Powering Our Future - Kyrene School District
... to make metals from raw ore, or plastic from oil, denim fabric from cotton, as well as making cars, computers, or blue jeans with processed materials. ...
... to make metals from raw ore, or plastic from oil, denim fabric from cotton, as well as making cars, computers, or blue jeans with processed materials. ...
types of energy
... matter by direct contact of particles. This can happen in solids, liquids and gases. • CONVECTION: the transfer of energy because of the movement of bulk masses of particles. This can happen only in liquids and gases not in solids. • RADIATION: the transfer of energy by ...
... matter by direct contact of particles. This can happen in solids, liquids and gases. • CONVECTION: the transfer of energy because of the movement of bulk masses of particles. This can happen only in liquids and gases not in solids. • RADIATION: the transfer of energy by ...
Lecture 06 Notes
... b. Cell converts potential energy to kinetic energy to perform work Thermodynamics = study of energy transformations that occur in a collection of matter, or system 1. First Law of Thermodynamics = total ...
... b. Cell converts potential energy to kinetic energy to perform work Thermodynamics = study of energy transformations that occur in a collection of matter, or system 1. First Law of Thermodynamics = total ...
Investigating Energy - Trinity Christian School
... ii. Neutrons shoot out and split other atoms, which release more energy. (Nuclear Fission) b. Nuclear Fission is used to generate electrical energy in nuclear power plants i. The heat produced by nuclear fission heats water to make steam, which turns a turbine to generate electrical energy. ii. Beca ...
... ii. Neutrons shoot out and split other atoms, which release more energy. (Nuclear Fission) b. Nuclear Fission is used to generate electrical energy in nuclear power plants i. The heat produced by nuclear fission heats water to make steam, which turns a turbine to generate electrical energy. ii. Beca ...
Chapter 12: Energy and Energy Resources
... • The particles in steam move faster than the particles in ice. • The more particles the more thermal energy. • A bathtub full of 75 degree water would have more thermal energy than a cup full of 75 degree water. ...
... • The particles in steam move faster than the particles in ice. • The more particles the more thermal energy. • A bathtub full of 75 degree water would have more thermal energy than a cup full of 75 degree water. ...
E m = E k + E p
... capacity of a substance (J/g°C), T = Tf – Ti which is the change in temperature & where Tf is final temperature and Ti is initial temperature, all 3 are in °C -If Q is negative the substance has lost thermal energy; it has liberated heat; it has less energy than it previously had - If Q is positive ...
... capacity of a substance (J/g°C), T = Tf – Ti which is the change in temperature & where Tf is final temperature and Ti is initial temperature, all 3 are in °C -If Q is negative the substance has lost thermal energy; it has liberated heat; it has less energy than it previously had - If Q is positive ...
Physical Science – 2nd Semester – Final Exam Study
... Example: Roller coaster as it is getting ready to take off. c. When does an object possess kinetic energy? As it’s moving. i. Example: Roller Coaster. d. Chemical PE (def.) Capable of transferring chemical energy. i. Example: Plants using photosynthesis to make food. ...
... Example: Roller coaster as it is getting ready to take off. c. When does an object possess kinetic energy? As it’s moving. i. Example: Roller Coaster. d. Chemical PE (def.) Capable of transferring chemical energy. i. Example: Plants using photosynthesis to make food. ...
Kinetic Energy
... is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate — the energy is transferred through the substance in a wave. Typically, the energy in sound is far less than other forms of energy. ...
... is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate — the energy is transferred through the substance in a wave. Typically, the energy in sound is far less than other forms of energy. ...
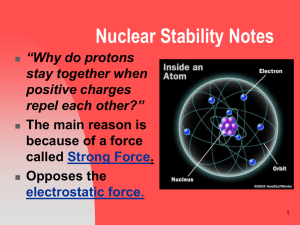
Nuclear Stability Notes
... with mass (protons and neutrons) to attract other masses together and works within a very short distance. Neutrons act as insulation, since they have no charge, but have the strong force to bring other nucleons (protons and neutrons) together. ...
... with mass (protons and neutrons) to attract other masses together and works within a very short distance. Neutrons act as insulation, since they have no charge, but have the strong force to bring other nucleons (protons and neutrons) together. ...
Chap-13 Simple Machines and its - Environmental-Chemistry
... Efficiency of machines • All of the work done by machine is not useful work. Only a portion of the work done by any machine is useful work. • In real machine, the work output is always less than the work input because other forces like friction use up some of the input work. Some input work is bein ...
... Efficiency of machines • All of the work done by machine is not useful work. Only a portion of the work done by any machine is useful work. • In real machine, the work output is always less than the work input because other forces like friction use up some of the input work. Some input work is bein ...
TYPES OF ENERGY
... determines how active its atoms are. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement. ...
... determines how active its atoms are. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement. ...
New Energy transfer
... • Gravitational Potential energy is only stored in the height of the object. Any time that a heavy object is kept high up, a force or power is likely to be holding it up there. This is the reason why it stays up and does not fall. It is important to note that the heavier the object, the more its po ...
... • Gravitational Potential energy is only stored in the height of the object. Any time that a heavy object is kept high up, a force or power is likely to be holding it up there. This is the reason why it stays up and does not fall. It is important to note that the heavier the object, the more its po ...
Mechanical Energy (pages 151–152)
... • Electrical energy is the energy of electrical charges. Lightning is a form of electrical energy. • Chemical energy is the energy in chemical bonds. Your body uses the chemical energy in food. • Nuclear energy is the energy stored in the nuclei of atoms. Nuclear power plants use nuclear energy to m ...
... • Electrical energy is the energy of electrical charges. Lightning is a form of electrical energy. • Chemical energy is the energy in chemical bonds. Your body uses the chemical energy in food. • Nuclear energy is the energy stored in the nuclei of atoms. Nuclear power plants use nuclear energy to m ...
energy changes
... Energy can be transformed into another sort of energy. But it cannot be created AND it cannot be destroyed. Energy has always existed in one form or another. This is called the Law of Conservation of Energy. When you turn on a lamp, not all of the electricity flowing through the filament is converte ...
... Energy can be transformed into another sort of energy. But it cannot be created AND it cannot be destroyed. Energy has always existed in one form or another. This is called the Law of Conservation of Energy. When you turn on a lamp, not all of the electricity flowing through the filament is converte ...
Awareness of Stored Energy - Part I
... • Look – for and identify the hazards • Analyze – what needs to be done • Manage – safety by developing & implementing controls • Remember – to look for changes • Identify – all potential risks • Share –what you find, include others impacted by job & risk • Know – what others on your jobsite are doi ...
... • Look – for and identify the hazards • Analyze – what needs to be done • Manage – safety by developing & implementing controls • Remember – to look for changes • Identify – all potential risks • Share –what you find, include others impacted by job & risk • Know – what others on your jobsite are doi ...
Chapter 1 * Energy and Matter
... from a wood fire Also, electromagnetic energy may cause both chemical and physical changes in matter to occur For example, a microwave oven can change a frozen block of food into a hot meal, which is a physical change ...
... from a wood fire Also, electromagnetic energy may cause both chemical and physical changes in matter to occur For example, a microwave oven can change a frozen block of food into a hot meal, which is a physical change ...
Forms of Energy
... Forms of Energy Forms of Energy Basics What is energy? Energy makes change possible. It moves cars along the road and boats through the water. It bakes a cake in the oven, keeps ice frozen in the freezer, and lights our homes. Scientists define energy as the ability to do work. Modern civilization i ...
... Forms of Energy Forms of Energy Basics What is energy? Energy makes change possible. It moves cars along the road and boats through the water. It bakes a cake in the oven, keeps ice frozen in the freezer, and lights our homes. Scientists define energy as the ability to do work. Modern civilization i ...
Energy Sources and Properties Notes
... electromagnetic that travels in waves such as visible light, ultraviolet light or X-rays. - Sources: stars, lightbulbs, microwaves Solar Energy (SE) is a type of radiant energy. -Energy from the Sun through space which provides heat and light energy for Earth Properties: -Solar photovoltaic cells ca ...
... electromagnetic that travels in waves such as visible light, ultraviolet light or X-rays. - Sources: stars, lightbulbs, microwaves Solar Energy (SE) is a type of radiant energy. -Energy from the Sun through space which provides heat and light energy for Earth Properties: -Solar photovoltaic cells ca ...
Work and Energy
... CQ You want to decrease the kinetic energy of an object as much as you can. You can do so by either reducing the mass by half or reducing the speed by half. Which option should you pick, and why? A 1200-kg automobile travels at 90 km h. (a) What is its kinetic energy? (b) What net work would be re ...
... CQ You want to decrease the kinetic energy of an object as much as you can. You can do so by either reducing the mass by half or reducing the speed by half. Which option should you pick, and why? A 1200-kg automobile travels at 90 km h. (a) What is its kinetic energy? (b) What net work would be re ...
Unit 6 - Royal International School • Portal
... Oxygen is a solvent. Nitrogen is a solvent. The two gases cannot be separated. The two gases can melt to form water. On a hot summer day, Jenna poured juice into an ice cube tray. She put the tray into the freezer. When she removed the tray, the juice was frozen. How many physical changes took place ...
... Oxygen is a solvent. Nitrogen is a solvent. The two gases cannot be separated. The two gases can melt to form water. On a hot summer day, Jenna poured juice into an ice cube tray. She put the tray into the freezer. When she removed the tray, the juice was frozen. How many physical changes took place ...
Properties of Mixtures
... • Solids = A state of matter with a definite shape and volume • The particles in solids are packed tightly together and stay in fixed positions (the particles are still moving, but it is extremely slow) • Liquids = A state of matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape • The particles in ...
... • Solids = A state of matter with a definite shape and volume • The particles in solids are packed tightly together and stay in fixed positions (the particles are still moving, but it is extremely slow) • Liquids = A state of matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape • The particles in ...