What is meiosis? - Perry Local Schools
... and general appearance. With copies of the same genes, although the two copies may differ. Autosomes chromosomes that contain genes for charcteristics not directly related to the sex of the organism. Chromosomes 122 in humans Sex Chromosomes directly control the development of sexual chara ...
... and general appearance. With copies of the same genes, although the two copies may differ. Autosomes chromosomes that contain genes for charcteristics not directly related to the sex of the organism. Chromosomes 122 in humans Sex Chromosomes directly control the development of sexual chara ...
Slide 1 - ap biology
... results in too little blood clotting factor produced, leading to uncontrolled bleeding ...
... results in too little blood clotting factor produced, leading to uncontrolled bleeding ...
Document
... The body cells of humans have 46 chromosomes that form 23 pairs. Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together. You have 23 pairs of chromosome. Each chromosome has 200 – 3000 genes. Therefore, you have between 20,000 – 25,000 genes. Each gene controls a trait. About Chromosome 1 Chromosome ...
... The body cells of humans have 46 chromosomes that form 23 pairs. Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together. You have 23 pairs of chromosome. Each chromosome has 200 – 3000 genes. Therefore, you have between 20,000 – 25,000 genes. Each gene controls a trait. About Chromosome 1 Chromosome ...
Genetics of Sex - University of San Francisco
... down of X–Y crossing over during evolution triggered a monotonic decline in gene function PAR1 homology maintained by recombination in male meiosis, genes in this region not subject to dosage compensation ...
... down of X–Y crossing over during evolution triggered a monotonic decline in gene function PAR1 homology maintained by recombination in male meiosis, genes in this region not subject to dosage compensation ...
Test 4 Review
... – Kinetochore – proteins that spindle fibers attach to…all around the chromosome ...
... – Kinetochore – proteins that spindle fibers attach to…all around the chromosome ...
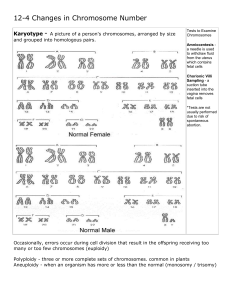
Chromosome Number Mutations
... is still one present to code for vital life functions NOTE: one X must be present, without an X, life ceases ...
... is still one present to code for vital life functions NOTE: one X must be present, without an X, life ceases ...
Advanced Biology Vocabulary
... Autopolyploid An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
... Autopolyploid An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
14-2 Human Chromosomes – Reading Guide
... 9. Males have just one __________ chromosome. So, all X-linked alleles are expressed in ____________ even if they are ______________________. 10. ________________________ is another example of a sex-linked disorder in which two genes on the X chromosome help control ___________________ _____________ ...
... 9. Males have just one __________ chromosome. So, all X-linked alleles are expressed in ____________ even if they are ______________________. 10. ________________________ is another example of a sex-linked disorder in which two genes on the X chromosome help control ___________________ _____________ ...
Topic 2
... In 1961 she proposed the concept of X-inactivation: one of the two X chromosomes inside a female mammal shuts off under normal circumstances. Yet in some circumstances different X chromosomes will shut off, resulting in the calico appearance. She observed this in the coat color patterns in mice. ...
... In 1961 she proposed the concept of X-inactivation: one of the two X chromosomes inside a female mammal shuts off under normal circumstances. Yet in some circumstances different X chromosomes will shut off, resulting in the calico appearance. She observed this in the coat color patterns in mice. ...
SEX-RELATED INHERITANCE
... Mary Lyon correctly hypothesized that the Barr Bodies are actually condensed, inactive X chromosomes: She also said that: • Every X > 1 is condensed and inactive in gene expression; • X-inactivation occurs early in development; • When it occurs, which X is inactivated in any cell is chance; • The sa ...
... Mary Lyon correctly hypothesized that the Barr Bodies are actually condensed, inactive X chromosomes: She also said that: • Every X > 1 is condensed and inactive in gene expression; • X-inactivation occurs early in development; • When it occurs, which X is inactivated in any cell is chance; • The sa ...
SexChromosomes - life.illinois.edu
... inactivated is random. As development proceeds, all cells arising by cell division after than time have the same X inactivated as the parent cell. ...
... inactivated is random. As development proceeds, all cells arising by cell division after than time have the same X inactivated as the parent cell. ...
Lecture 7 - Brandeis Life Sciences
... RSV LTR and a translocated c-myc gene obeys very unusual rules. If the transgene is inherited from the male parent, it is expressed in the heart and no other tissue. If it is inherited from the female parent, it is not expressed at all. This pattern of expression correlates precisely with a parental ...
... RSV LTR and a translocated c-myc gene obeys very unusual rules. If the transgene is inherited from the male parent, it is expressed in the heart and no other tissue. If it is inherited from the female parent, it is not expressed at all. This pattern of expression correlates precisely with a parental ...
genetics 2-2
... Law of Segregation: a pair of factors called genes segregate independently during the formation of gametes. Law of Dominance and Recessiveness: one gene in a pair may mask or prevent the expression of the other. GENETIC DISORDERS PKU: A genetic disease due to a lack of an enzyme. Klinefelter’s Syndr ...
... Law of Segregation: a pair of factors called genes segregate independently during the formation of gametes. Law of Dominance and Recessiveness: one gene in a pair may mask or prevent the expression of the other. GENETIC DISORDERS PKU: A genetic disease due to a lack of an enzyme. Klinefelter’s Syndr ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resembles a twisted ladder or double helix. The steps within the ladder are ...
... The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resembles a twisted ladder or double helix. The steps within the ladder are ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Males and females express the same levels of certain genes found on the X chromosome Dosage compensation In females one X chromosome is randomly selected for modification 13.3 Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA is inherited only from the egg cell. 1 ...
... Males and females express the same levels of certain genes found on the X chromosome Dosage compensation In females one X chromosome is randomly selected for modification 13.3 Exceptions to the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA is inherited only from the egg cell. 1 ...
Lecture #6 Date ______
... the probability that a crossover will occur between them and therefore the higher the recombination frequency Linkage maps Genetic map based on recombination frequencies ...
... the probability that a crossover will occur between them and therefore the higher the recombination frequency Linkage maps Genetic map based on recombination frequencies ...
SexChrom_posted
... Presence of a single gene (SRY) that usually, but not always, occurs on the Y chromosome. If the Y chromosome is missing (this gene deleted) or has a non-functional mutation in the gene, an XY individual can be a perfectly normal female. If the SRY gene becomes translocated to another chromosome, an ...
... Presence of a single gene (SRY) that usually, but not always, occurs on the Y chromosome. If the Y chromosome is missing (this gene deleted) or has a non-functional mutation in the gene, an XY individual can be a perfectly normal female. If the SRY gene becomes translocated to another chromosome, an ...
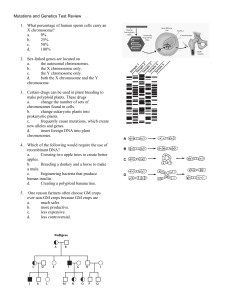
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
Lyonization - National Foundation for Ectodermal Dysplasias
... pairs of chromosomes, but differ in the pair known as the sex chromosomes. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. The X chromosome is loaded with genetic information. The Y chromosome carries very little except factors that help determine maleness. In order ...
... pairs of chromosomes, but differ in the pair known as the sex chromosomes. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. The X chromosome is loaded with genetic information. The Y chromosome carries very little except factors that help determine maleness. In order ...
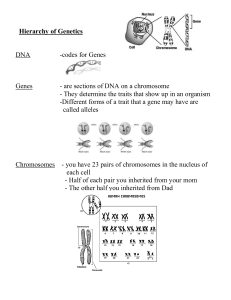
Hierarchy of Genetics
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
371_section quiz
... of the disorder. A carrier is a person who a. does not have the disorder but can pass it on to offspring. b. can develop the disorder later in life but cannot pass it on. c. has a dominant normal allele that has been inactivated. d. passes the disorder to offspring on the Y chromosome only. 4. Genes ...
... of the disorder. A carrier is a person who a. does not have the disorder but can pass it on to offspring. b. can develop the disorder later in life but cannot pass it on. c. has a dominant normal allele that has been inactivated. d. passes the disorder to offspring on the Y chromosome only. 4. Genes ...
Genetics - the science of heredity and variation
... Genes - the smallest unit of inheritance; a portion of a DNA molecule, occur in pairs on chromosomes in the nucleus of every cell Haploid - refers to the number of chromosomes in a sex cell which is half of the original number Heritability - proportion of observed variation in a particular trait whi ...
... Genes - the smallest unit of inheritance; a portion of a DNA molecule, occur in pairs on chromosomes in the nucleus of every cell Haploid - refers to the number of chromosomes in a sex cell which is half of the original number Heritability - proportion of observed variation in a particular trait whi ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.