Nerve Impulse Transmission
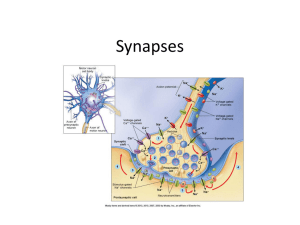
... Transmission at the Synapse • There is a tiny gap between the synaptic knobs of one neuron and the dendrites of the next one. • This gap is called the synapse or synaptic cleft. • The nerve impulse needs to cross this gap and it does so by the release of special chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
... Transmission at the Synapse • There is a tiny gap between the synaptic knobs of one neuron and the dendrites of the next one. • This gap is called the synapse or synaptic cleft. • The nerve impulse needs to cross this gap and it does so by the release of special chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
Brainsignals, Synaptic Transmission and Short
... 1012 neurons, each of which is connected with thousands of other cells by synapses ...
... 1012 neurons, each of which is connected with thousands of other cells by synapses ...
Stochastic fluctuations of the synaptic function
... synapses produced quantal Excitatory PostSynaptic Currents (EPSCs) with peak amplitudes having a 5-65 pA range. The histogram of the peak amplitudes showed a long right tail. If the variability of the postsynaptic response observed in hippocampal neurons should be extended to all the neurons of brai ...
... synapses produced quantal Excitatory PostSynaptic Currents (EPSCs) with peak amplitudes having a 5-65 pA range. The histogram of the peak amplitudes showed a long right tail. If the variability of the postsynaptic response observed in hippocampal neurons should be extended to all the neurons of brai ...
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... – Excitatory: cause depolarization in postsynaptic neuron (stimulate next neuron) – Inhibitory: cause hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane that inhibits/stops the potential from moving on • Drugs can be inhibitory or excitatory • Endorphins are inhibitory- block pain ...
... – Excitatory: cause depolarization in postsynaptic neuron (stimulate next neuron) – Inhibitory: cause hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane that inhibits/stops the potential from moving on • Drugs can be inhibitory or excitatory • Endorphins are inhibitory- block pain ...
File
... from pressure sensed on the skin (PNS) sends signal to the brain (CNS) that the touch was accidental brain activates motor neurons in your arm (PNS) you move your arm away (R) 3. The motor end plate is the junction where the neuron sends a chemical signal to the muscles to produce a physical r ...
... from pressure sensed on the skin (PNS) sends signal to the brain (CNS) that the touch was accidental brain activates motor neurons in your arm (PNS) you move your arm away (R) 3. The motor end plate is the junction where the neuron sends a chemical signal to the muscles to produce a physical r ...
"TOPICS IN THEORETICAL NEUROBIOLOGY"
... Writing the HH auxiliary equations in the following form ...
... Writing the HH auxiliary equations in the following form ...
Exercise 5: Synaptic Integration - הפקולטה למדעי הבריאות
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
... The EPSP occuring first will now be closest to the cell soma. Will this sequence of EPSPs cause an action potential to initiate? ...
biopsychology-2-synaptic-transmission
... • Each neurotransmitter has its own specific molecular structure that fits perfectly into a post-synaptic receptor site, similar to a lock and a key. • When the right key (i.e. neurotransmitter) meets the right lock (i.e. receptor) a specific ion channel in the membrane is opened. • Ions then flow t ...
... • Each neurotransmitter has its own specific molecular structure that fits perfectly into a post-synaptic receptor site, similar to a lock and a key. • When the right key (i.e. neurotransmitter) meets the right lock (i.e. receptor) a specific ion channel in the membrane is opened. • Ions then flow t ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
... 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse with the knob membrane 4. Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane causing the channels to open and allow sodium to leak in-thus setting up the action potential. ...
... 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse with the knob membrane 4. Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane causing the channels to open and allow sodium to leak in-thus setting up the action potential. ...
ppt - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... Principles of how the CNS manages noise • The principle of averaging can be applied whenever redundant information is present across the sensory inputs to the CNS or is generated by the CNS. • Averaging can counter noise if several units (such as receptor molecules, neurons or muscles) carry the sa ...
... Principles of how the CNS manages noise • The principle of averaging can be applied whenever redundant information is present across the sensory inputs to the CNS or is generated by the CNS. • Averaging can counter noise if several units (such as receptor molecules, neurons or muscles) carry the sa ...
Nerve Cell Signaling - Mr. Moore`s Web Page
... 2. Describe the sequence of events that lead to an action potential and a depolarization of the neuron. 3. Describe the passage of neurotransmitter across a synaptic cleft. 4. Identify what a motor neuron and sensory neurons do and where they are located in the body. ...
... 2. Describe the sequence of events that lead to an action potential and a depolarization of the neuron. 3. Describe the passage of neurotransmitter across a synaptic cleft. 4. Identify what a motor neuron and sensory neurons do and where they are located in the body. ...
Hearing, Ribbon Synapses and Noise Induced Hearing Loss
... Experiments are underway in my Department, and in Harvard If it does work, will need to define therapeutic window, and determine whether treatment protects or regenerates the peripheral dendrites ...
... Experiments are underway in my Department, and in Harvard If it does work, will need to define therapeutic window, and determine whether treatment protects or regenerates the peripheral dendrites ...
Membrane Biophysics and Synaptic Physiology
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...
Abstract View ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERSION USING RECURRENT SPIKING NEURAL NETWORKS ;
... 5200, 91). The individual neurons are coordinated using feedback in a manner that suppresses noise and makes the output spike rate proportional to the level of the analog input signal without a predetermined progression of states or an explicit clock. We explored the possibility that cortical networ ...
... 5200, 91). The individual neurons are coordinated using feedback in a manner that suppresses noise and makes the output spike rate proportional to the level of the analog input signal without a predetermined progression of states or an explicit clock. We explored the possibility that cortical networ ...
Our brain is made of so many neurons, which communicate each
... Institution: National Institute for Physiological Sciences 1. Background of research ...
... Institution: National Institute for Physiological Sciences 1. Background of research ...
Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely
... molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity for fundamental and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, simultaneous photocontrol of synaptic receptors and fluorescence imaging of neuronal activity in vivo will allow studying synaptic plasticity from the single dendrit ...
... molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity for fundamental and therapeutic purposes. In the first case, simultaneous photocontrol of synaptic receptors and fluorescence imaging of neuronal activity in vivo will allow studying synaptic plasticity from the single dendrit ...
Neurons, Synapses and Long-term Potentiation
... changes in behaviour and are therefore linked to changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
... changes in behaviour and are therefore linked to changes in the cellular level • So what are the cellular changes? ...
A synaptic memory trace for cortical receptive field plasticity
... Neural networks of the cerebral cortex continually change throughout life, allowing us to learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordinati ...
... Neural networks of the cerebral cortex continually change throughout life, allowing us to learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordinati ...
9.3 Synaptic Transmission
... neurons are needed to create an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... neurons are needed to create an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Modeling Synaptic Plasticity
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
... Synapses are the structures through which neurons communicate, and the loci of information storage in neural circuits. Synapses store information (‘learn’) thanks to synaptic plasticity: the efficacy of the communication between the two neurons connected by the synapse can change, as a function of t ...
We are investigating the use of novel stimulus
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...