franck-hertz apparatus
... Scanning Voltage at tube 0 ~ 50V Scanning Frequency 115 ± 20Hz Scanning output amplitude to oscilloscope 1V Low-current Measuring ranges: Number of observable peaks in spectrum: Point–by-point measurement Automatic observation on oscilloscope Operating conditions Ambient temperature Relative humid ...
... Scanning Voltage at tube 0 ~ 50V Scanning Frequency 115 ± 20Hz Scanning output amplitude to oscilloscope 1V Low-current Measuring ranges: Number of observable peaks in spectrum: Point–by-point measurement Automatic observation on oscilloscope Operating conditions Ambient temperature Relative humid ...
PolySwitch Device Enhances Overcurrent
... Once a fault condition is removed and the PolySwitch device temperature drops, the device returns to a lowresistance value, restoring normal circuit operation. throughout the PolySwitch device’s hold-current range prior to tripping. If the PolySwitch device trips and changes to a high-impedance stat ...
... Once a fault condition is removed and the PolySwitch device temperature drops, the device returns to a lowresistance value, restoring normal circuit operation. throughout the PolySwitch device’s hold-current range prior to tripping. If the PolySwitch device trips and changes to a high-impedance stat ...
ZXSC310 LED DRIVER SOLUTION FOR LCD BACKLIGHTING
... backlight application for Digital Still Cameras and PDA’s. The input voltage for these backlight circuits are usually fixed from the main system power, typically 3.3V or 5V. The LED’s are connected serially so that the light is distributed uniformly in each LED. The current provided to the LED’s can ...
... backlight application for Digital Still Cameras and PDA’s. The input voltage for these backlight circuits are usually fixed from the main system power, typically 3.3V or 5V. The LED’s are connected serially so that the light is distributed uniformly in each LED. The current provided to the LED’s can ...
... Experiment 3: Frequency of Response of RC Circuits A. Introduction The response of an electronic circuit depends on the frequency of the input signal. Although there are many variations, two circuits are primarily responsible for amplitude change as a function of signal frequency, one for high frequ ...
Standing Waves - Oregon State EECS
... (b) Using pencil and paper, plot the voltage and current standing-wave patterns on the line for f0 = 10M Hz. (c) Determine the input impedance of the line if the operating frequency f0 is 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz. 3. An unknown load impedance Zt is connected to a lossless coaxial transmission line ...
... (b) Using pencil and paper, plot the voltage and current standing-wave patterns on the line for f0 = 10M Hz. (c) Determine the input impedance of the line if the operating frequency f0 is 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz. 3. An unknown load impedance Zt is connected to a lossless coaxial transmission line ...
ELEC 225L Circuit Theory I Laboratory Fall 2006
... Use the oscilloscope to measure the open-circuit output voltage of the function generator. Note that Rth is not a physical resistor but represents the internal circuitry of the generator. Without changing the amplitude setting of the generator, connect its output across a 5.1- resistor, which will ...
... Use the oscilloscope to measure the open-circuit output voltage of the function generator. Note that Rth is not a physical resistor but represents the internal circuitry of the generator. Without changing the amplitude setting of the generator, connect its output across a 5.1- resistor, which will ...
Lab Physics, Chapter 1 review
... 76. How can a battery, wires, and light bulb be hooked up to make the light bulb glow? (Think about the first lab we did in this unit). 27. Construct the circuit diagrams from the pictures.—Use the appropriate symbols. a ...
... 76. How can a battery, wires, and light bulb be hooked up to make the light bulb glow? (Think about the first lab we did in this unit). 27. Construct the circuit diagrams from the pictures.—Use the appropriate symbols. a ...
Parallel and Series Circuits
... Characteristics of a Parallel Circuit • The total current flowing from the source of electrical energy is equal to the sum of the branch circuits • Adding another load will cause the total current to increase • Separate branch circuits can be used without affecting any of the others (example: using ...
... Characteristics of a Parallel Circuit • The total current flowing from the source of electrical energy is equal to the sum of the branch circuits • Adding another load will cause the total current to increase • Separate branch circuits can be used without affecting any of the others (example: using ...
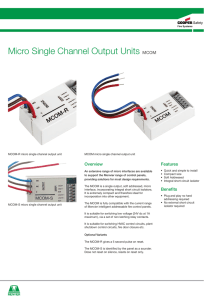
Micro Single Channel Output Units MCOM
... The MCOM is a single output, soft addressed, micro interface, incorporating integral short circuit isolators. It is extremely compact and therefore ideal for incorporation into other equipment. ...
... The MCOM is a single output, soft addressed, micro interface, incorporating integral short circuit isolators. It is extremely compact and therefore ideal for incorporation into other equipment. ...
Chapter 16 Practice Test #2
... ____ 12. Resistance is caused by a. internal friction. c. proton charge. b. electron charge. d. a heat source. ____ 13. The SI unit of resistance is the a. volt. c. ohm. b. ampere. d. joule. ____ 14. Whether or not charges will move in a material depends partly on how tightly _____ are held in the ...
... ____ 12. Resistance is caused by a. internal friction. c. proton charge. b. electron charge. d. a heat source. ____ 13. The SI unit of resistance is the a. volt. c. ohm. b. ampere. d. joule. ____ 14. Whether or not charges will move in a material depends partly on how tightly _____ are held in the ...
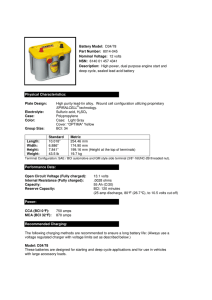
Battery Model: D34/78 Part Number: 8014
... Recommended Charging: The following charging methods are recommended to ensure a long battery life: (Always use a voltage regulated charger with voltage limits set as described below.) Model: D34/78 These batteries are designed for starting and deep cycle applications and for use in vehicles with la ...
... Recommended Charging: The following charging methods are recommended to ensure a long battery life: (Always use a voltage regulated charger with voltage limits set as described below.) Model: D34/78 These batteries are designed for starting and deep cycle applications and for use in vehicles with la ...
Current and Electric Circuits Lesson Plans
... connecting them with a wires and a charge pump, or something that keeps charge in motion. The pump keeps the charge moving so that potential difference is never zero. When the potential difference is zero, the charge flow stops. One thing we uses is a ...
... connecting them with a wires and a charge pump, or something that keeps charge in motion. The pump keeps the charge moving so that potential difference is never zero. When the potential difference is zero, the charge flow stops. One thing we uses is a ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.