The RNA world meets behavior: AfiI pre
... which a coding position is modified within messages. Certain pre-mRNA editing sites vary greatly in the frequency with which their editing is detected in vivo, ranging from a few percent to nearly 100%. Thus, editing introduces levels of expression intermediate to the usual genetic variation (i.e. 0 ...
... which a coding position is modified within messages. Certain pre-mRNA editing sites vary greatly in the frequency with which their editing is detected in vivo, ranging from a few percent to nearly 100%. Thus, editing introduces levels of expression intermediate to the usual genetic variation (i.e. 0 ...
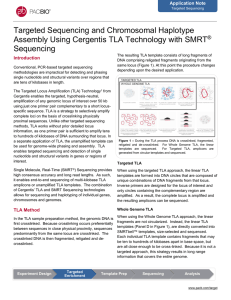
Application Note: Targeted sequencing and chromosomal haplotype
... Conventional, PCR-based targeted sequencing methodologies are impractical for detecting and phasing single nucleotide and structural variants over regions that are tens of kilobases in length. The Targeted Locus Amplification (TLA) Technology1 from Cergentis enables the targeted, hypothesis-neutral, ...
... Conventional, PCR-based targeted sequencing methodologies are impractical for detecting and phasing single nucleotide and structural variants over regions that are tens of kilobases in length. The Targeted Locus Amplification (TLA) Technology1 from Cergentis enables the targeted, hypothesis-neutral, ...
2. In vivo Maternal Haploid Induction in Maize
... Mechanism of in vivo maternal haploid induction The exact sequence of events underlying maternal haploid induction has not been clearly understood. Several hypotheses were proposed to explain in vivo mater ...
... Mechanism of in vivo maternal haploid induction The exact sequence of events underlying maternal haploid induction has not been clearly understood. Several hypotheses were proposed to explain in vivo mater ...
Tandem Genetic Duplications in Phage and Bacteria
... Selection schemes designed to detect tandem duplication mutants in a haploid population must capitalize upon some special property conferred by the diploid state. The merodiploid nature of tandem duplications and the sequence impropriety found at the join point between duplicated regions are often t ...
... Selection schemes designed to detect tandem duplication mutants in a haploid population must capitalize upon some special property conferred by the diploid state. The merodiploid nature of tandem duplications and the sequence impropriety found at the join point between duplicated regions are often t ...
... The Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology is a peer reviewed on-line journal in open access, devoted to genes, cytogenetics, and clinical entities in cancer, and cancer-prone diseases. It presents structured review articles (“cards”) on genes, leukaemias, solid tumours, canc ...
Mendelian genetics
... anaphase I. • For each chromosome pair, there is a 50% chance of getting either chromosome. • Independent assortment: the idea that each gamete randomly receives chromosomes in meiosis. ...
... anaphase I. • For each chromosome pair, there is a 50% chance of getting either chromosome. • Independent assortment: the idea that each gamete randomly receives chromosomes in meiosis. ...
MGF 360-17R Missing
... Trunc – 014 [MGF 110-7L/MGF 360-6L Fusion Protein]: This gene is a fusion between the MGF 110-7L ortholog and MGF 360-6L. The carboxy terminus of this fusion is shown as a small box between the 3L and 4L orthologs as the MGF 110 orthologs are outside of the scope of this diagram. The annotated ortho ...
... Trunc – 014 [MGF 110-7L/MGF 360-6L Fusion Protein]: This gene is a fusion between the MGF 110-7L ortholog and MGF 360-6L. The carboxy terminus of this fusion is shown as a small box between the 3L and 4L orthologs as the MGF 110 orthologs are outside of the scope of this diagram. The annotated ortho ...
Charcot-Marie
... investigations, as some mildly affected family members may not have any symptoms. What is the cause of CMT? There have been major advances in the last decade in the identification of the causative genes for CMT. To date there have been 16 causative genes identified and at least 8 other loci (locatio ...
... investigations, as some mildly affected family members may not have any symptoms. What is the cause of CMT? There have been major advances in the last decade in the identification of the causative genes for CMT. To date there have been 16 causative genes identified and at least 8 other loci (locatio ...
Practice final key
... locus closely linked to the centromere of a chromosome and heterozygous Bb for another locus weakly linked to the centromere of the same chromosome. It is found that cells of the teratoma have the normal human female karyotype (XX; 22AA) and are homozygous A/A and heterozygous B/b. Which of the foll ...
... locus closely linked to the centromere of a chromosome and heterozygous Bb for another locus weakly linked to the centromere of the same chromosome. It is found that cells of the teratoma have the normal human female karyotype (XX; 22AA) and are homozygous A/A and heterozygous B/b. Which of the foll ...
exam_3 - Homework Market
... There are many genetically inherited diseases or conditions. When the allele, causing the condition, is recessive the parents can be carriers of the allele but they are unaffected by the disease themselves. The dominant allele protects them. However, there are conditions caused by dominant alleles. ...
... There are many genetically inherited diseases or conditions. When the allele, causing the condition, is recessive the parents can be carriers of the allele but they are unaffected by the disease themselves. The dominant allele protects them. However, there are conditions caused by dominant alleles. ...
Transcriptome analysis of Drosophila CNS midline cells reveals
... revealed that midline cells express 9 neuropeptide precursor genes, 13 neuropeptide receptor genes, and 31 small-molecule neurotransmitter receptor genes. In situ hybridization and high-resolution confocal analyses were carried-out to determine the midline cell identity for these neuropeptides and t ...
... revealed that midline cells express 9 neuropeptide precursor genes, 13 neuropeptide receptor genes, and 31 small-molecule neurotransmitter receptor genes. In situ hybridization and high-resolution confocal analyses were carried-out to determine the midline cell identity for these neuropeptides and t ...
Genetics - York University
... They each began a search of the scientific literature to see if anyone had done any experimental work that would help to confirm this view. ...
... They each began a search of the scientific literature to see if anyone had done any experimental work that would help to confirm this view. ...
Gene Section DLX6 (distal-less homeobox 6) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... defects progressively afflicting young girls suffering of Rett syndrome (OMIM #312750). This late onset disorder features fatal motor abnormalities, seizures, autism and mental retardation. While the genomic sequence of the DLX5/DXL6 locus remains unaffected in all reported cases, it is a direct tar ...
... defects progressively afflicting young girls suffering of Rett syndrome (OMIM #312750). This late onset disorder features fatal motor abnormalities, seizures, autism and mental retardation. While the genomic sequence of the DLX5/DXL6 locus remains unaffected in all reported cases, it is a direct tar ...
lecture
... Nosce te ipsum: the human genome Part II: genetics, diagnostics, and gene therapy of inherited disease ...
... Nosce te ipsum: the human genome Part II: genetics, diagnostics, and gene therapy of inherited disease ...
Genetics - Brook Biology
... Gene Expression Multicellular organisms need a variety of cell types to perform specific functions for the organism; therefore, individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. • Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, ...
... Gene Expression Multicellular organisms need a variety of cell types to perform specific functions for the organism; therefore, individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. • Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, ...
The phenotypic consequences of MECP2 mutations extend beyond
... XCI patterns in RTT indicate that most probands have random inactivation patterns in blood, skin, and brain [Vorsanova et al., 1996; Webb and Watkiss, 1996; Zoghbi et al., 1990]. Nonetheless, for girls with classic or atypical RTT resulting from MECP2 mutation, it is likely that the individual varia ...
... XCI patterns in RTT indicate that most probands have random inactivation patterns in blood, skin, and brain [Vorsanova et al., 1996; Webb and Watkiss, 1996; Zoghbi et al., 1990]. Nonetheless, for girls with classic or atypical RTT resulting from MECP2 mutation, it is likely that the individual varia ...
New functions of the Drosophila rhomboid gene
... have dominant constitutive extra wing vein phenotypes (Sturtevant et al., 1993), we expected that a more systematic attempt to generate dominant alleles might reveal new functions of rho. Furthermore, such dominant phenotypes could serve as valuable genetic tools for isolating second site suppressor ...
... have dominant constitutive extra wing vein phenotypes (Sturtevant et al., 1993), we expected that a more systematic attempt to generate dominant alleles might reveal new functions of rho. Furthermore, such dominant phenotypes could serve as valuable genetic tools for isolating second site suppressor ...
Alu Human Polymorphism
... • Alu elements are only found in the primate branch • Each Alu insertion is a unique event and is inherited from each parent – Most occurred millions of years ago and are often on both pairs of chromosomes – There are Alu elements that have occurred since humans branched from other primates – This g ...
... • Alu elements are only found in the primate branch • Each Alu insertion is a unique event and is inherited from each parent – Most occurred millions of years ago and are often on both pairs of chromosomes – There are Alu elements that have occurred since humans branched from other primates – This g ...
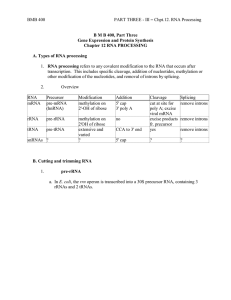
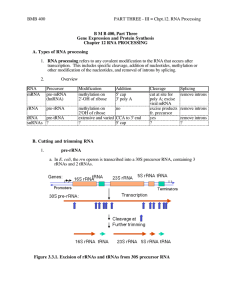
Chpt12_RNAProcessing.doc
... cleave a particular mRNA, thereby turning off expression of a particular gene. If over-expression or ectopic expression of a defined gene were the cause of some pathology (e.g. some form of cancer), then reducing its expression could have therapeutic value. Other RNAs possibly involved in catalysis, ...
... cleave a particular mRNA, thereby turning off expression of a particular gene. If over-expression or ectopic expression of a defined gene were the cause of some pathology (e.g. some form of cancer), then reducing its expression could have therapeutic value. Other RNAs possibly involved in catalysis, ...
Hemoglobin A2: origin, evolution, and aftermath
... of maturity. These experiments showed that there was a progressive decrease in &-globin synthesis in relation to P-globin in increasingly mature cells. A relative instability of 8-globin mRNA was proposed as a mechanism for the premature decrease in &globin synthesis? Using highly selective probes f ...
... of maturity. These experiments showed that there was a progressive decrease in &-globin synthesis in relation to P-globin in increasingly mature cells. A relative instability of 8-globin mRNA was proposed as a mechanism for the premature decrease in &globin synthesis? Using highly selective probes f ...
Got Lactase? The Co-evolution of Genes and Culture
... Students may have questions about the difference between the terms lactase persistence and lactose tolerance. These terms are used interchangeably in the film and this activity, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing. Lactase persistence refers to the persistent production of the lactase enzyme ...
... Students may have questions about the difference between the terms lactase persistence and lactose tolerance. These terms are used interchangeably in the film and this activity, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing. Lactase persistence refers to the persistent production of the lactase enzyme ...
PHANTASTICA Regulates Development of the Adaxial Mesophyll in
... is shown in Figure 1 with identical residues shaded. All have a highly conserved MYB DNA binding domain at the N terminus, consisting of two imperfect repeats (55 and 51 residues), both of which are essential for sequence-specific DNA binding based on structural analysis of c-MYB (Jin and Martin, 19 ...
... is shown in Figure 1 with identical residues shaded. All have a highly conserved MYB DNA binding domain at the N terminus, consisting of two imperfect repeats (55 and 51 residues), both of which are essential for sequence-specific DNA binding based on structural analysis of c-MYB (Jin and Martin, 19 ...
Genomic imprinting in the development and evolution of
... ‘autistic spectrum’ used for Kanner (infantile) autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and some other conditions (Table 1). I thus refer to ‘psychosis’ throughout this paper in a general sense as disordered cognition, emotionality, or both, commonly involving some component of positive symptoms s ...
... ‘autistic spectrum’ used for Kanner (infantile) autism, Asperger syndrome, Rett syndrome, and some other conditions (Table 1). I thus refer to ‘psychosis’ throughout this paper in a general sense as disordered cognition, emotionality, or both, commonly involving some component of positive symptoms s ...
pdf
... CFI and CFII are cleavage factors. PAP is the polyA polymerase. CFI, CFII and PAP form a complex that binds to the nascent RNA at the cleavage site, directed by the CPSF specificity factor. CstF is an additional protein implicated in this process in vitro, but its precise function is currently unkno ...
... CFI and CFII are cleavage factors. PAP is the polyA polymerase. CFI, CFII and PAP form a complex that binds to the nascent RNA at the cleavage site, directed by the CPSF specificity factor. CstF is an additional protein implicated in this process in vitro, but its precise function is currently unkno ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.