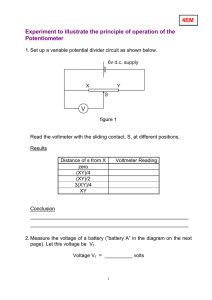
Exercise 3
... 1. Measure and record the voltage supplied to the circuit:___________________. 2. Measure and record the voltage drop across each resistor: R1:____________________ R2:____________________ R3:____________________ 3. Is it true that the sum of the voltage drops across the circuit is equal the voltage ...
... 1. Measure and record the voltage supplied to the circuit:___________________. 2. Measure and record the voltage drop across each resistor: R1:____________________ R2:____________________ R3:____________________ 3. Is it true that the sum of the voltage drops across the circuit is equal the voltage ...
Simulating a non-ideal voltage source in LTSpice
... equivalent resistance, and can be considered ideal. Batteries and solar cells however are both examples of non-ideal voltage sources, to accurately model them their internal series resistance must be included. After building the circuit to be analyzed, include the series resistance in LTSpice by rig ...
... equivalent resistance, and can be considered ideal. Batteries and solar cells however are both examples of non-ideal voltage sources, to accurately model them their internal series resistance must be included. After building the circuit to be analyzed, include the series resistance in LTSpice by rig ...
PMT Circuits
... output current (low incident light) As light intensity increases, dynode voltages begin to vary from ideal (shift to earlier stages) Region B: shift results in increased current amplification Region C: saturation occurs as voltage between last dynode and anode goes to zero. If large linear region is ...
... output current (low incident light) As light intensity increases, dynode voltages begin to vary from ideal (shift to earlier stages) Region B: shift results in increased current amplification Region C: saturation occurs as voltage between last dynode and anode goes to zero. If large linear region is ...
N45 Electronics 20Q
... • Switches on and off a separate electrical circuit which might have high current or voltage. ...
... • Switches on and off a separate electrical circuit which might have high current or voltage. ...
AC CIRCUITS : RC CIRCUIT 1. Aim 1. To study current voltage
... The RC circuit consists of a Capacitor and a Resistor connected in series supplied by a AC power supply in form of a Function Generator. As the applies signal is sinusoidal the current in each element is also sinusoidal, but are not in phase.A series combination of a resistor R and capacitor C if co ...
... The RC circuit consists of a Capacitor and a Resistor connected in series supplied by a AC power supply in form of a Function Generator. As the applies signal is sinusoidal the current in each element is also sinusoidal, but are not in phase.A series combination of a resistor R and capacitor C if co ...
Normal Distribution Problems
... Normal Distribution Problems A constant or DC current source that outputs 1 amp is connected to a resistor of nominal resistance of 1 ohm. If the resistance value can vary according to R ∼ Normal(1, 0.01), what is the probability that the voltage across the resistor will be between 0.9 and 1.1 volts ...
... Normal Distribution Problems A constant or DC current source that outputs 1 amp is connected to a resistor of nominal resistance of 1 ohm. If the resistance value can vary according to R ∼ Normal(1, 0.01), what is the probability that the voltage across the resistor will be between 0.9 and 1.1 volts ...
Slide 1
... • Resistance- the opposition to the flow of charge by a material or device. • Symbol is R, unit is ohms (W). • Ohms law R = V/I or V = IR • Resistance depends on the following factors: Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials hav ...
... • Resistance- the opposition to the flow of charge by a material or device. • Symbol is R, unit is ohms (W). • Ohms law R = V/I or V = IR • Resistance depends on the following factors: Length – short wires have less resistance Area- thick wires have less resistance Material- different materials hav ...
HP ADS SIMULATION EXAMPLE – Basic Harmonic Balance
... response of a circuit, which contains nonlinear components. The basic HB analysis is usually applied to a single periodic source. The periodic source can be sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal. The HB method works by assuming the steady state response of a circuit being driven by a periodic source is als ...
... response of a circuit, which contains nonlinear components. The basic HB analysis is usually applied to a single periodic source. The periodic source can be sinusoidal or non-sinusoidal. The HB method works by assuming the steady state response of a circuit being driven by a periodic source is als ...
Equations and Key Concepts (Excellence Project)
... Voltage is the potential or difference. It is the energy or pressure in a circuit. In S.I. units it is 1 joule/coulomb. (See p. 4). Current is the flow of electrons in a circuit. It is measured in amperes. 1 ampere = 6.24 x 1018/sec. Resistance is the tendency of a material to resist the flow of ele ...
... Voltage is the potential or difference. It is the energy or pressure in a circuit. In S.I. units it is 1 joule/coulomb. (See p. 4). Current is the flow of electrons in a circuit. It is measured in amperes. 1 ampere = 6.24 x 1018/sec. Resistance is the tendency of a material to resist the flow of ele ...
Chapter 13 Electricity!
... You have a large flashlight that takes 6 Dcell batteries. If the current in the flashlight is 2 amps, what is the resistance of the light bulb? (Hint: A D-cell battery ...
... You have a large flashlight that takes 6 Dcell batteries. If the current in the flashlight is 2 amps, what is the resistance of the light bulb? (Hint: A D-cell battery ...
circuits and current review
... 19. What are the schematic symbols for the resistor, battery cell, and connecting wire? 20. Does a battery produce dc or ac? 21. How does the total resistance of a parallel combination of resistors compare with each individual resistor? 22. How are the circuits in our home connected together? 23. Wh ...
... 19. What are the schematic symbols for the resistor, battery cell, and connecting wire? 20. Does a battery produce dc or ac? 21. How does the total resistance of a parallel combination of resistors compare with each individual resistor? 22. How are the circuits in our home connected together? 23. Wh ...
Notes18
... electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the energy in various ways such as light (light bulb) or in the form of heat ...
... electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the energy in various ways such as light (light bulb) or in the form of heat ...
Lecture
... • Maximum power transfer is obtained when load resistance is equal to the Thévenin resistance of the circuit • In some situations we need maximum voltage transfer or maximum current transfer instead of maximum power transfer. This typically requires the use of active amplifier circuits. ...
... • Maximum power transfer is obtained when load resistance is equal to the Thévenin resistance of the circuit • In some situations we need maximum voltage transfer or maximum current transfer instead of maximum power transfer. This typically requires the use of active amplifier circuits. ...
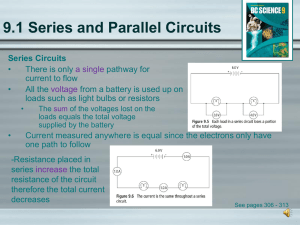
PP-Series and Parrellel circuts
... Current measured anywhere is equal since the electrons only have one path to follow -Resistance placed in series increase the total resistance of the circuit therefore the total current decreases ...
... Current measured anywhere is equal since the electrons only have one path to follow -Resistance placed in series increase the total resistance of the circuit therefore the total current decreases ...
What is a series-parallel circuit
... Voltage drops add to equal total voltage. All components share the same (equal) current. Resistances add to equal total resistance. ...
... Voltage drops add to equal total voltage. All components share the same (equal) current. Resistances add to equal total resistance. ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.