post-class version, 374 KB - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 2. There are two basic types of planets: terrestrial and jovian • The inner (terrestrial) planets are smaller and denser than the outer (jovian) planets. • Moreover, among the terrestrial planets, the densities are greater, the closer the planet is to the Sun. • Exception: the Earth and the Moon ar ...
... 2. There are two basic types of planets: terrestrial and jovian • The inner (terrestrial) planets are smaller and denser than the outer (jovian) planets. • Moreover, among the terrestrial planets, the densities are greater, the closer the planet is to the Sun. • Exception: the Earth and the Moon ar ...
Dr. Nancy Grace Roman - Journey through the Universe
... What are some of the things we need for life? Where might we find life in the solar system? Why did you pick these possibilities? Why not others? These are the questions we hope to answer by discussing where life exists on Earth and the different types of habitats that support life. The Search for L ...
... What are some of the things we need for life? Where might we find life in the solar system? Why did you pick these possibilities? Why not others? These are the questions we hope to answer by discussing where life exists on Earth and the different types of habitats that support life. The Search for L ...
Chapter 17 Tour: Formation of the Solar System
... REGIONS ON THE SUN’S SURFACE, RELATED TO CHANGES IN THE MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THE SUN ...
... REGIONS ON THE SUN’S SURFACE, RELATED TO CHANGES IN THE MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THE SUN ...
The Formation of Our Solar System
... The Formation of Our Solar System • Most scientists believe that the universe began about 13.5 billion years ago in a great explosion, called the Big Bang. • Matter from the explosion came together to form the first stars. • These stars were drawn together by gravity to produce family of stars, cal ...
... The Formation of Our Solar System • Most scientists believe that the universe began about 13.5 billion years ago in a great explosion, called the Big Bang. • Matter from the explosion came together to form the first stars. • These stars were drawn together by gravity to produce family of stars, cal ...
solution
... c. Stopping at a stop sign. Accelerating (changing speed). d. Traveling uphill at 30 mph on a straight road. Not accelerating (constant speed and direction). 7. According to Newton’s Laws, is there gravity on the moon? What about on Mars? How about within the space between the planets? According to ...
... c. Stopping at a stop sign. Accelerating (changing speed). d. Traveling uphill at 30 mph on a straight road. Not accelerating (constant speed and direction). 7. According to Newton’s Laws, is there gravity on the moon? What about on Mars? How about within the space between the planets? According to ...
Astronomy Library wk5.cwk (WP)
... These bodies eventually become the planets in our Solar System. Near the end of the formation of the planets, a period of heavy bombardment occurs as the planets sweep up any remaining debris in the Solar System. It is during this period, about 4 to 4.5 billion years ago, that most of the craters se ...
... These bodies eventually become the planets in our Solar System. Near the end of the formation of the planets, a period of heavy bombardment occurs as the planets sweep up any remaining debris in the Solar System. It is during this period, about 4 to 4.5 billion years ago, that most of the craters se ...
Solar System Study Guide
... What is the difference between a planet’s period of rotation and period of revolution? ...
... What is the difference between a planet’s period of rotation and period of revolution? ...
Teacher`s Show Guide
... faster and faster. We look at the solar system from afar and watch the planets and asteroids orbit the Sun, then leave the solar system to fly past some of the nearer stars. We then look at our Galaxy and our place in it before seeing it as part of a cluster called the Local Group. Finally the Local ...
... faster and faster. We look at the solar system from afar and watch the planets and asteroids orbit the Sun, then leave the solar system to fly past some of the nearer stars. We then look at our Galaxy and our place in it before seeing it as part of a cluster called the Local Group. Finally the Local ...
solar observables and typical scales
... • Only p-modes observed so far =>oscillation driven by pressure involve solar structure only down to 0.1R ...
... • Only p-modes observed so far =>oscillation driven by pressure involve solar structure only down to 0.1R ...
Lecture13 - University of Waterloo
... • This reaction requires the neutrino to have an energy of 0.814 MeV or more, and can only detect neutrinos from the “side-reactions” in the PP chain: ...
... • This reaction requires the neutrino to have an energy of 0.814 MeV or more, and can only detect neutrinos from the “side-reactions” in the PP chain: ...
LIGHT YEARS FROM HOME
... faster and faster. We look at the solar system from afar and watch the planets and asteroids orbit the Sun, then leave the solar system to fly past some of the nearer stars. We then look at our Galaxy and our place in it before seeing it as part of a cluster called the Local Group. Finally the Local ...
... faster and faster. We look at the solar system from afar and watch the planets and asteroids orbit the Sun, then leave the solar system to fly past some of the nearer stars. We then look at our Galaxy and our place in it before seeing it as part of a cluster called the Local Group. Finally the Local ...
File
... Other Objects • Meteoroids are pieces of rock moving though space - Believed to be pieces of asteroids and planets • When meteoroids collide with Earth’s atmosphere they burn up due to atmospheric friction forming meteors • When Earth passes through an area where there is a lot of excess material ( ...
... Other Objects • Meteoroids are pieces of rock moving though space - Believed to be pieces of asteroids and planets • When meteoroids collide with Earth’s atmosphere they burn up due to atmospheric friction forming meteors • When Earth passes through an area where there is a lot of excess material ( ...
Other Solar System Bodies
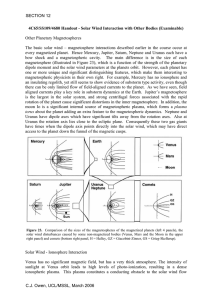
... that the moon spends part of its orbit inside the terrestrial magnetosphere, such that its interaction at these times is with the various magnetospheric fields and plasma populations discussed above, rather than the solar wind. Comets A comet nucleus is a relatively small body (~ a few 10’s of kilom ...
... that the moon spends part of its orbit inside the terrestrial magnetosphere, such that its interaction at these times is with the various magnetospheric fields and plasma populations discussed above, rather than the solar wind. Comets A comet nucleus is a relatively small body (~ a few 10’s of kilom ...
Spaceship Earth
... Spaceship Earth What are the motions of spaceship Eearth? • Earth SPINS on its axis towards the EAST once every 24 hours • Earth ORBITS around the Sun once every 365.25 days. Speed ~ 1x105 km/hr. • Earth, the Sun & the Solar System all orbit around the center of the Milky Way galaxy once every 2.3x ...
... Spaceship Earth What are the motions of spaceship Eearth? • Earth SPINS on its axis towards the EAST once every 24 hours • Earth ORBITS around the Sun once every 365.25 days. Speed ~ 1x105 km/hr. • Earth, the Sun & the Solar System all orbit around the center of the Milky Way galaxy once every 2.3x ...
Our Solar System
... Milky Way Galaxy. • It is made up of planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids and comets. ...
... Milky Way Galaxy. • It is made up of planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids and comets. ...
Flat Earth / Round Earth Activity
... orbital speed, but the same is not true with comets or asteroids on highly elliptical orbits. Consider the orbit of Halley’s Comet shown at the top of the next page (eccentricity = 0.967). In this drawing the planets move in a clockwise direction, while Halley’s Comet moves in a counter-clockwise di ...
... orbital speed, but the same is not true with comets or asteroids on highly elliptical orbits. Consider the orbit of Halley’s Comet shown at the top of the next page (eccentricity = 0.967). In this drawing the planets move in a clockwise direction, while Halley’s Comet moves in a counter-clockwise di ...
Our Star*the Sun
... located between Jupiter and Mars. If an asteroid falls to Earth is called a Meteor. If it does not burn up completely before it falls to the ground it is a Meteorite. ...
... located between Jupiter and Mars. If an asteroid falls to Earth is called a Meteor. If it does not burn up completely before it falls to the ground it is a Meteorite. ...
The Inner Planets of Our Solar System
... The Inner Planets of Our Solar System Why are they called the Inner planets? • They are closer together and closer to the sun Mercury l Closest planet to our sun l Smallest planet in the solar system l Planet with the longest day l Fastest orbiting planet l Caloris Basin is the largest impact c ...
... The Inner Planets of Our Solar System Why are they called the Inner planets? • They are closer together and closer to the sun Mercury l Closest planet to our sun l Smallest planet in the solar system l Planet with the longest day l Fastest orbiting planet l Caloris Basin is the largest impact c ...
Study Guide 8th Grade Ocean Motions In the Northern Hemisphere
... Patterns of stars in the sky are called constellations Sound waves are not part of the electromagnetic spectrum A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a pulsar The earliest stage of a star’s life is called a protostar The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram graphs stars’ abso ...
... Patterns of stars in the sky are called constellations Sound waves are not part of the electromagnetic spectrum A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a pulsar The earliest stage of a star’s life is called a protostar The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram graphs stars’ abso ...
Study Guide 8th Grade 2nd Semester Test Ocean Motions In the
... Patterns of stars in the sky are called constellations Sound waves are not part of the electromagnetic spectrum A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a pulsar The earliest stage of a star’s life is called a protostar The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram graphs stars’ abso ...
... Patterns of stars in the sky are called constellations Sound waves are not part of the electromagnetic spectrum A neutron star that appears to produce pulses of radio waves is called a pulsar The earliest stage of a star’s life is called a protostar The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram graphs stars’ abso ...
Tuesday Nov 14 Agenda Saturn`s Hurricane
... • They were further from the Sun and gravity was weaker • They formed beyond the frost line where ices can condense so they included hydrogen compounds • They were far enough from the Sun to escape the heavy bombardment that battered the early solar system ...
... • They were further from the Sun and gravity was weaker • They formed beyond the frost line where ices can condense so they included hydrogen compounds • They were far enough from the Sun to escape the heavy bombardment that battered the early solar system ...
Asteroids and comets
... the Sun. Be sure to include the comet's orbital path and the direction towards the Sun in your sketch. 5. Explain why astronomers infer two separate reservoirs for comets and briefly describe the shape and size (in terms of distance from the Sun) of each reservoir. 6. Explain what the three-fold div ...
... the Sun. Be sure to include the comet's orbital path and the direction towards the Sun in your sketch. 5. Explain why astronomers infer two separate reservoirs for comets and briefly describe the shape and size (in terms of distance from the Sun) of each reservoir. 6. Explain what the three-fold div ...
Chapter One Technology, Science, and Scientific Measurement
... in diameter, that travel through space Definition: a small chunk of rock, no larger than a few feet in diameter, that is traveling through space and enters the Earth’s atmosphere; commonly known as a shooting star Definition: a meteor that does not burn up in the atmosphere, and strikes the Earth’s ...
... in diameter, that travel through space Definition: a small chunk of rock, no larger than a few feet in diameter, that is traveling through space and enters the Earth’s atmosphere; commonly known as a shooting star Definition: a meteor that does not burn up in the atmosphere, and strikes the Earth’s ...
Heliosphere

The heliosphere is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun, which extends far beyond the orbit of Pluto. Plasma ""blown"" out from the Sun, known as the solar wind, creates and maintains this bubble against the outside pressure of the interstellar medium, the hydrogen and helium gas that permeates the Milky Way Galaxy. The solar wind flows outward from the Sun until encountering the termination shock, where motion slows abruptly. The Voyager spacecraft have actively explored the outer reaches of the heliosphere, passing through the shock and entering the heliosheath, a transitional region which is in turn bounded by the outermost edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause. The overall shape of the heliosphere is controlled by the interstellar medium, through which it is traveling, as well as the Sun, and does not appear to be perfectly spherical. The limited data available and unexplored nature of these structures have resulted in many theories.On September 12, 2013, NASA announced that Voyager 1 had exited the heliosphere on August 25, 2012, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times. Because the heliopause marks one boundary between the Sun's solar wind and the rest of the galaxy, a spacecraft such as Voyager 1 which has departed the heliosphere can be said to have reached interstellar space.