lab4a - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... Part 1 Using the ALD1106 chip in your kit, build the circuit below. Make sure to ground the body of the MOSFET (pin 4). Be careful with these chips – they are more static sensitive than BJTs. Note that 510 and 470 are acceptable (and more common) resistor values to use. ...
... Part 1 Using the ALD1106 chip in your kit, build the circuit below. Make sure to ground the body of the MOSFET (pin 4). Be careful with these chips – they are more static sensitive than BJTs. Note that 510 and 470 are acceptable (and more common) resistor values to use. ...
Slide 1
... 1. Plot a graph of current against voltage for both components. - plot both sets of data on the same graph - use a sheet of A4 graph paper in a landscape orientation - make sure current is on the y-axis and voltage is on the x-axis ...
... 1. Plot a graph of current against voltage for both components. - plot both sets of data on the same graph - use a sheet of A4 graph paper in a landscape orientation - make sure current is on the y-axis and voltage is on the x-axis ...
Problem 4.62 - Instructure
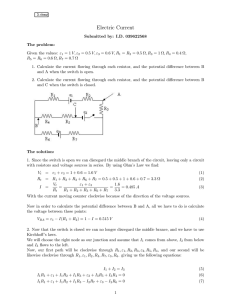
... All we can do is collapse the circuit by de-activating the current and voltage sources De-activating the 1A source turns it into an open circuit. De-activating the 520V source turns it into short circuit. The equivalent résistance is then: 40 + 4 + 6 = 50 Ohms The Thevenin voltage is then the open c ...
... All we can do is collapse the circuit by de-activating the current and voltage sources De-activating the 1A source turns it into an open circuit. De-activating the 520V source turns it into short circuit. The equivalent résistance is then: 40 + 4 + 6 = 50 Ohms The Thevenin voltage is then the open c ...
Document
... (or devices) and conducting wires to connect different components. It typically has other components like current or voltage measuring devices and switches. There are two types of circuits, series and parallel. Compound circuits are a combination of one or more series and parallel circuits. ...
... (or devices) and conducting wires to connect different components. It typically has other components like current or voltage measuring devices and switches. There are two types of circuits, series and parallel. Compound circuits are a combination of one or more series and parallel circuits. ...
Course summary for Unit 3 "Electronics and photonics"
... Coulomb of charge consists of 6.25 x 1018 electrons or the other way round, the charge on one electron is 1.6 x 10-19 Coulomb. Current is the rate at which electric charge flows through a wire. It is calculated as the amount of charge passing a point every second. It has the units of Coulomb/Second ...
... Coulomb of charge consists of 6.25 x 1018 electrons or the other way round, the charge on one electron is 1.6 x 10-19 Coulomb. Current is the rate at which electric charge flows through a wire. It is calculated as the amount of charge passing a point every second. It has the units of Coulomb/Second ...
Science and Engineering Saturday Seminars What Electrical
... Resistors: A resistor (symbol = R) is typically made of a small “rod” of carbon-based material that looks like the lead in a mechanical pencil. The resistance value on the component is indicated by a color-code scheme. Resistance is measured in units of ohms (). Capacitors: A capacitor (symbol = C) ...
... Resistors: A resistor (symbol = R) is typically made of a small “rod” of carbon-based material that looks like the lead in a mechanical pencil. The resistance value on the component is indicated by a color-code scheme. Resistance is measured in units of ohms (). Capacitors: A capacitor (symbol = C) ...
Science 9 Unit 4: Electricity Name - Science 9 Portfolio
... Transformer- An apparatus for reducing or increasing the voltage of an alternating current Circuit breaker- An automatic device for stopping the flow of current in an electric circuit as a safety measure Fuse- An automatic device for stopping the flow of current in an electric circuit as a safety me ...
... Transformer- An apparatus for reducing or increasing the voltage of an alternating current Circuit breaker- An automatic device for stopping the flow of current in an electric circuit as a safety measure Fuse- An automatic device for stopping the flow of current in an electric circuit as a safety me ...
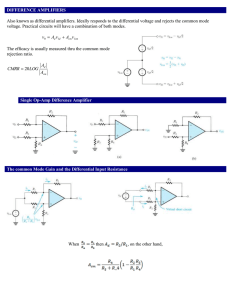
Circuit Elements: capacitor, resistor, and Ohm`s law
... centered below them. The left slot is slightly larger than the right. The left slot is called "neutral," the right slot is called "hot" and the hole below them is called "ground." The prongs on a plug fit into these slots in the outlet. ...
... centered below them. The left slot is slightly larger than the right. The left slot is called "neutral," the right slot is called "hot" and the hole below them is called "ground." The prongs on a plug fit into these slots in the outlet. ...
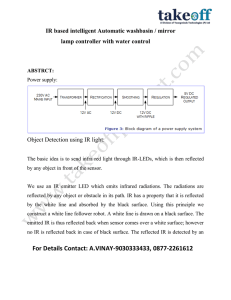
Abstract - PG Embedded systems
... An optical coupler or optocoupler is a passive device for branching or coupling an optical signal. An optocoupler is a combination of a light source and a photosensitive detector. In the optocoupler, or photon coupled pair, the coupling is achieved by light being generated on one side of a transpare ...
... An optical coupler or optocoupler is a passive device for branching or coupling an optical signal. An optocoupler is a combination of a light source and a photosensitive detector. In the optocoupler, or photon coupled pair, the coupling is achieved by light being generated on one side of a transpare ...
Ohm`s Law and Basic Circuit Theory – Answer Sheet
... Q1) On your worksheet sketch the circuit. Set the resistance to 140 ohms. Complete the table on your worksheet. As you increase the voltage the number of batteries will increase in 1.5-volt increments. Note hat the simulation shows current flow not electron flow. Current flows from positive to negat ...
... Q1) On your worksheet sketch the circuit. Set the resistance to 140 ohms. Complete the table on your worksheet. As you increase the voltage the number of batteries will increase in 1.5-volt increments. Note hat the simulation shows current flow not electron flow. Current flows from positive to negat ...
P5 – Electrical Circuits
... increase the voltage, which decreases the current. • This reduces the lose of energy due to heat/friction in the cables. • The voltage is then stepped down at a local level to be safe when people use it. ...
... increase the voltage, which decreases the current. • This reduces the lose of energy due to heat/friction in the cables. • The voltage is then stepped down at a local level to be safe when people use it. ...
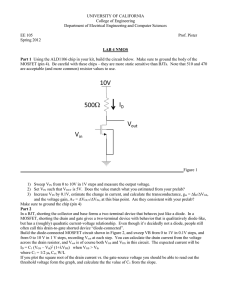
The Field Effect Transistor
... Self-bias Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is be ...
... Self-bias Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is be ...
DS9503 ESD Protection Diode with Resistors
... • On–chip 5Ω resistors for isolation at both anode and cathode terminals ...
... • On–chip 5Ω resistors for isolation at both anode and cathode terminals ...
Downlaod File
... 1- what is potential difference? charge flows from one end to the other. 2- what is Ohm’s Law? States that the current in a circuit varies in direct proportion to the potential difference, or voltage, and inversely with the resistance. 3- what is Electric Power? Rate at which electric energy is conv ...
... 1- what is potential difference? charge flows from one end to the other. 2- what is Ohm’s Law? States that the current in a circuit varies in direct proportion to the potential difference, or voltage, and inversely with the resistance. 3- what is Electric Power? Rate at which electric energy is conv ...
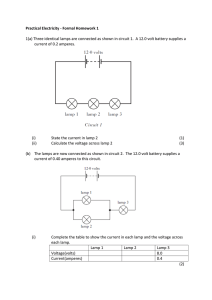
Practical Electricity 1
... A student has 4 resistors labelled A, B, C and D. The student sets up Circuit 1 to identify the value of each resistor. ...
... A student has 4 resistors labelled A, B, C and D. The student sets up Circuit 1 to identify the value of each resistor. ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.