Lab 2
... upon it. They are used to make light-sensitive switching and devices. Photoresistors are often made from cadmium sulfide (CdS). The resistance of a CdS photoresistor varies inversely to the amount of light incident upon it. In other words, its resistance will be high in the dark and low in the light ...
... upon it. They are used to make light-sensitive switching and devices. Photoresistors are often made from cadmium sulfide (CdS). The resistance of a CdS photoresistor varies inversely to the amount of light incident upon it. In other words, its resistance will be high in the dark and low in the light ...
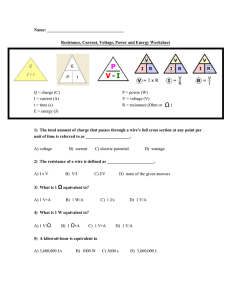
Name: Resistance, Current, Voltage, Power and Energy Worksheet
... 6) How much charge must pass by a point in 10 s for the current to be 0.50 A? A) 0.050 C ...
... 6) How much charge must pass by a point in 10 s for the current to be 0.50 A? A) 0.050 C ...
Gen2.1 SupIRBuck™ Integrated Voltage Regulators
... technologies to deliver up to 12A output current in a low profile, thermally enhanced 5x6mm Power QFN package. Capable of handling input voltages as wide as 1.5V to 16V, the new family of integrated voltage regulators is designed to deliver output voltages from 0.7V to 90% of the input voltage with ...
... technologies to deliver up to 12A output current in a low profile, thermally enhanced 5x6mm Power QFN package. Capable of handling input voltages as wide as 1.5V to 16V, the new family of integrated voltage regulators is designed to deliver output voltages from 0.7V to 90% of the input voltage with ...
Introduction to Photovoltaics Powerpoint
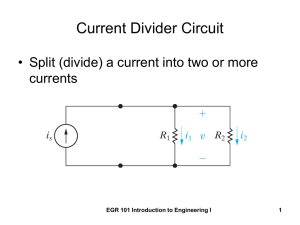
... Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
... Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
- IEEE Projects IN MADURAI
... Diode-assisted buck-boost voltage source inverter (VSI) boosts the dc source voltage by introducing diode-assisted capacitor network. With parallel capacitive charging and series capacitive discharging, the new topology extends voltage regulation range and avoids extreme duty ratio of switching devi ...
... Diode-assisted buck-boost voltage source inverter (VSI) boosts the dc source voltage by introducing diode-assisted capacitor network. With parallel capacitive charging and series capacitive discharging, the new topology extends voltage regulation range and avoids extreme duty ratio of switching devi ...
VEGEtek - 003 - Instructables
... circuit and convert it to a proportional voltage. These methods are suitable more for high current systems. Figure 2: Current transformer ...
... circuit and convert it to a proportional voltage. These methods are suitable more for high current systems. Figure 2: Current transformer ...
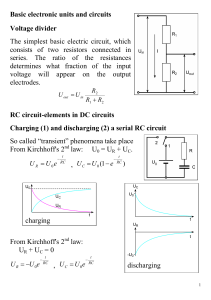
Basic electronic units and circuits Voltage divider The simplest basic
... FET (Field Effect Transistor) The controlling voltage sets the thickness of the empty layer, which can be seen in a diode. Changing the cross section area of a conductor can be used to regulate the current. The great advantage of the FET is that, practically, there is no current on the controlling e ...
... FET (Field Effect Transistor) The controlling voltage sets the thickness of the empty layer, which can be seen in a diode. Changing the cross section area of a conductor can be used to regulate the current. The great advantage of the FET is that, practically, there is no current on the controlling e ...
Two – wires method: Circuit 1. Two-wire resistance measurement, R
... RX is very small, or when very high accuracy is required. The method is immune to the influence of lead resistance and is limited by the quality of the constant current source and voltage measurement. Thermo-electric voltages can be eliminated by averaging two measurements with the polarity of the e ...
... RX is very small, or when very high accuracy is required. The method is immune to the influence of lead resistance and is limited by the quality of the constant current source and voltage measurement. Thermo-electric voltages can be eliminated by averaging two measurements with the polarity of the e ...
Circuit Analysis Vocabulary Teachers Guide
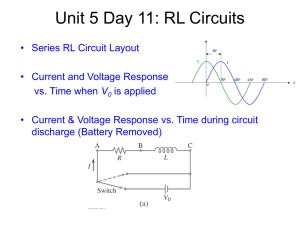
... Nodal analysis – a circuit analysis technique of using Kirchhoff’s Current Law to define the currents at nodes Mesh analysis – a circuit analysis technique of creating virtual mesh currents Superposition Theorem – States that the effects on a circuit of multiple power sources is the linear sum of th ...
... Nodal analysis – a circuit analysis technique of using Kirchhoff’s Current Law to define the currents at nodes Mesh analysis – a circuit analysis technique of creating virtual mesh currents Superposition Theorem – States that the effects on a circuit of multiple power sources is the linear sum of th ...
ECE 3041 - ECE Users Pages
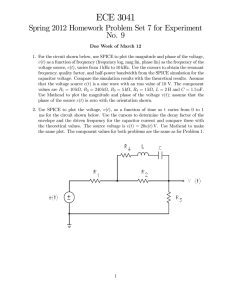
... ECE 3041 Spring 2012 Homework Problem Set 7 for Experiment No. 9 Due Week of March 12 1. For the circuit shown below, use SPICE to plot the magnitude and phase of the voltage, () as a function of frequency (frequency log, mag lin, phase lin) as the frequency of the voltage source, (), varies fro ...
... ECE 3041 Spring 2012 Homework Problem Set 7 for Experiment No. 9 Due Week of March 12 1. For the circuit shown below, use SPICE to plot the magnitude and phase of the voltage, () as a function of frequency (frequency log, mag lin, phase lin) as the frequency of the voltage source, (), varies fro ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.