Muddiest Points Week 8 2016
... to 0, but not quite. In doing so the output voltage can be controlled and is usually equal to the input voltage. Question: How to find out the values of Vs and Rs when a complicated circuit is connected to a Basic Inv Op Am Design. Answer: According to the example in class today, what I need to do i ...
... to 0, but not quite. In doing so the output voltage can be controlled and is usually equal to the input voltage. Question: How to find out the values of Vs and Rs when a complicated circuit is connected to a Basic Inv Op Am Design. Answer: According to the example in class today, what I need to do i ...
MP65 HIGH VOLTAGE DC FROM AC BY USING COCKCROFT
... factor to 8 such that the output would be within 2KV. This concept of generation is used in electronic appliances like the CRT’s, TV Picture tubes, oscilloscope and also used in industrial applications. The design of the circuit involves voltage multiplier, whose principle is to go on doubling the v ...
... factor to 8 such that the output would be within 2KV. This concept of generation is used in electronic appliances like the CRT’s, TV Picture tubes, oscilloscope and also used in industrial applications. The design of the circuit involves voltage multiplier, whose principle is to go on doubling the v ...
EGM 180 Take Home Quiz 1
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
Power Conditioning Glossary
... AC: Alternating Current. The voltage varies constantly above and below zero in a 50 or 60 Hertz sine-wave. Used for power distribution because the voltage can easily be changed by a transformer. Ampere (or Amp): The unit of electric current. An analogy would be the amount of water going over a water ...
... AC: Alternating Current. The voltage varies constantly above and below zero in a 50 or 60 Hertz sine-wave. Used for power distribution because the voltage can easily be changed by a transformer. Ampere (or Amp): The unit of electric current. An analogy would be the amount of water going over a water ...
cp26
... (1) The AC current through a 50Ω resistor has a maximum of 3.0A. What is the average power dissipated in the resistor? ...
... (1) The AC current through a 50Ω resistor has a maximum of 3.0A. What is the average power dissipated in the resistor? ...
Ohm`s Law & Electrical Power
... electrons with the positive pole. Current will only be produced if there is a _____ path (_______) for the electrons to flow from the negative pole to the positive pole. ...
... electrons with the positive pole. Current will only be produced if there is a _____ path (_______) for the electrons to flow from the negative pole to the positive pole. ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... Equivalence Resistance: The resistance with which all resistors can be thought of as. ...
... Equivalence Resistance: The resistance with which all resistors can be thought of as. ...
Electrical Systems for Fifth Grade
... you think the light will be brighter or dimmer than the 100-Ohm circuit?________________ Now test it. Was your guess correct?________________ Make the circuit using the 10-Ohm resistor. In parallel and Series. Before you try it, do you think the light will be brighter or dimmer than the 100-Ohm circ ...
... you think the light will be brighter or dimmer than the 100-Ohm circuit?________________ Now test it. Was your guess correct?________________ Make the circuit using the 10-Ohm resistor. In parallel and Series. Before you try it, do you think the light will be brighter or dimmer than the 100-Ohm circ ...
Factsheet: Conductors, Connections and Polarity
... It takes a minimum of two wires to have an electrical circuit. Electric current involves the flow of electrons. Current is measured in amperes (amps for short). It travels from a source, through the device it operates, called the load, and then back to the source. In AC wiring, present in buildings, ...
... It takes a minimum of two wires to have an electrical circuit. Electric current involves the flow of electrons. Current is measured in amperes (amps for short). It travels from a source, through the device it operates, called the load, and then back to the source. In AC wiring, present in buildings, ...
Electric Current and Electrical Energy
... • Voltage and Electric Current As long as there is a voltage between two points on a wire, charge will flow in the wire. The amount of the current depends on the voltage. • Varying Nature of Voltage Different devices need different levels of voltage. ...
... • Voltage and Electric Current As long as there is a voltage between two points on a wire, charge will flow in the wire. The amount of the current depends on the voltage. • Varying Nature of Voltage Different devices need different levels of voltage. ...
Ch 2 PPt 2 Basic Theories
... • The sum of the current in each leg equals the total current in the parallel circuit ...
... • The sum of the current in each leg equals the total current in the parallel circuit ...
Chap 2 Circuit Elements
... carbon composition – in use for nearly 100 years carbon film – have supplanted carbon composition for general-purpose use because of their lower costs and better tolerances. metal film wirewound – temperature sensitivity of resistors Resistors are sensitive to temperature change from an assumed am ...
... carbon composition – in use for nearly 100 years carbon film – have supplanted carbon composition for general-purpose use because of their lower costs and better tolerances. metal film wirewound – temperature sensitivity of resistors Resistors are sensitive to temperature change from an assumed am ...
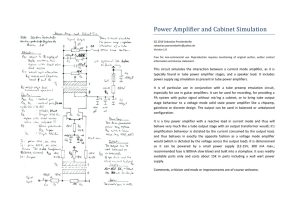
Power Amplifier and Cabinet Simulation
... It is of particular use in conjunction with a tube preamp emulation circuit, especially for use in guitar amplifiers. It can be used for recording, for providing a PA system with guitar signal without mic'ing a cabinet, or to bring tube output stage behaviour to a voltage mode solid state power ampl ...
... It is of particular use in conjunction with a tube preamp emulation circuit, especially for use in guitar amplifiers. It can be used for recording, for providing a PA system with guitar signal without mic'ing a cabinet, or to bring tube output stage behaviour to a voltage mode solid state power ampl ...
12BH7 TJ FullMusic
... Classification- It is a Twin triode. It is a nine golden pins tube. Oxide coated of indirect heated. Application -It intended for use a voltage amplifier or Phase inuerter. Dimensions -Dimensions, outline diagrams of the tube and bases, and the arrangement of electrode connections to the base termin ...
... Classification- It is a Twin triode. It is a nine golden pins tube. Oxide coated of indirect heated. Application -It intended for use a voltage amplifier or Phase inuerter. Dimensions -Dimensions, outline diagrams of the tube and bases, and the arrangement of electrode connections to the base termin ...
Exercise 3.4.1
... space charge region, but with a built in series resistance Rser and a shunt resistance Rshunt We have the following equivalent circuit diagram (also defining what is meant by a shunt resistance). See also the "Solar Cell Primer" in a basic module The shunt resistance takes into account that the huge ...
... space charge region, but with a built in series resistance Rser and a shunt resistance Rshunt We have the following equivalent circuit diagram (also defining what is meant by a shunt resistance). See also the "Solar Cell Primer" in a basic module The shunt resistance takes into account that the huge ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.