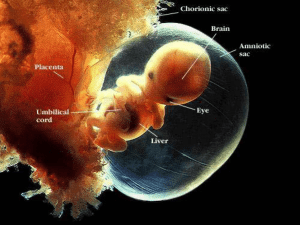
The Biological Basis of Life
... • A Karyotype is a photomicrograph of the chromosomal complement of an individual • The chromosomes are arranged according to size, and numbered, with the first pair being the largest chromosomes and the twentysecond pair being the smallest in humans, except for the Y (male-determining) chromosome ...
... • A Karyotype is a photomicrograph of the chromosomal complement of an individual • The chromosomes are arranged according to size, and numbered, with the first pair being the largest chromosomes and the twentysecond pair being the smallest in humans, except for the Y (male-determining) chromosome ...
DNA, RNA, Genes, Chromosomes
... hair and eye color, as well as more subtle characteristics, such as the oxygencarrying ability of the blood. Complex traits, such as IQ and physical strength, may be shaped by the interaction of a number of different genes along with environmental influences. It is estimated that humans have 100,000 ...
... hair and eye color, as well as more subtle characteristics, such as the oxygencarrying ability of the blood. Complex traits, such as IQ and physical strength, may be shaped by the interaction of a number of different genes along with environmental influences. It is estimated that humans have 100,000 ...
ch 10 Human GeneticsTest Qustions Study Guide
... a. About half of the symbols are circles b. All of the symbols are unshaded c. All of the symbols are half-shaded d. All of the symbols are shaded 10. Some gametes may have an extra copy of some genes if nondisjunction occurs during meiosis 11. Is PKU caused by a dominant allele? PKU? Huntington’s? ...
... a. About half of the symbols are circles b. All of the symbols are unshaded c. All of the symbols are half-shaded d. All of the symbols are shaded 10. Some gametes may have an extra copy of some genes if nondisjunction occurs during meiosis 11. Is PKU caused by a dominant allele? PKU? Huntington’s? ...
Unit A Topic 3
... complete set of chromosomes. 12. In most organisms the chromosomes are arranged into ___________________. 13. Chromosome number ______________ from one species to another. 14. A single gene is an ____________________________________ of DNA, which contains coded instructions. 15. Researchers found th ...
... complete set of chromosomes. 12. In most organisms the chromosomes are arranged into ___________________. 13. Chromosome number ______________ from one species to another. 14. A single gene is an ____________________________________ of DNA, which contains coded instructions. 15. Researchers found th ...
Sem 1 Revision Chem and Biol File
... b) phenotypic ratio of the offsprings. 50% black D:\873996652.doc ...
... b) phenotypic ratio of the offsprings. 50% black D:\873996652.doc ...
Practice Exam 3
... d. an animal cell in the S phase of the cell cycle e. a plant cell in metaphase 2.) A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in mitotically active tissues. The cell in question is most likely in: a. G1 b. G2 c. prophase d. metaphase e.anaphase 3.) In some organisms, mitosis occurs ...
... d. an animal cell in the S phase of the cell cycle e. a plant cell in metaphase 2.) A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in mitotically active tissues. The cell in question is most likely in: a. G1 b. G2 c. prophase d. metaphase e.anaphase 3.) In some organisms, mitosis occurs ...
GENETICS VOCABULARY STUDY GUIDE Chapter 2 – section 3 1
... 22. A number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur. 23. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. 24. The offspring of many ...
... 22. A number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur. 23. A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross. 24. The offspring of many ...
Mendelian Genetics - FSCJ - Library Learning Commons
... chromosomes. Ex: The different alleles for plant height can be represented by “T” for tall and “t” for short. Sexual reproduction – Entails the union of two gametes to form a single celled zygote. Introduces genetic variation in offspring that allows adaptation to environmental changes. Haploid (n) ...
... chromosomes. Ex: The different alleles for plant height can be represented by “T” for tall and “t” for short. Sexual reproduction – Entails the union of two gametes to form a single celled zygote. Introduces genetic variation in offspring that allows adaptation to environmental changes. Haploid (n) ...
Nov07-BalancersFinal
... If you do steps 2 and 3 many times (a separate vial for each) one can clone many * chromosomes and if you discard all vials that yield straight winged flies, you will be left with a bunch of vials each containing a particular * chromosome over a balancer and each of these retained chromosomes will c ...
... If you do steps 2 and 3 many times (a separate vial for each) one can clone many * chromosomes and if you discard all vials that yield straight winged flies, you will be left with a bunch of vials each containing a particular * chromosome over a balancer and each of these retained chromosomes will c ...
Genetics Answers
... Pros- widely available, treat many different diseases Cons- possible harm to embryo, may not work, embryos not consulted. Adult stem cell use is quick, well tested, safe but is painful and can currently treat few diseases. 14. What is an allele? Forms of the same gene 15. What does recessive mean? O ...
... Pros- widely available, treat many different diseases Cons- possible harm to embryo, may not work, embryos not consulted. Adult stem cell use is quick, well tested, safe but is painful and can currently treat few diseases. 14. What is an allele? Forms of the same gene 15. What does recessive mean? O ...
Mendel and Meiosis
... Nondisjunction leading to polyploidy • When a gamete with an extra set of chromosomes is fertilized by a normal haploid gamete, the offspring has three sets of chromosomes and is triploid. ...
... Nondisjunction leading to polyploidy • When a gamete with an extra set of chromosomes is fertilized by a normal haploid gamete, the offspring has three sets of chromosomes and is triploid. ...
Human Genetics
... • Genetic disorders and abnormalities are inherited as alleles • Alleles for abnormalities and disorders may either be dominant or recessive to alleles carrying normal traits. • Alleles for abnormalities and disorders may either be carried on autosomes or on one of the sex chromosomes ...
... • Genetic disorders and abnormalities are inherited as alleles • Alleles for abnormalities and disorders may either be dominant or recessive to alleles carrying normal traits. • Alleles for abnormalities and disorders may either be carried on autosomes or on one of the sex chromosomes ...
Genetics SHOW
... the recipe (mRNA). The amino acids fold together to make the protein. The protein moves to the needed area in the body. ...
... the recipe (mRNA). The amino acids fold together to make the protein. The protein moves to the needed area in the body. ...
mendel-test-AP-gibbs..
... Sex-linked traits are never seen in girls. The allele is carried on the Y chromosome. Nondisjunction occurs in males but not in females. To express an X-linked recessive allele, a female must have two copies of the allele. A sex-linked allele cannot be passed from mother to daughter. ...
... Sex-linked traits are never seen in girls. The allele is carried on the Y chromosome. Nondisjunction occurs in males but not in females. To express an X-linked recessive allele, a female must have two copies of the allele. A sex-linked allele cannot be passed from mother to daughter. ...
File
... Huntington’s Disease Caused by a dominant allele Late-onset of symptoms (age 40) result in the ...
... Huntington’s Disease Caused by a dominant allele Late-onset of symptoms (age 40) result in the ...
Non-Mendellian Genetics Part II
... 332 expressing the phenotypes of the dominant Q and H alleles; 324 expressing phenotypes of the dominant Q and recessive h allele; 346 expressing the phenotypes of the recessive q and dominant H alleles; and no progeny expressing both recessive phenotypes. Does this follow the predicted pattern of i ...
... 332 expressing the phenotypes of the dominant Q and H alleles; 324 expressing phenotypes of the dominant Q and recessive h allele; 346 expressing the phenotypes of the recessive q and dominant H alleles; and no progeny expressing both recessive phenotypes. Does this follow the predicted pattern of i ...
Chromosomes
... • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduces" by copying itself and ...
... • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduces" by copying itself and ...
Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Notes
... coiled around proteins (*this is after replication but before cell division) B. Chromatid- each copy of the DNA on a chromosome C. Centromere- place where the chromatids attach to make a chromosome D. Genes- Segments of DNA on a chromosome that code for a specific protein/trait A. ...
... coiled around proteins (*this is after replication but before cell division) B. Chromatid- each copy of the DNA on a chromosome C. Centromere- place where the chromatids attach to make a chromosome D. Genes- Segments of DNA on a chromosome that code for a specific protein/trait A. ...
Designer Genes - Heredity
... Transcription: Synthesis of RNA from a DNA Template. Requires DNA-dependent RNA polymerase plus the four nucleotides (ATP, GTP. CTP and UTP). Synthesis begins at a the initiation site on DNA The template strand is read 3' to 5' and the mRNA is synthesized 5' to 3' ...
... Transcription: Synthesis of RNA from a DNA Template. Requires DNA-dependent RNA polymerase plus the four nucleotides (ATP, GTP. CTP and UTP). Synthesis begins at a the initiation site on DNA The template strand is read 3' to 5' and the mRNA is synthesized 5' to 3' ...
AP Biology – PowerPoint Notes – Chapter 11 & 12 ‐ Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics
... Before Mendel, it was believed that parental traits were blended in offspring and could not be separated in later generations. ...
... Before Mendel, it was believed that parental traits were blended in offspring and could not be separated in later generations. ...
Genetics
... – Diploid organisms contain 2 alleles of each locus (gene) • Alleles can be identical – homozygous • Alleles can be different – heterozygous • If only one allele is present – hemizygous – Case in males for genes on X and Y chromosomes ...
... – Diploid organisms contain 2 alleles of each locus (gene) • Alleles can be identical – homozygous • Alleles can be different – heterozygous • If only one allele is present – hemizygous – Case in males for genes on X and Y chromosomes ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.