemophilia and colour blindness. For this reason these genes are said to be sex-linked. ...
... Each person normally has one pair of sex chromosomes in each cell. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. The X chromosome contains about 1000 genes, including the genes for haemophilia and colour blindness. For this reason these genes are said to be sex-linked. ...
chapter 13 lecture slides
... the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
... the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
What is the difference between Autotrophs and heterotrophs?
... a. separation of alleles during gamete formation b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g ...
... a. separation of alleles during gamete formation b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g ...
when a woman is color blind ______.
... since both identical twins always either suffer the disease or do not may have genetic susceptibilities but do not appear to be caused by a single gene. appear to be caused by an autosomal-dominant gene appear to have some sex linkage since men suffer NBDs more often than women ...
... since both identical twins always either suffer the disease or do not may have genetic susceptibilities but do not appear to be caused by a single gene. appear to be caused by an autosomal-dominant gene appear to have some sex linkage since men suffer NBDs more often than women ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)