The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... white eyed fruit fly that was male. • Wild type is red eyed. • Bred with a WT ...
... white eyed fruit fly that was male. • Wild type is red eyed. • Bred with a WT ...
W
... way to find out is to study the tumor cells themselves, particularly their chromosomes. In most cases of cancer, these chromosomes have tell-tale abnormalities, ranging from the blatant (an entire chromosome missing, for example) to the less obvious (translocations, in which a piece of one chromosom ...
... way to find out is to study the tumor cells themselves, particularly their chromosomes. In most cases of cancer, these chromosomes have tell-tale abnormalities, ranging from the blatant (an entire chromosome missing, for example) to the less obvious (translocations, in which a piece of one chromosom ...
Sources of Genetic Variation
... chromosomes pair by forming loops) This allows alleles at a sequence of genes to preserved together. If two genes are near each other on a chromosome, and crossover products never occur, the alleles at these genes will always be transmitted together. So if alleles at a series of genes work particula ...
... chromosomes pair by forming loops) This allows alleles at a sequence of genes to preserved together. If two genes are near each other on a chromosome, and crossover products never occur, the alleles at these genes will always be transmitted together. So if alleles at a series of genes work particula ...
S3 Cells, cell uses and DNA Revision summary Fill in any spaces
... Adult cells have _____ copies of every ______. Sperm and egg cells have ____ copy of every gene. Each parent will pass on a copy of each gene to their ___________. The differences between organisms are called __________. There are two types of variation. __________ where the characteristic can be ob ...
... Adult cells have _____ copies of every ______. Sperm and egg cells have ____ copy of every gene. Each parent will pass on a copy of each gene to their ___________. The differences between organisms are called __________. There are two types of variation. __________ where the characteristic can be ob ...
Chapter 10 Mitosis and Chapter 11
... 8. Cancer cells form masses of cells called tumors. 9. An organisms diploid number is 14, its haploid number is7. 10. Gametes (sex cells) have one allele for each gene. 11. Gametes are produced by the process of Meiosis. 12. Chromosomes form tetrads during Prophase I of meiosis. 13. Unlike mitosis, ...
... 8. Cancer cells form masses of cells called tumors. 9. An organisms diploid number is 14, its haploid number is7. 10. Gametes (sex cells) have one allele for each gene. 11. Gametes are produced by the process of Meiosis. 12. Chromosomes form tetrads during Prophase I of meiosis. 13. Unlike mitosis, ...
mitosis meiosis study guide answers
... ~asexual reproduction (budding, fragmentation, binary fission) 16. Living things continue their species through sexual and/or asexual reproduction. Which of the following is true for both sexual and asexual reproduction? Sperm and egg cells are needed. Offspring is an exact copy of the parent. ...
... ~asexual reproduction (budding, fragmentation, binary fission) 16. Living things continue their species through sexual and/or asexual reproduction. Which of the following is true for both sexual and asexual reproduction? Sperm and egg cells are needed. Offspring is an exact copy of the parent. ...
16. Unit 7 Mitosis and Meiosis Study Guide
... ~asexual reproduction (budding, fragmentation, binary fission) 16. Living things continue their species through sexual and/or asexual reproduction. Which of the following is true for both sexual and asexual reproduction? Sperm and egg cells are needed. Offspring is an exact copy of the parent. ...
... ~asexual reproduction (budding, fragmentation, binary fission) 16. Living things continue their species through sexual and/or asexual reproduction. Which of the following is true for both sexual and asexual reproduction? Sperm and egg cells are needed. Offspring is an exact copy of the parent. ...
Genetic Principles
... • The probability of a fit this good by chance is .00007 • Possible that Mendel’s sample size was larger than he reported. ...
... • The probability of a fit this good by chance is .00007 • Possible that Mendel’s sample size was larger than he reported. ...
Patterns of Inheritance and Meiosis
... produces four functional gametes, while meiosis in females (the sex with the larger gamete) produces one functional gamete and three polar bodies, which disintegrate. This difference in gamete size is called anisogamy. Some plants are isogamous and do not produce polar bodies. B. Meiosis also differ ...
... produces four functional gametes, while meiosis in females (the sex with the larger gamete) produces one functional gamete and three polar bodies, which disintegrate. This difference in gamete size is called anisogamy. Some plants are isogamous and do not produce polar bodies. B. Meiosis also differ ...
Baby Reebops: Marshmallow Meiosis
... 3. One color of chromosomes is from the mother and the other is from the father. On your answer sheet, designate which chromosomes belong to which parent before you start. (ie. Mother‟s Chromosomes = red, Father‟s Chromosomes = red) 4. A chromosome pair will be the same length. Cut out your chromoso ...
... 3. One color of chromosomes is from the mother and the other is from the father. On your answer sheet, designate which chromosomes belong to which parent before you start. (ie. Mother‟s Chromosomes = red, Father‟s Chromosomes = red) 4. A chromosome pair will be the same length. Cut out your chromoso ...
Document
... DNA Forensics and Civil Liberties Workshop Summary •Perspective on DNA Testing & Forensics - Rothstein •Daubert Standard •Listen to the Experts -- Daubert, Frye, and California ...
... DNA Forensics and Civil Liberties Workshop Summary •Perspective on DNA Testing & Forensics - Rothstein •Daubert Standard •Listen to the Experts -- Daubert, Frye, and California ...
Genetic Disorders, Disease, and Karyotypes
... chromosomes (X and Y) *XX=Female, XY=Male *Picture of chromosomes=karyotype *Doctors use to determine sex of baby and ...
... chromosomes (X and Y) *XX=Female, XY=Male *Picture of chromosomes=karyotype *Doctors use to determine sex of baby and ...
Heredity Influences on Development Chapter 3
... • About 1 in every 1,000 individual has an X chromosome that is fragile and may have separated into two or more pieces, known as the Fragile-X syndrome. ...
... • About 1 in every 1,000 individual has an X chromosome that is fragile and may have separated into two or more pieces, known as the Fragile-X syndrome. ...
1. Explain why organisms only reproduce their own
... All chromosomes besides the X and Ys are known as _____________. What keeps sister chromatids together until anaphase? What is the purpose of meiosis? What is the term for a fertilized egg? ...
... All chromosomes besides the X and Ys are known as _____________. What keeps sister chromatids together until anaphase? What is the purpose of meiosis? What is the term for a fertilized egg? ...
Meiosis packet
... Mitotic cell division insures that cells are genetically the same, and Meiotic division produces cells that are genetically different. In other words, Mitosis guarantees continuity (continuation of life) and meiosis guarantees variation. So the types of cell division differ in several important ways ...
... Mitotic cell division insures that cells are genetically the same, and Meiotic division produces cells that are genetically different. In other words, Mitosis guarantees continuity (continuation of life) and meiosis guarantees variation. So the types of cell division differ in several important ways ...
Meiosis Information Sheet
... Mitotic cell division insures that cells are genetically the same, and Meiotic division produces cells that are genetically different. In other words, Mitosis guarantees continuity (continuation of life) and meiosis guarantees variation. So the types of cell division differ in several important ways ...
... Mitotic cell division insures that cells are genetically the same, and Meiotic division produces cells that are genetically different. In other words, Mitosis guarantees continuity (continuation of life) and meiosis guarantees variation. So the types of cell division differ in several important ways ...
Chapter 6 Homework Questions- Meiosis and Genetics Section 6.1
... 3. If you are working with two tall pea plants and know that one is Tt, how could you determine the genotype of the other plant? Section 6.6 – Meiosis and Genetic Variation 1. Suppose you know two genes exist on the same chromosome. How could you determine whether they are located close to each othe ...
... 3. If you are working with two tall pea plants and know that one is Tt, how could you determine the genotype of the other plant? Section 6.6 – Meiosis and Genetic Variation 1. Suppose you know two genes exist on the same chromosome. How could you determine whether they are located close to each othe ...
MT REVIEW #1
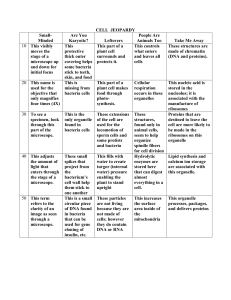
... 1. Figure B (meiosis) produces 4 haploid cells 2. Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up and form tetrads only in meiosis. 3. Meiosis involves 2 processes of division 4. Mitosis – one division, 2 daughter cells genetically identical to each other & the parent cell. Both types of processes above occ ...
... 1. Figure B (meiosis) produces 4 haploid cells 2. Homologous pairs of chromosomes line up and form tetrads only in meiosis. 3. Meiosis involves 2 processes of division 4. Mitosis – one division, 2 daughter cells genetically identical to each other & the parent cell. Both types of processes above occ ...
Genetics - Aurora City Schools
... chromosomes are sex linked These genes are inherited differently in males and females because the X and Y chromosomes do not carry the same genes. Genetic disorders that have genes on the X chromosome show up more frequently in males than females. While Y-linked disorders only show up in males. Male ...
... chromosomes are sex linked These genes are inherited differently in males and females because the X and Y chromosomes do not carry the same genes. Genetic disorders that have genes on the X chromosome show up more frequently in males than females. While Y-linked disorders only show up in males. Male ...
Reproduction
... formed by meiosis fertilization = gamete + gamete = zygote zygote grows into fetus ...
... formed by meiosis fertilization = gamete + gamete = zygote zygote grows into fetus ...
Oct24 - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... Mr. R. Bair Biology Teacher Mrs. MV Smith Resource Teacher Date: October 24, 2007 Drill Why is meiosis important in reproduction? What is pulled apart in Anaphase I? What is pulled apart in Anaphase II? ...
... Mr. R. Bair Biology Teacher Mrs. MV Smith Resource Teacher Date: October 24, 2007 Drill Why is meiosis important in reproduction? What is pulled apart in Anaphase I? What is pulled apart in Anaphase II? ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.