Genetics Test - dublin.k12.ca.us
... D) an allele passed from parent to child on a sex chromosome 26. If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes do the sex cells have? A) 12 B) 23 C) 46 D) 6 27. An allele whose trait always shows up in an organism when the allele is present is called a A) mutation B) dominate allele ...
... D) an allele passed from parent to child on a sex chromosome 26. If a human body cell has 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes do the sex cells have? A) 12 B) 23 C) 46 D) 6 27. An allele whose trait always shows up in an organism when the allele is present is called a A) mutation B) dominate allele ...
Test Corrections for Genetics Test B Test corrections are available to
... Below show the alleles (individual forms of genes) for the two individuals. The male has brown eyes with a genotype of Bb and the female has blue eyes with alleles bb. The chromosomes represent autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). ...
... Below show the alleles (individual forms of genes) for the two individuals. The male has brown eyes with a genotype of Bb and the female has blue eyes with alleles bb. The chromosomes represent autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). ...
pdffile - UCI Math
... Institute, Division of Intramural Research, http://www.genome.gov/Pages/Hyperion//DIR/VIP/Glossary/Illustration/rna.shtml (accessed September ...
... Institute, Division of Intramural Research, http://www.genome.gov/Pages/Hyperion//DIR/VIP/Glossary/Illustration/rna.shtml (accessed September ...
Genetics of prokaryotic organisms
... Single-strand enters the conjugation bridge, the donor cell synthesizes a new strand at the same time. The second strand is also synthesized in the acceptor cell. Then there is recombination between donor and acceptor parts of the chromosome and excision and elimination of incomplete replication. ...
... Single-strand enters the conjugation bridge, the donor cell synthesizes a new strand at the same time. The second strand is also synthesized in the acceptor cell. Then there is recombination between donor and acceptor parts of the chromosome and excision and elimination of incomplete replication. ...
cdev-1st-edition-rathus-solution-manual
... helix composed of phosphates, sugars, and bases Mitosis: the form of cell division in which each chromosome splits lengthwise to double in number; half of each chromosome combines with chemicals to retake its original form and then moves to the new cell Mutation: a sudden variation in a heritable ch ...
... helix composed of phosphates, sugars, and bases Mitosis: the form of cell division in which each chromosome splits lengthwise to double in number; half of each chromosome combines with chemicals to retake its original form and then moves to the new cell Mutation: a sudden variation in a heritable ch ...
Biology or Genes?
... Chromosomes • Chromosomes are the complex DNA and Protein units that carry the genetic code in all cells with nuclei • In sexuallysexually-reproducing organisms, chromosomes come in homologous pairs – Each member of the pair contains information on how to build the same protein products – One member ...
... Chromosomes • Chromosomes are the complex DNA and Protein units that carry the genetic code in all cells with nuclei • In sexuallysexually-reproducing organisms, chromosomes come in homologous pairs – Each member of the pair contains information on how to build the same protein products – One member ...
Genes, Chromosomes and Human Genetics
... Calculated by RFs Measured in map units or centimorgans (cM) RF can not exceed 50%, at 50% cannot distinguish between genes on the same or different chromosomes Double crossovers – underestimate distance ...
... Calculated by RFs Measured in map units or centimorgans (cM) RF can not exceed 50%, at 50% cannot distinguish between genes on the same or different chromosomes Double crossovers – underestimate distance ...
Sex Linkage - Ms. Petrauskas' Class
... show the recessive trait (Ie: Blue eyed individuals have the genotype: bb) and having at least 1 copy of the dominant allele causes the dominant trait to be expressed. (Ie: The genotype Bb would result in a brown eyed individual) ...
... show the recessive trait (Ie: Blue eyed individuals have the genotype: bb) and having at least 1 copy of the dominant allele causes the dominant trait to be expressed. (Ie: The genotype Bb would result in a brown eyed individual) ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Every cell in your body, with the exception of gametes, or sex cells, contains a complete copy of your DNA. Why, then, are some cells nerve cells with dendrites and axons, while others are red blood cells that have lost their nuclei and are packed with hemoglobin? Why are cells so different in str ...
... • Every cell in your body, with the exception of gametes, or sex cells, contains a complete copy of your DNA. Why, then, are some cells nerve cells with dendrites and axons, while others are red blood cells that have lost their nuclei and are packed with hemoglobin? Why are cells so different in str ...
Plant vs. Animal Cells
... Cell Cycle has 4 parts: G1 S G2 M (with cytokinesis) OR 5 parts: I P M A T --during interphase, the cell grows, copies DNA, makes organelles, and gets ready to divide; this is the “growth” period for the cell; G1 S G2; it is the longest phase --mitosis only involves BODY CELLS (also known ...
... Cell Cycle has 4 parts: G1 S G2 M (with cytokinesis) OR 5 parts: I P M A T --during interphase, the cell grows, copies DNA, makes organelles, and gets ready to divide; this is the “growth” period for the cell; G1 S G2; it is the longest phase --mitosis only involves BODY CELLS (also known ...
DNA and Genealogy
... Mitochondrial DNA passes from mother to all children with little change Y DNA passes from father to boys only with little change X DNA has a specific inheritance pathway Autosomal DNA is ‘shuffled’ during the making of sperm and egg cells This ‘shuffling’ (recombination) is random, but allows large ...
... Mitochondrial DNA passes from mother to all children with little change Y DNA passes from father to boys only with little change X DNA has a specific inheritance pathway Autosomal DNA is ‘shuffled’ during the making of sperm and egg cells This ‘shuffling’ (recombination) is random, but allows large ...
Karyotyping, FISH and CGH array
... A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), a variation at a single site in DNA, is the most frequent type of variation in the genome. For example, there are around 50 million SNPs that have been identified in the human genome. Most of them are non pathological. The basic principles and techniques of SN ...
... A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), a variation at a single site in DNA, is the most frequent type of variation in the genome. For example, there are around 50 million SNPs that have been identified in the human genome. Most of them are non pathological. The basic principles and techniques of SN ...
I. The Emerging Role of Genetics and Genomics in Medicine
... 6. Mode of inheritance refers to whether a trait is dominant or recessive, autosomal or carried on a sex chromosome. 7. An autosomal condition is equally likely to affect either sex. 8. X-linked characteristics affect males much more than females. 9. Recessive conditions can skip a generation becaus ...
... 6. Mode of inheritance refers to whether a trait is dominant or recessive, autosomal or carried on a sex chromosome. 7. An autosomal condition is equally likely to affect either sex. 8. X-linked characteristics affect males much more than females. 9. Recessive conditions can skip a generation becaus ...
(Genetics).
... a significant role in the expression of their genes. 2) Their DNA is essentially the same and the environment plays a significant role in the expression of their genes. 3) Their DNA is essentially the same and the environment plays little or no role in the expression of their genes. 4) Their DNA is ...
... a significant role in the expression of their genes. 2) Their DNA is essentially the same and the environment plays a significant role in the expression of their genes. 3) Their DNA is essentially the same and the environment plays little or no role in the expression of their genes. 4) Their DNA is ...
Principles of Genetics
... 2. Genes control the traits of an organism. • A gene is a section of a chromosome, that codes for a specific trait. • Chromosomes are made of tightly wound strands of DNA ...
... 2. Genes control the traits of an organism. • A gene is a section of a chromosome, that codes for a specific trait. • Chromosomes are made of tightly wound strands of DNA ...
- 10EssentialScience
... Each cell contains the same DNA. The DNA is found inside the nucleus of the cell. ...
... Each cell contains the same DNA. The DNA is found inside the nucleus of the cell. ...
Biology- Semester 2 Final Exam Review 2012
... State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. Differentiate genes from alleles. How did Mendel’s F1 generation plants differ from his F2 generation plants? Many inherited disorders of humans appear in children of parents who do not have the disorder. How can you explain this? 6. ...
... State two laws of heredity that were developed from Mendel’s work. Differentiate genes from alleles. How did Mendel’s F1 generation plants differ from his F2 generation plants? Many inherited disorders of humans appear in children of parents who do not have the disorder. How can you explain this? 6. ...
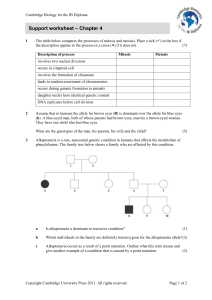
Support worksheet – Chapter 4 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Cambridge Biology for the IB Diploma ...
... Cambridge Biology for the IB Diploma ...
Leukaemia Section t(14;21)(q22;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... MM, Rowley JD. CBFA2(AML1) translocations with novel partner chromosomes in myeloid leukemias: association with prior therapy. Blood. 1998 Oct 15;92(8):2879-85 ...
... MM, Rowley JD. CBFA2(AML1) translocations with novel partner chromosomes in myeloid leukemias: association with prior therapy. Blood. 1998 Oct 15;92(8):2879-85 ...
meiosis
... 8.4 The large, complex chromosomes of eukaryotes duplicate with each cell division Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of chromatin – Chromatin = DNA + proteins – To prepare for division, the chromatin becomes highly compact, and the chromosomes are visible with a microscope – Early in the divisi ...
... 8.4 The large, complex chromosomes of eukaryotes duplicate with each cell division Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of chromatin – Chromatin = DNA + proteins – To prepare for division, the chromatin becomes highly compact, and the chromosomes are visible with a microscope – Early in the divisi ...
Biology Study guide 2 with standards-DNA-evolution
... Mutations- Sometimes when DNA is replicating there are mistakes in the coding called mutations. It could be an addition, deletion, or substitution of bases. Mutations can be good or harmful. They cause variations and are passed on to offspring if they occur in the gametes. Mutations can be random ...
... Mutations- Sometimes when DNA is replicating there are mistakes in the coding called mutations. It could be an addition, deletion, or substitution of bases. Mutations can be good or harmful. They cause variations and are passed on to offspring if they occur in the gametes. Mutations can be random ...
File
... A. Is recessive to the father’s dominant allele. B. Is dominant over the father’s allele. ...
... A. Is recessive to the father’s dominant allele. B. Is dominant over the father’s allele. ...
Electrical induction hypothesis to explain enhancer-promoter
... (Nelson and Wardle 2013). However, despite having the entire sequence of the genome, very little has been understood about three‐dimensional chromosome conformation beyond the scale of the nucleosome. But, recent advances in molecular biology and computational analysis have lent insight into chromat ...
... (Nelson and Wardle 2013). However, despite having the entire sequence of the genome, very little has been understood about three‐dimensional chromosome conformation beyond the scale of the nucleosome. But, recent advances in molecular biology and computational analysis have lent insight into chromat ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.