Basic Electricity
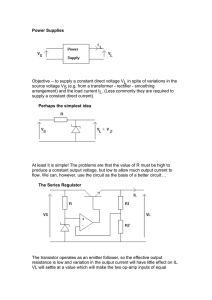
... would be 20 V ÷ 33 W = 0.61 A The power would be 0.61 × 20 V = 12 watts. Plenty enough to fry a 1 watt resistor. It is important that we ensure that any current limiting resistors can dissipate the power through them. The above situation could be highly dangerous. ...
... would be 20 V ÷ 33 W = 0.61 A The power would be 0.61 × 20 V = 12 watts. Plenty enough to fry a 1 watt resistor. It is important that we ensure that any current limiting resistors can dissipate the power through them. The above situation could be highly dangerous. ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
... 1. What happens to current if resistance is decreased? 2. What happens to current if voltage is decreased? 3. What happens to resistance if wire diameter is decreased? 4. What happens to resistance if wire length is decreased? 5. What happens to power if current is decreased (but voltage is constant ...
Ohm`s Law Lab
... 3. NOTE Leave the switch open until your teacher has checked your circuit and told you to close the switch. The meters you are using are expensive and can be ruined with improper use. 4. Close the switch and quickly read the meters. Open the switch as soon as you are done recording the readings. Rec ...
... 3. NOTE Leave the switch open until your teacher has checked your circuit and told you to close the switch. The meters you are using are expensive and can be ruined with improper use. 4. Close the switch and quickly read the meters. Open the switch as soon as you are done recording the readings. Rec ...
POWER QUALITY -- An Indian Perspective
... over-drawal : Maximize generation, and allow over-drawal, as long as grid can sustain it, and it is paid for. b) LOAD - SHEDDING to curtail over-loading or under-voltage : If too frequent, ask for system augmentation, additional capacitors. ...
... over-drawal : Maximize generation, and allow over-drawal, as long as grid can sustain it, and it is paid for. b) LOAD - SHEDDING to curtail over-loading or under-voltage : If too frequent, ask for system augmentation, additional capacitors. ...
생체계측 #5
... Thévenin's theorem(or Norton) for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V(or current source) and a single series resistor R ...
... Thévenin's theorem(or Norton) for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V(or current source) and a single series resistor R ...
LM317AHV 3-Terminal Positive Adjustable Regulator Features Description
... 1. Load and line regulation are specified at constant junction temperature. Change in VD due to heating effects must be taken into account separately. Pulse testing with low duty is used. (PMAX = 20W) 2. CADJ, when used, is connected between the adjustment pin and ground. ...
... 1. Load and line regulation are specified at constant junction temperature. Change in VD due to heating effects must be taken into account separately. Pulse testing with low duty is used. (PMAX = 20W) 2. CADJ, when used, is connected between the adjustment pin and ground. ...
Electric Circuits
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
... than one path for the electric current to flow through – current flows through every path, so if one pathway is broken, it may not affect the others – The current in each path can be different depending on the devices connected to the circuit on that path ...
ap physics b lesson 72 kirchoff`s laws
... of charge must enter a junction in a given time interval as the amount of charge that leave the junction in the same time interval. – Itotal = I1 + I2 + I3 …… ...
... of charge must enter a junction in a given time interval as the amount of charge that leave the junction in the same time interval. – Itotal = I1 + I2 + I3 …… ...
Summary of Series and Parallel Circuits
... to a series circuit is equal to the total number of individual voltage drops in the series circuit. VT = sum of all voltage drops. ...
... to a series circuit is equal to the total number of individual voltage drops in the series circuit. VT = sum of all voltage drops. ...
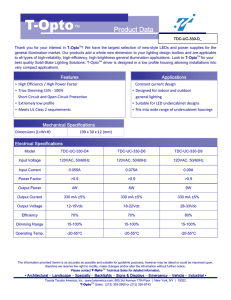
TDC-UC-330-DX - T-Opto
... Thank you for your interest in T-OptoTM! We have the largest selection of new-style LEDs and power supplies for the general illumination market. Our products add a whole new dimension to your lighting design toolbox and are applicable to all types of high-reliability, high-efficiency, high-brightnes ...
... Thank you for your interest in T-OptoTM! We have the largest selection of new-style LEDs and power supplies for the general illumination market. Our products add a whole new dimension to your lighting design toolbox and are applicable to all types of high-reliability, high-efficiency, high-brightnes ...
lecture23.1
... AC Circuits All the equipment in this operating room use alternating current circuits. ...
... AC Circuits All the equipment in this operating room use alternating current circuits. ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.