Objects that are changing their speed or their direction are said to be
... which the speed or direction changes is referred to as acceleration. Some amusement park rides (such as roller coasters) are characterized by rapid changes in speed and or direction. These rides have large accelerations. Rides such as the carousel result in small accelerations; the speed and directi ...
... which the speed or direction changes is referred to as acceleration. Some amusement park rides (such as roller coasters) are characterized by rapid changes in speed and or direction. These rides have large accelerations. Rides such as the carousel result in small accelerations; the speed and directi ...
Лексико-грамматический тест по тексту «Energy» для студентов
... when the spring has finished moving up and down? This brings in another form of energy: heat energy. There are many other forms of energy but we cannot describe them in any more detail just now. There is electrical energy, which has to do with pushing and pulling by electric charges. There is radian ...
... when the spring has finished moving up and down? This brings in another form of energy: heat energy. There are many other forms of energy but we cannot describe them in any more detail just now. There is electrical energy, which has to do with pushing and pulling by electric charges. There is radian ...
Chapter 5
... Hess’s law states that “If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, ∆H for the overall reaction will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps.” Hess’s Law Because ∆H is a state function, the total enthalpy change depends only on the initial state of the reactants a ...
... Hess’s law states that “If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, ∆H for the overall reaction will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps.” Hess’s Law Because ∆H is a state function, the total enthalpy change depends only on the initial state of the reactants a ...
Energy Transformations - A`Takamul Grade 6 Science
... Key Concept What is the law of conservation of energy? Directions: In the diagram, a ball has just been thrown and is about to be caught. Use the diagram to answer each question. Write the letter of the correct stage on the lines provided. Some stages may be used more than once. At the ball’s highes ...
... Key Concept What is the law of conservation of energy? Directions: In the diagram, a ball has just been thrown and is about to be caught. Use the diagram to answer each question. Write the letter of the correct stage on the lines provided. Some stages may be used more than once. At the ball’s highes ...
Safari Montage - What is Energy
... some of this kinetic energy into heat, also known as t______________________ energy . Chapter 6: Renewable Energy: Finding Nemo Submarine Voyage 15. Most energy used worldwide today comes from n_________________________________ sources that cause pollution and cannot be replenished in a short amount ...
... some of this kinetic energy into heat, also known as t______________________ energy . Chapter 6: Renewable Energy: Finding Nemo Submarine Voyage 15. Most energy used worldwide today comes from n_________________________________ sources that cause pollution and cannot be replenished in a short amount ...
LIFEPAC® 12th Grade Science Unit 3 Worktext - HomeSchool
... contains energy in the bonds of the hydrogen and carbon atoms of which the fuel is comprised. Substances may contain energy but the substance should not be confused with the energy it contains. ...
... contains energy in the bonds of the hydrogen and carbon atoms of which the fuel is comprised. Substances may contain energy but the substance should not be confused with the energy it contains. ...
The Meaning of Work Energy, Work, and Power
... object that causes the object to move some distance. Work is done on an object when the object moves in the same direction in which the force is exerted. If you push a child on a swing, for example, you are doing work on the child. If you pull your books out of your backpack, you do work on the book ...
... object that causes the object to move some distance. Work is done on an object when the object moves in the same direction in which the force is exerted. If you push a child on a swing, for example, you are doing work on the child. If you pull your books out of your backpack, you do work on the book ...
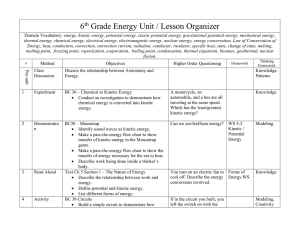
6th Grade Energy Unit / Lesson Organizer Domain Vocabulary
... Identify the pros and cons of building more nuclear power plants. BC73 Quiz Review lessons 65 – 72 with a quiz. Play Energy Guess Who game to identify sources of energy. BC74 Distillation Review phases or states of matter and the properties of each state. Identify heat as energy. ...
... Identify the pros and cons of building more nuclear power plants. BC73 Quiz Review lessons 65 – 72 with a quiz. Play Energy Guess Who game to identify sources of energy. BC74 Distillation Review phases or states of matter and the properties of each state. Identify heat as energy. ...
Energy: Review
... 3. Mechanical (motion) energy – The movement of objects or substances from one place to another. 4. Sound Energy – Sound is the movement of energy (vibrations) through objects or substances in longitudinal waves. 5. Electrical Energy – the movement of electrons. Example: Lightning and electricity ...
... 3. Mechanical (motion) energy – The movement of objects or substances from one place to another. 4. Sound Energy – Sound is the movement of energy (vibrations) through objects or substances in longitudinal waves. 5. Electrical Energy – the movement of electrons. Example: Lightning and electricity ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... Learning Scale for Energy … I can 4 – All of 3, 2, & 1 + Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 – All of 2 & 1 + Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 – All of 1 + Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identif ...
... Learning Scale for Energy … I can 4 – All of 3, 2, & 1 + Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 – All of 2 & 1 + Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 – All of 1 + Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identif ...
Energy Review
... This energy comes from the motion of atoms and molecules. The faster the particles in an object move, the more thermal energy is produced. ...
... This energy comes from the motion of atoms and molecules. The faster the particles in an object move, the more thermal energy is produced. ...
Chapter 12 Notes - Londonderry NH School District
... When energy is changed from one form to another, some energy is always lost as heat. 100% of energy cannot be converted into useful work ...
... When energy is changed from one form to another, some energy is always lost as heat. 100% of energy cannot be converted into useful work ...
Chapter 11 Modern Atomic Theory
... – Can only be solved for simple systems, but approximated for others ...
... – Can only be solved for simple systems, but approximated for others ...
Lesson 3: An Energy Mix Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
... This lesson provides students with an introduction to forms of potential and kinetic energy; potential energy – chemical, mechanical, nuclear, and gravitational and kinetic energy – radiant, thermal, motion, sound, and electrical. Renewables and nonrenewables can be classified as either potential or ...
... This lesson provides students with an introduction to forms of potential and kinetic energy; potential energy – chemical, mechanical, nuclear, and gravitational and kinetic energy – radiant, thermal, motion, sound, and electrical. Renewables and nonrenewables can be classified as either potential or ...
Ch. 9 notes 2015
... Note what happens when you double mass – (double mass, double KE) Note what happens when you double speed - (double velocity, quadruple KE) It takes four times as much work to double the speed or an object moving twice as fast takes four times as much work to stop it. What happens when you triple th ...
... Note what happens when you double mass – (double mass, double KE) Note what happens when you double speed - (double velocity, quadruple KE) It takes four times as much work to double the speed or an object moving twice as fast takes four times as much work to stop it. What happens when you triple th ...
Science - 08
... Production of electricity by fossil-fueled and nuclear power plants, wind generators, geothermal plants, and solar cells Use of electricity by appliances and equipment (e.g., calculators, hair dryers, light bulbs, motors) Waves 5. Understand how light and radio waves carry energy through vacuum ...
... Production of electricity by fossil-fueled and nuclear power plants, wind generators, geothermal plants, and solar cells Use of electricity by appliances and equipment (e.g., calculators, hair dryers, light bulbs, motors) Waves 5. Understand how light and radio waves carry energy through vacuum ...
What is energy?
... 2. __________ makes __________ possible. It___________ cars along the road and boats through the water. It bakes a cake in the oven, keeps ice frozen in the freezer, and __________ our homes. 3. Scientists define energy ___________________. Modern civilization is possible because we have learned how ...
... 2. __________ makes __________ possible. It___________ cars along the road and boats through the water. It bakes a cake in the oven, keeps ice frozen in the freezer, and __________ our homes. 3. Scientists define energy ___________________. Modern civilization is possible because we have learned how ...
MATTER AND ENERGY
... Second law of thermodynamics • When energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is always degraded to lower quality less useful energy usually heat lost to the environment • We ALWAYS end up with less useful energy than we started with. • An incandescent light bulb - 5 % light, 9 ...
... Second law of thermodynamics • When energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is always degraded to lower quality less useful energy usually heat lost to the environment • We ALWAYS end up with less useful energy than we started with. • An incandescent light bulb - 5 % light, 9 ...
What is Energy?
... Elastic Potential Energy (EPE) energy stored in an object that is stretched or compressed EPE can be stored in springs, elastic bands, bouncy balls and bows. Wind-up toys and old watches use springs that store EPE ...
... Elastic Potential Energy (EPE) energy stored in an object that is stretched or compressed EPE can be stored in springs, elastic bands, bouncy balls and bows. Wind-up toys and old watches use springs that store EPE ...
PowerPoint Lecture
... – Transmitters start counting for participation credit Tuesday 4/11 – HW1: Chapter 1 in Bloomfield: 1.E.4, 1.E.7, 1.E.8, 1.E.20, 1.E.25, 1.E.34, 1.P.1, 1.P.8, 1.P.9, 1.P.10, 1.P.14, 1.P.16, 1.P.18, 1.P.22; Chapter 2: 2.E.28, 2.P.10, 2.P.11 • E Exercise; P Problem • due Thursday 4/13 in class (or ...
... – Transmitters start counting for participation credit Tuesday 4/11 – HW1: Chapter 1 in Bloomfield: 1.E.4, 1.E.7, 1.E.8, 1.E.20, 1.E.25, 1.E.34, 1.P.1, 1.P.8, 1.P.9, 1.P.10, 1.P.14, 1.P.16, 1.P.18, 1.P.22; Chapter 2: 2.E.28, 2.P.10, 2.P.11 • E Exercise; P Problem • due Thursday 4/13 in class (or ...
Classification of energy - Development of e
... waves. It enables us to see, as objects are only visible when they reflect light into our eyes Nuclear Energy Nuclear energy is a controversial energy source. It is not a renewable energy source, but because it is a technology not based on fossil fuels many people think nuclear power plants could pl ...
... waves. It enables us to see, as objects are only visible when they reflect light into our eyes Nuclear Energy Nuclear energy is a controversial energy source. It is not a renewable energy source, but because it is a technology not based on fossil fuels many people think nuclear power plants could pl ...