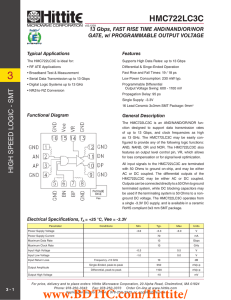
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications. ...
... susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications. ...
Voltage Sag Mitigation in Distribution Line using DSTATCOM
... issue in distribution system. If the reactive current increases, the system losses also increase. Various methods have been applied to mitigate voltage sags. For voltage sag mitigation we generally use capacitor banks, parallel feeder’s etc.But the power quality problems are not completely solved by ...
... issue in distribution system. If the reactive current increases, the system losses also increase. Various methods have been applied to mitigate voltage sags. For voltage sag mitigation we generally use capacitor banks, parallel feeder’s etc.But the power quality problems are not completely solved by ...
NZT560/NZT560A NPN Low Saturation Transistor N Z
... * These ratings are limiting values above which the serviceability of any semiconductor device may be impaired. NOTES: 1)These ratings are based on a maximum junction temperature of 150°C. 2)These are steady state limits. The factory should be consulted on applications involving pulsed or low duty c ...
... * These ratings are limiting values above which the serviceability of any semiconductor device may be impaired. NOTES: 1)These ratings are based on a maximum junction temperature of 150°C. 2)These are steady state limits. The factory should be consulted on applications involving pulsed or low duty c ...
TL072
... Latch-Up-Free Operation High Slew Rate…13V/μs Typ Common-Mode Input Voltage Range Includes VCC+ SOP-8L: Available in “Green” Molding Compound (No Br, Sb) Lead Free Finish/ RoHS Compliant (Note 1) ...
... Latch-Up-Free Operation High Slew Rate…13V/μs Typ Common-Mode Input Voltage Range Includes VCC+ SOP-8L: Available in “Green” Molding Compound (No Br, Sb) Lead Free Finish/ RoHS Compliant (Note 1) ...
GAAS: A Fully Integrated SiGe Low Phase Noise Push
... a constant emitter bias current is impressed by a current mirror. At the base terminals 350 µm long microstrip lines serving as an inductors are connected. At the connecting point of the base networks a virtual ground for the fundamental frequency signal at f 0 exists due to the odd mode operation. ...
... a constant emitter bias current is impressed by a current mirror. At the base terminals 350 µm long microstrip lines serving as an inductors are connected. At the connecting point of the base networks a virtual ground for the fundamental frequency signal at f 0 exists due to the odd mode operation. ...
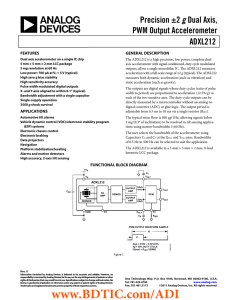
g PWM Output Accelerometer ADXL212
... structure over the surface of the wafer and provide a resistance against acceleration forces. Deflection of the structure is measured using a differential capacitor that consists of independent fixed plates and plates attached to the moving mass. The fixed plates are driven by 180° out-of-phase squa ...
... structure over the surface of the wafer and provide a resistance against acceleration forces. Deflection of the structure is measured using a differential capacitor that consists of independent fixed plates and plates attached to the moving mass. The fixed plates are driven by 180° out-of-phase squa ...
Statistical Performance Measures - pes-psrc
... Our topic of interest – new sensors New transducers for sensing power system primary voltages and currents: ...
... Our topic of interest – new sensors New transducers for sensing power system primary voltages and currents: ...
Chapter 26
... Ch 26-4 Resistance and Resistivity Resistance R : measured from ratio of applied voltage V across a conductor and the resulting current through the conductor R= V/i Unit of resistance Ohm (): 1 = 1V/1A i=V/R Instead of V if we consider electric field E in a conductor then we deal with J inst ...
... Ch 26-4 Resistance and Resistivity Resistance R : measured from ratio of applied voltage V across a conductor and the resulting current through the conductor R= V/i Unit of resistance Ohm (): 1 = 1V/1A i=V/R Instead of V if we consider electric field E in a conductor then we deal with J inst ...
Winding resistance meter with one-time-connection system
... magnetization method drastically reduces measuring time. The simultaneous winding magnetization (SWM) method guarantees fast and reliable measurements even on large power transformers with delta windings on the low voltage side, where stable measurements can be seldom reached using traditional windi ...
... magnetization method drastically reduces measuring time. The simultaneous winding magnetization (SWM) method guarantees fast and reliable measurements even on large power transformers with delta windings on the low voltage side, where stable measurements can be seldom reached using traditional windi ...
DRV591 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... common. If the 10 µH inductor is used, delivering 250 mA of ripple current to the capacitor (as calculated above), then the ripple voltage is 25 mV. This is over ten times that of the 10 µF ceramic capacitor, as ceramic capacitors typically have negligible ESR. ...
... common. If the 10 µH inductor is used, delivering 250 mA of ripple current to the capacitor (as calculated above), then the ripple voltage is 25 mV. This is over ten times that of the 10 µF ceramic capacitor, as ceramic capacitors typically have negligible ESR. ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.