File
... with temperatures. Black pigment is produced only in those areas of the skin which are lowest in temperature, such as the ears and tail ...
... with temperatures. Black pigment is produced only in those areas of the skin which are lowest in temperature, such as the ears and tail ...
1. In dogs the allele for dark Brown hair color (E)
... A drone (male bee) is haploid. He developed from an unfertilized egg cell. In the forming of body cells and in the forming of reproductive cells by this drone there are divisions. Which divisions occur in a drone? A. only mitosis B. only meiosis II C. only mitosis and meiosis I D. mitosis, meiosis I ...
... A drone (male bee) is haploid. He developed from an unfertilized egg cell. In the forming of body cells and in the forming of reproductive cells by this drone there are divisions. Which divisions occur in a drone? A. only mitosis B. only meiosis II C. only mitosis and meiosis I D. mitosis, meiosis I ...
Disorders review - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Males only have one X. If they get the gene it will show. Females have a 2nd X that can “hide” the disorder gene. They need 2 copies of the gene to show disorder. Males don’t have a “back up” X. ...
... Males only have one X. If they get the gene it will show. Females have a 2nd X that can “hide” the disorder gene. They need 2 copies of the gene to show disorder. Males don’t have a “back up” X. ...
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
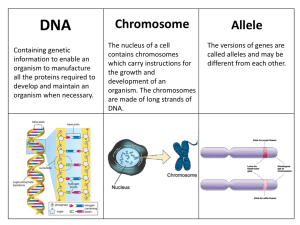
... DNA Containing genetic information to enable an organism to manufacture all the proteins required to develop and maintain an organism when necessary. ...
... DNA Containing genetic information to enable an organism to manufacture all the proteins required to develop and maintain an organism when necessary. ...
ppt
... Sexual reproduction: Two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents (offspring varies genetically from their siblings and their parents). ...
... Sexual reproduction: Two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes inherited from the two parents (offspring varies genetically from their siblings and their parents). ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... which allele for a different gene is found in the same gamete. This also shuffles the genes and increases the genetic diversity of a species. 2. What are the fundamental principles of the chromosome theory of inheritance? Answer: a. Chromosomes contain the genetic information that is passed from par ...
... which allele for a different gene is found in the same gamete. This also shuffles the genes and increases the genetic diversity of a species. 2. What are the fundamental principles of the chromosome theory of inheritance? Answer: a. Chromosomes contain the genetic information that is passed from par ...
Name
... Humans (and most other sexually reproducing organisms) contain two types of cells; diploid and haploid. These cells differ in their chromosome content. Diploid cells contain homologous chromosomes; pairs of chromosomes that carry the same complement of genes with one member of the pair inherited fro ...
... Humans (and most other sexually reproducing organisms) contain two types of cells; diploid and haploid. These cells differ in their chromosome content. Diploid cells contain homologous chromosomes; pairs of chromosomes that carry the same complement of genes with one member of the pair inherited fro ...
unit 7 overview: genetics
... 7. How many chromosomes do human body cells have? Are they 2n or n? How many pairs of homologous chromosomes do they have? What about sex cells? 8. Differentiate between mitosis and meiosis. How many cell divisions? Which cells are involved? 9. Compare and contrast zygote with gametes. Haploid or di ...
... 7. How many chromosomes do human body cells have? Are they 2n or n? How many pairs of homologous chromosomes do they have? What about sex cells? 8. Differentiate between mitosis and meiosis. How many cell divisions? Which cells are involved? 9. Compare and contrast zygote with gametes. Haploid or di ...
Genetics Practice Examination #3 Name: Date: 1. Which statement
... Potatoes were the main crop in Ireland in the 1800s. Almost the entire population of Ireland was dependent on a single variety of potato, the “lumper.” These potatoes were reproduced by a method of asexual reproduction known as vegetative propagation. In the middle of the 1800s, a disease caused by ...
... Potatoes were the main crop in Ireland in the 1800s. Almost the entire population of Ireland was dependent on a single variety of potato, the “lumper.” These potatoes were reproduced by a method of asexual reproduction known as vegetative propagation. In the middle of the 1800s, a disease caused by ...
Hematologic Malignancies - Jacquie Hirsch For ALL Foundation
... Norma J. Nowak PhD Roswell Park Cancer Institute ...
... Norma J. Nowak PhD Roswell Park Cancer Institute ...
Schedule - Learning on the Loop
... structures to reproduce itself so relies on the host cells structures. A virus will inject its genetic material into the host cell, which then carries out the instructions to make many new viruses before rupturing. Bacteria feed by extra cellular digestion to supply the materials needed for growth a ...
... structures to reproduce itself so relies on the host cells structures. A virus will inject its genetic material into the host cell, which then carries out the instructions to make many new viruses before rupturing. Bacteria feed by extra cellular digestion to supply the materials needed for growth a ...
Chapter 12: Mendel and Heredity Study Guide (Pages 280 – 284
... a. __________________________- genetic disorder in which a person cannot distinguish between 2 colors such as red and green. b. Hemophilia – genetic disorder in which a person’s _________________ does NOT clot properly; a serious injury may cause them to bleed to death. 7. Human males inherit the re ...
... a. __________________________- genetic disorder in which a person cannot distinguish between 2 colors such as red and green. b. Hemophilia – genetic disorder in which a person’s _________________ does NOT clot properly; a serious injury may cause them to bleed to death. 7. Human males inherit the re ...
Nov07-BalancersFinal
... If you do steps 2 and 3 many times (a separate vial for each) one can clone many * chromosomes and if you discard all vials that yield straight winged flies, you will be left with a bunch of vials each containing a particular * chromosome over a balancer and each of these retained chromosomes will c ...
... If you do steps 2 and 3 many times (a separate vial for each) one can clone many * chromosomes and if you discard all vials that yield straight winged flies, you will be left with a bunch of vials each containing a particular * chromosome over a balancer and each of these retained chromosomes will c ...
Chromosome - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Chromosomes look thread-like under the microscope. How is DNA packaged to form Chromosomes? ...
... • Chromosomes look thread-like under the microscope. How is DNA packaged to form Chromosomes? ...
LUCA - University of Washington
... innards of a computer. Additional support for the idea that eukaryotes evolved before prokaryotes can be seen in the structure of their chromosomes. Each chromosome is a very long molecule of DNA. We humans have twenty-three pairs of them--forty-six separate DNA molecules. Other species of eukaryote ...
... innards of a computer. Additional support for the idea that eukaryotes evolved before prokaryotes can be seen in the structure of their chromosomes. Each chromosome is a very long molecule of DNA. We humans have twenty-three pairs of them--forty-six separate DNA molecules. Other species of eukaryote ...
Cell Reproduction Mitosis and Meiosis aka Cell Division
... the center or equator of the cell and line up along the equator • The centromere of each pair of chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber from the centriole ...
... the center or equator of the cell and line up along the equator • The centromere of each pair of chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber from the centriole ...
Unit 1 Topic 5 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... No individual plant or animal lives forever. Plants and animals exist today because their ancestors reproduced, either sexually or asexually. Remember that asexual reproduction requires only a single cell, such as a bacterium, to divide by binary fission. This process allows an organism to produce ma ...
... No individual plant or animal lives forever. Plants and animals exist today because their ancestors reproduced, either sexually or asexually. Remember that asexual reproduction requires only a single cell, such as a bacterium, to divide by binary fission. This process allows an organism to produce ma ...
Chp 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
... Chromosomes = 0rganizational unit of heredity material in the nucleus of eukaryotic organisms ï Consist of a single long DNA molecule (double helix) that is highly folded and coiled along with proteins ï Contain genetic information arranged in a linear sequence ï Contain hundreds or thousands of gen ...
... Chromosomes = 0rganizational unit of heredity material in the nucleus of eukaryotic organisms ï Consist of a single long DNA molecule (double helix) that is highly folded and coiled along with proteins ï Contain genetic information arranged in a linear sequence ï Contain hundreds or thousands of gen ...
Recombinant DNA and Plasmids
... Antibiotic resistance genes give us a way to select for a transformation event (find the bacteria with the plasmid). The plasmids carry an origin of replication that is a start point for DNA polymerase. Without it a plasmid would dilute out of the population. ...
... Antibiotic resistance genes give us a way to select for a transformation event (find the bacteria with the plasmid). The plasmids carry an origin of replication that is a start point for DNA polymerase. Without it a plasmid would dilute out of the population. ...
DISCOVERY OF DNAhandout
... Read the Nature article by Watson & Crick Discuss how they used the work of others to come up with the structure of DNA. How does the structure account for identical replication of DNA to be the conveyer of inheritance? ...
... Read the Nature article by Watson & Crick Discuss how they used the work of others to come up with the structure of DNA. How does the structure account for identical replication of DNA to be the conveyer of inheritance? ...
GENETICS - 123seminarsonly.com
... Chromosomes are the organized form of DNA found in cells. Chromosomes contain one very long, continuous piece of DNA, which contains many genes, regulatory elements and other intervening nucleotide sequences. A broader definition of "chromosome" also includes the DNA-bound proteins which serve to pa ...
... Chromosomes are the organized form of DNA found in cells. Chromosomes contain one very long, continuous piece of DNA, which contains many genes, regulatory elements and other intervening nucleotide sequences. A broader definition of "chromosome" also includes the DNA-bound proteins which serve to pa ...
Document
... main pigment in plants, absorbs sunlight male reproductive structure of a flower another name for fermentation carbohydrate made by plants as food builds up in muscles after exercise ...
... main pigment in plants, absorbs sunlight male reproductive structure of a flower another name for fermentation carbohydrate made by plants as food builds up in muscles after exercise ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.