“First” Peloponnesian War – Video 16Not the GREAT
... 460-445 BC…not to be confused with the “GREAT” war that begins in 431 BC. This is far smaller in scale. You would think after winning the Greco-Persian War, the Greeks would be all chill with each other. Nope. The _______________ spirit of the Greeks is just too great. Hmmmmm.......if the Persians h ...
... 460-445 BC…not to be confused with the “GREAT” war that begins in 431 BC. This is far smaller in scale. You would think after winning the Greco-Persian War, the Greeks would be all chill with each other. Nope. The _______________ spirit of the Greeks is just too great. Hmmmmm.......if the Persians h ...
Section Two: The Greek City-States
... A military State • Stayed in the army until 60 • Women & men lived apart • Women expected to remain fit to bear & raise healthy children • Men expected to be brave in battle, to win or be killed ...
... A military State • Stayed in the army until 60 • Women & men lived apart • Women expected to remain fit to bear & raise healthy children • Men expected to be brave in battle, to win or be killed ...
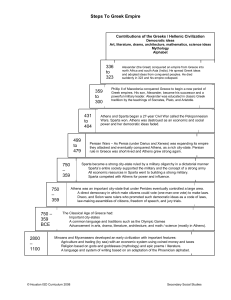
Steps To Greek Empire 2800
... Phillip II of Macedonia conquered Greece to begin a new period of Greek empires. His son, Alexander, became his successor and a powerful military leader. Alexander was educated in classic Greek tradition by the teachings of Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. ...
... Phillip II of Macedonia conquered Greece to begin a new period of Greek empires. His son, Alexander, became his successor and a powerful military leader. Alexander was educated in classic Greek tradition by the teachings of Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. ...
Military Achievements and Leaders: Ancient Greece
... Each soldier learned absolute and unwavering loyalty Also learned to swim, jump, run, wrestle, box, and most importantly dance Thought dancing helped in the movements of battle “Spartans do not ask how many, but where” ...
... Each soldier learned absolute and unwavering loyalty Also learned to swim, jump, run, wrestle, box, and most importantly dance Thought dancing helped in the movements of battle “Spartans do not ask how many, but where” ...
The Greek City-State: Democratic Politics
... ships. Spartan troops held off Persians for awhile The Athenians abandoned their city. Persians sacked and burned Athens to the ground. Greeks formed the largest Greek army seen and decisively defeated the Persian army at Plataea . The Greeks had won the war. ...
... ships. Spartan troops held off Persians for awhile The Athenians abandoned their city. Persians sacked and burned Athens to the ground. Greeks formed the largest Greek army seen and decisively defeated the Persian army at Plataea . The Greeks had won the war. ...
Ancient Greece (Chapter 7)
... The government controlled the lives of the Spartans and only the healthiest babies were raised Training began at age seven and boys left their homes to train at a barrack for 13 years At age 12 boys practiced with swords and spears Children were fed very little so they were forced to steal – Sparta ...
... The government controlled the lives of the Spartans and only the healthiest babies were raised Training began at age seven and boys left their homes to train at a barrack for 13 years At age 12 boys practiced with swords and spears Children were fed very little so they were forced to steal – Sparta ...
Greek Warfare - Little Miami Schools
... strength of lions or of bulls shall hold him, Strength against strength; for he has the power of Zeus, And will not be checked till one of these two he has consumed.” ...
... strength of lions or of bulls shall hold him, Strength against strength; for he has the power of Zeus, And will not be checked till one of these two he has consumed.” ...
Wk_24_Ancient Greece_6_4_6_Thursday
... Athens, Sparta, and the Wars • Before we begin to learn about these two citystates and the Wars that affected them, it is important to look back at the geography and political difference of the two: – Sparta is located in the Peloponnesian Peninsula between the mountains and the sea – Athens is loc ...
... Athens, Sparta, and the Wars • Before we begin to learn about these two citystates and the Wars that affected them, it is important to look back at the geography and political difference of the two: – Sparta is located in the Peloponnesian Peninsula between the mountains and the sea – Athens is loc ...
Different City States
... • When they got older, boys went to military school to help them prepare for another important duty of citizenship—defending Athens • Women did not attend school, educated to become good wives and mothers ...
... • When they got older, boys went to military school to help them prepare for another important duty of citizenship—defending Athens • Women did not attend school, educated to become good wives and mothers ...
geography - Humble ISD
... 2. age 7 - boys leave home and live in military barracks 3. youths are expected to get by (___________________) on their own 4. learned to read and write - No free discussion! 5. married at age 20 - live in barracks for another 40 years 6. age 30 - men become citizens and state provides land and sla ...
... 2. age 7 - boys leave home and live in military barracks 3. youths are expected to get by (___________________) on their own 4. learned to read and write - No free discussion! 5. married at age 20 - live in barracks for another 40 years 6. age 30 - men become citizens and state provides land and sla ...
greece test 2011answers
... Sparta had a stronger naval fleet at the start of the war c Athens routinely exiled or executed any General who lost a battle d Athens wasted it’s resources on an unsuccessful attempt to take Syracuse Peloponnesian war notes Thursday april 7th ...
... Sparta had a stronger naval fleet at the start of the war c Athens routinely exiled or executed any General who lost a battle d Athens wasted it’s resources on an unsuccessful attempt to take Syracuse Peloponnesian war notes Thursday april 7th ...
17- Warring City-States Rule and Order in Greek City
... counseled the assembly. Council members were chosen by lot, or at random. The reforms of Cleisthenes allowed Athenian citizens to participate in a limited democracy. However, citizenship was restricted to a relatively small number of Athenians. Only free adult male property owners born in Athens wer ...
... counseled the assembly. Council members were chosen by lot, or at random. The reforms of Cleisthenes allowed Athenian citizens to participate in a limited democracy. However, citizenship was restricted to a relatively small number of Athenians. Only free adult male property owners born in Athens wer ...
Questions - World Book Online
... Click eBook icon and search for Early Peoples. Click title: Ancient Greeks. 1. Physical Features and Trade a) Look at the map of Ancient Greece on page 4. From a geographical perspective, what does it tell you about Ancient Greece? b) Why did ancient Greeks trade? c) Who did they trade with and how? ...
... Click eBook icon and search for Early Peoples. Click title: Ancient Greeks. 1. Physical Features and Trade a) Look at the map of Ancient Greece on page 4. From a geographical perspective, what does it tell you about Ancient Greece? b) Why did ancient Greeks trade? c) Who did they trade with and how? ...
Persian Wars
... • King of the Persian Empire and Son of Darius • Led the 2nd invasion of Greece to avenge his father’s defeat and add the Greeks into his Army • His campaign to take control over Greece is a failure (initially victory at the Battle of Thermopylae) • Location: Persepolis, Greece ...
... • King of the Persian Empire and Son of Darius • Led the 2nd invasion of Greece to avenge his father’s defeat and add the Greeks into his Army • His campaign to take control over Greece is a failure (initially victory at the Battle of Thermopylae) • Location: Persepolis, Greece ...
Early Greece
... Sparta was an oligarchy: rule by the few! Sparta was ruled by two kings Helots outnumbered Spartans 7 to 1! This was the main reason for the strict war-like society… • Breakdown of Spartan Social Structure Spartiates Perioeci (Perioikoi) Helots ...
... Sparta was an oligarchy: rule by the few! Sparta was ruled by two kings Helots outnumbered Spartans 7 to 1! This was the main reason for the strict war-like society… • Breakdown of Spartan Social Structure Spartiates Perioeci (Perioikoi) Helots ...
Pelop War info kids
... After the Persian Wars, the Greeks wanted to make sure they were ready in case the Persians ever returned and so they formed the Delian League. The purpose of the Delian League was to put money into a shared treasury (like a bank) to have in case of war. It takes money to make weapons and ships and ...
... After the Persian Wars, the Greeks wanted to make sure they were ready in case the Persians ever returned and so they formed the Delian League. The purpose of the Delian League was to put money into a shared treasury (like a bank) to have in case of war. It takes money to make weapons and ships and ...
1.1 Greek Democracy
... Tyranny reduced power of aristocracy who ruled Athens through reforms • Early democracy, council of 500 chosen at random from all citizens, prepare laws for assembly, supervised day to day work • The assembly was all male citizens 30+, they became a true legislature, debated merits of laws and voted ...
... Tyranny reduced power of aristocracy who ruled Athens through reforms • Early democracy, council of 500 chosen at random from all citizens, prepare laws for assembly, supervised day to day work • The assembly was all male citizens 30+, they became a true legislature, debated merits of laws and voted ...
LastStandOfThe300Video
... 27. Why wasn’t there a great loss of life? 28. What would the Greeks eventually do years later to the Persian threat? 29. In the end, what were the main accomplishments of the 300 Spartans? 30. What idea might have been destroyed if the Persians had conquered the Greeks? ...
... 27. Why wasn’t there a great loss of life? 28. What would the Greeks eventually do years later to the Persian threat? 29. In the end, what were the main accomplishments of the 300 Spartans? 30. What idea might have been destroyed if the Persians had conquered the Greeks? ...
A short tract on first principles
... 1. How many years were Spartans required to train for the military? 23 years 2. What were some of the ways Spartans made sure their children grew up to be tough? Spartan children were not coddled when they cried; they were made to go barefoot; at the age of seven, Spartan boys began military trainin ...
... 1. How many years were Spartans required to train for the military? 23 years 2. What were some of the ways Spartans made sure their children grew up to be tough? Spartan children were not coddled when they cried; they were made to go barefoot; at the age of seven, Spartan boys began military trainin ...
Ancient Greece QR Code Questions
... 1) What geographic features do you notice in this image? (Do not include things made by people) 2) How did these geographic features lead to Greece developing into vastly different societies? 3) How could this geography both help and hurt ancient Greek society? C) Ancient Sparta ...
... 1) What geographic features do you notice in this image? (Do not include things made by people) 2) How did these geographic features lead to Greece developing into vastly different societies? 3) How could this geography both help and hurt ancient Greek society? C) Ancient Sparta ...
Glory that was Greece Part 1
... •Created Festivals •Initiated Public Building Projects •Made People Proud to be Athenian ...
... •Created Festivals •Initiated Public Building Projects •Made People Proud to be Athenian ...
Honors LastStandOfThe300Video
... 20. What did the Persians do on day three of the battle? 21. What does King Leonidas order most of the Greek soldiers to do? 22. What does he decide to do? 23. Describe how King Leonidas was killed? 24. What is the end result of this “Last Stand”? 25. How many Persians had been killed in the three d ...
... 20. What did the Persians do on day three of the battle? 21. What does King Leonidas order most of the Greek soldiers to do? 22. What does he decide to do? 23. Describe how King Leonidas was killed? 24. What is the end result of this “Last Stand”? 25. How many Persians had been killed in the three d ...
Persian War I Persian War I Peloponnesian War 500 BC Greek
... On the way there is a storm that destroys half his fleet The other half of the fleet sails on to fight. They off load at Marathon. It is a swampy and foggy place where the Athenians can slip up and attack the Persians. They run them all the way back to the boats. Nearly 2,000 are killed. Darius is d ...
... On the way there is a storm that destroys half his fleet The other half of the fleet sails on to fight. They off load at Marathon. It is a swampy and foggy place where the Athenians can slip up and attack the Persians. They run them all the way back to the boats. Nearly 2,000 are killed. Darius is d ...
Spartan army
The Spartan army stood at the centre of the Spartan state, whose male and female citizens were trained in the discipline and honor of the warrior society. Subject to military drill from early manhood, the Spartans were one of the most feared military forces in the Greek world. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – it was commonly accepted that, ""one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."" According to Thucydides, the famous moment of Spartan surrender at the island of Sphacteria off of Pylos was highly unexpected. He said that ""it was the common perception at the time that Spartans would never lay down their weapons for any reason, be it hunger, or danger.""The iconic army was first coined by the Spartan legislator Lycurgus. In his famous quote of Sparta having a ""wall of men, instead of bricks"", he proposed to create a military-focused lifestyle reformation in the Spartan society in accordance to proper virtues such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. A Spartan man's involvement with the army began in infancy when he was inspected by the Gerousia. If the baby was found to be weak or deformed he was left at Mount Taygetus to die, since the world of the Spartans was no place for those who could not already fend for themselves. It should be noted, however, that the practice of discarding children at birth took place in Athens as well. Those deemed strong were then put in the agoge at the age of seven. Under the agoge the young boys or Spartiates were kept under intense and rigorous military training. Their education focused primarily on cunning, sports and war tactics, but also included poetry, music, academics, and sometimes politics. Those who passed the agoge by the age of 30 were given full Spartan citizenship.The term ""spartan"" became synonymous with multiple meanings such as: fearlessness, harsh and cruel life, bland and lacking creativity, or simplicity by design.