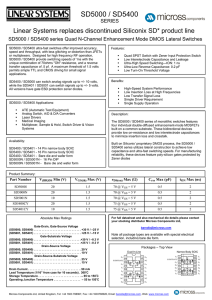
MIL-STD-883H METHOD 3021 HIGH IMPEDANCE (OFF
... applicable acquisition document in regard to output leakage current when an output is in the high-impedance state with a high-level voltage applied. This current should normally be specified as a maximum positive value (I OHZ maximum). This method applies to digital microelectronic devices, such as ...
... applicable acquisition document in regard to output leakage current when an output is in the high-impedance state with a high-level voltage applied. This current should normally be specified as a maximum positive value (I OHZ maximum). This method applies to digital microelectronic devices, such as ...
Figure Q5 - University of Brighton
... The input voltage Vs to the circuit shown in Figure Q5 is a step of 350 V dc voltage having a series resistor R =5 to limit the maximum current through the capacitor to 500 A. Determine the values of snubber inductance if the maximum permitted vales of diT/dt and dVT/dt are 350A/s and 350 V/s. I ...
... The input voltage Vs to the circuit shown in Figure Q5 is a step of 350 V dc voltage having a series resistor R =5 to limit the maximum current through the capacitor to 500 A. Determine the values of snubber inductance if the maximum permitted vales of diT/dt and dVT/dt are 350A/s and 350 V/s. I ...
Ohm`s Law Practice Worksheet Key
... Ohm’s Law Practice! Name _____KEY____________________________________ Using Ohm’s Law, calculate the missing value (E, I, or R) for each of the following circuits: 1. R = 100 Ω, I = 10 a, E = ____1000 volt_______________ 2. I = 4 a, E = 120 v, R = ____30 ohms________________ 3. E = 75 v, R = 25 Ω, I ...
... Ohm’s Law Practice! Name _____KEY____________________________________ Using Ohm’s Law, calculate the missing value (E, I, or R) for each of the following circuits: 1. R = 100 Ω, I = 10 a, E = ____1000 volt_______________ 2. I = 4 a, E = 120 v, R = ____30 ohms________________ 3. E = 75 v, R = 25 Ω, I ...
TORTURE BY ELECTRICITY
... 2. Write the equation that shows the relationship between energy (in joules), potential difference (in volts) and charge (in coulombs): 3. Write the equation that represents Ohm’s Law: ...
... 2. Write the equation that shows the relationship between energy (in joules), potential difference (in volts) and charge (in coulombs): 3. Write the equation that represents Ohm’s Law: ...
Slide 1 - MrSimonPorter
... Vary the voltage and current using a variable resistor (rheostat). Plot a graph of resistance against current ...
... Vary the voltage and current using a variable resistor (rheostat). Plot a graph of resistance against current ...
BSN-10 is an 8–channel rf generator working at pulse width
... its own programmable high voltage generator and delay control and so it provides a perfect solution for applications with accurate focus control. For linear or annular array focus, apodization may need to be implemented to each channel in additional to time delay control. BSN-10 utilizes FGPA to gen ...
... its own programmable high voltage generator and delay control and so it provides a perfect solution for applications with accurate focus control. For linear or annular array focus, apodization may need to be implemented to each channel in additional to time delay control. BSN-10 utilizes FGPA to gen ...
Circuits and Ohm*s Law
... VT = V1 + V2 + V3 … V1 = I1R1 = 1 Amp x 50Ω = 50V Therefore, VT = 50V + 50V + 50V = 150V, which is the voltage the battery can provide. ...
... VT = V1 + V2 + V3 … V1 = I1R1 = 1 Amp x 50Ω = 50V Therefore, VT = 50V + 50V + 50V = 150V, which is the voltage the battery can provide. ...
Circuits and Ohm’s Law
... VT = V1 + V2 + V3 … V1 = I1R1 = 1 Amp x 50Ω = 50V Therefore, VT = 50V + 50V + 50V = 150V, which is the voltage the battery can provide. ...
... VT = V1 + V2 + V3 … V1 = I1R1 = 1 Amp x 50Ω = 50V Therefore, VT = 50V + 50V + 50V = 150V, which is the voltage the battery can provide. ...
instructions to tenderers
... of the phase voltage LIN(A, B, C) from the line-to line voltages; channel E switched into channel D for multiplexing. •Filter: Low pass active filter of the 2° order required for the recovery of the fundamental wave out of the PWM signals. Cut-off frequency: 1 kHz. Space vector indicator: •Voltage v ...
... of the phase voltage LIN(A, B, C) from the line-to line voltages; channel E switched into channel D for multiplexing. •Filter: Low pass active filter of the 2° order required for the recovery of the fundamental wave out of the PWM signals. Cut-off frequency: 1 kHz. Space vector indicator: •Voltage v ...
ch 23 S2016
... A sensor is inserted into the mother’s uterus and positioned against the cheek of the fetus. Two light-emitting diodes are located within the sensor, and each shines light of a different wavelength (or color) into the fetal tissue. The light is reflected by the oxygen-carrying red blood cells and is ...
... A sensor is inserted into the mother’s uterus and positioned against the cheek of the fetus. Two light-emitting diodes are located within the sensor, and each shines light of a different wavelength (or color) into the fetal tissue. The light is reflected by the oxygen-carrying red blood cells and is ...
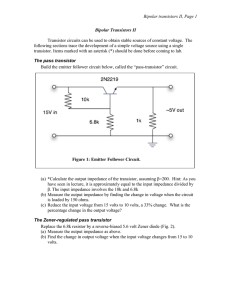
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
Electricity and Electronics
... Electricity and Electronics – ‘I Can’ Statements I Can: recall the meaning of electrical symbols and the function of each component state the meaning of the terms current (symbol I) and voltage (symbol V) state that the unit of current is the ampere or amp (symbol A) state that the unit of v ...
... Electricity and Electronics – ‘I Can’ Statements I Can: recall the meaning of electrical symbols and the function of each component state the meaning of the terms current (symbol I) and voltage (symbol V) state that the unit of current is the ampere or amp (symbol A) state that the unit of v ...
Standard signal generator GSS-6
... and the housing, shunted by the resistance of 27 ohms. Frequency energy from the master oscillator are fed to an amplifier with a coupling resistance of 1000 ohms, included in the anode circuit of the lamp 6S5. Power running scheme consistent supply is made on the lamp 6K7. Lamp 6K7 serves simultane ...
... and the housing, shunted by the resistance of 27 ohms. Frequency energy from the master oscillator are fed to an amplifier with a coupling resistance of 1000 ohms, included in the anode circuit of the lamp 6S5. Power running scheme consistent supply is made on the lamp 6K7. Lamp 6K7 serves simultane ...
95MET-4
... NB : (1)All Questions are Compulsory (2)All Questions carry equal marks (3)Neatness in handwriting and clarity in expression carries weightage 1. Describe an electric telegraph system and describe its operation. 2. (a) Draw a simple battery charging circuit showing a battery being charged from a sin ...
... NB : (1)All Questions are Compulsory (2)All Questions carry equal marks (3)Neatness in handwriting and clarity in expression carries weightage 1. Describe an electric telegraph system and describe its operation. 2. (a) Draw a simple battery charging circuit showing a battery being charged from a sin ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.