jupiter interpretive sign - Town of Cumberland, Indiana
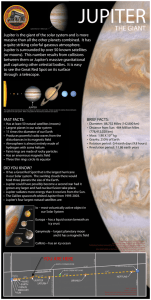
... Atmosphere is almost entirely made of hydrogen with some helium Faint rings are made of rocky particles Has an enormous magnetic field Three thin rings circle its equator ...
... Atmosphere is almost entirely made of hydrogen with some helium Faint rings are made of rocky particles Has an enormous magnetic field Three thin rings circle its equator ...
UBD - Solar System
... What objects exist in our solar system? How far apart are objects in our solar system? What causes objects in the solar system to move the way they do? Why do some objects have more gravity than others? How does the gravity of an object affect other objects in the solar system, including astronauts? ...
... What objects exist in our solar system? How far apart are objects in our solar system? What causes objects in the solar system to move the way they do? Why do some objects have more gravity than others? How does the gravity of an object affect other objects in the solar system, including astronauts? ...
Solar system intro and formation
... Rene Descartes (1596 -1650) nebular theory: Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". ...
... Rene Descartes (1596 -1650) nebular theory: Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". ...
Lecture 1 - Introduction - University of Iowa Astronomy and
... • What is the history of the Universe and what will eventually happen to the Universe? ...
... • What is the history of the Universe and what will eventually happen to the Universe? ...
Solar System Mobile Activity - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... Invite your children to make a solar system mobile. As you are working, sing or read "The Solar System I’m Rhyme”. Can they identify the Sun, planets, and asteroid belt by their characteristics? What is the order of the planets? What are their relative sizes? Provide your child with the planets temp ...
... Invite your children to make a solar system mobile. As you are working, sing or read "The Solar System I’m Rhyme”. Can they identify the Sun, planets, and asteroid belt by their characteristics? What is the order of the planets? What are their relative sizes? Provide your child with the planets temp ...
1.4 Our Solar Neighbourhood
... helium, and methane, Neptune (like Uranus) is bluish in colour. Very little of the Sun’s energy reaches the eighth planet. Neptune gives off about 3 times more energy than it receives. It boasts the fastest wind speeds in the solar system, at 2500 km/h. Like all the other gas giants, Neptune has its ...
... helium, and methane, Neptune (like Uranus) is bluish in colour. Very little of the Sun’s energy reaches the eighth planet. Neptune gives off about 3 times more energy than it receives. It boasts the fastest wind speeds in the solar system, at 2500 km/h. Like all the other gas giants, Neptune has its ...
PowerPoint
... neighborhood around its orbit.” Because Pluto’s orbit crosses paths with Neptune, it would not qualify This definition results in 8 planets This is the one the International Astronomical Union chose to accept Pluto hasn’t changed, just our definition of planet ...
... neighborhood around its orbit.” Because Pluto’s orbit crosses paths with Neptune, it would not qualify This definition results in 8 planets This is the one the International Astronomical Union chose to accept Pluto hasn’t changed, just our definition of planet ...
Student Pre-Survey (Marbleize)
... 1. _________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________ 9. The Sun is a: A. Planet B. Star C. Moon D. Meteor 10. The sun is made of: A. Rock B. Liquid C. Gas D. Plasma 11. The large objects that re ...
... 1. _________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________ 9. The Sun is a: A. Planet B. Star C. Moon D. Meteor 10. The sun is made of: A. Rock B. Liquid C. Gas D. Plasma 11. The large objects that re ...
5 th Grade Science Learning Targets The solar system includes the
... Earth pulls down on all objects with a gravitational force. Weight is a measure of the gravitational force between an object and the Earth. Any change in speed or direction of an object requires a force and is affected by the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. ...
... Earth pulls down on all objects with a gravitational force. Weight is a measure of the gravitational force between an object and the Earth. Any change in speed or direction of an object requires a force and is affected by the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. ...
Research - Clarion University
... that lack long-range order, like glass, are much less expensive to make, but it is difficult to control and maintain their electronic properties. In particular, the efficiency of energy conversion in typical amorphous photovoltaics tends to decrease as they are used. Dr. Pearce is working to underst ...
... that lack long-range order, like glass, are much less expensive to make, but it is difficult to control and maintain their electronic properties. In particular, the efficiency of energy conversion in typical amorphous photovoltaics tends to decrease as they are used. Dr. Pearce is working to underst ...
CH .20 The Solar System I. Observing the solar system – sun
... a. high temp. and pressure enables nuclear fusion 1) nuclear fusion – hydrogen atoms smash together to make helium a) some mass turns into energy in the form of heat and light 2. sun is about 5 billion years old, and should have enough fuel to burn another 5 billion years B. Sun’s Atmosphere – has 3 ...
... a. high temp. and pressure enables nuclear fusion 1) nuclear fusion – hydrogen atoms smash together to make helium a) some mass turns into energy in the form of heat and light 2. sun is about 5 billion years old, and should have enough fuel to burn another 5 billion years B. Sun’s Atmosphere – has 3 ...
A Teacher`s Guide - Center for Science Education
... The Sun sometimes stores so much energy in its magnetic field that when the energy is released it can accelerate solar wind protons to nearly the speed of light. These particles can be damaging to astronauts not protected by their spacecraft. This tremendous release of energy is sometimes associate ...
... The Sun sometimes stores so much energy in its magnetic field that when the energy is released it can accelerate solar wind protons to nearly the speed of light. These particles can be damaging to astronauts not protected by their spacecraft. This tremendous release of energy is sometimes associate ...
ASTRONOMY TEST 1 – STUDY GUIDE The layer of the Sun`s
... the tail of the comet is lighter than the head B. the Sun’s solar wind blows the tail outward C. the Sun’s gravity attracts the tail of the comet D. energy from other planets pulls the tail of the comet There are many meteors that enter Earth’s atmosphere, but very few of them actually land on Earth ...
... the tail of the comet is lighter than the head B. the Sun’s solar wind blows the tail outward C. the Sun’s gravity attracts the tail of the comet D. energy from other planets pulls the tail of the comet There are many meteors that enter Earth’s atmosphere, but very few of them actually land on Earth ...
Planets, Galaxies and Constellations
... The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, are terre ...
... The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, are terre ...
Chapter 3 - The Solar System
... D. Neptune – usually the eighth planet from the Sun, large and gaseous 1. Bluish-green colored atmosphere similar to that of Uranus 2. Storms on Neptune reveal an active and rapidly changing atmosphere 3. Has at least eleven moons, of which pinkish Triton is largest E. Pluto – usually the ninth plan ...
... D. Neptune – usually the eighth planet from the Sun, large and gaseous 1. Bluish-green colored atmosphere similar to that of Uranus 2. Storms on Neptune reveal an active and rapidly changing atmosphere 3. Has at least eleven moons, of which pinkish Triton is largest E. Pluto – usually the ninth plan ...
Lecture 9 - Angular Momentum Transport o
... o Particles lost from the star also carry away angular momentum. Given an initial mass, rotation rate, and radius, we can thus calculate the rate of AM loss. ...
... o Particles lost from the star also carry away angular momentum. Given an initial mass, rotation rate, and radius, we can thus calculate the rate of AM loss. ...
Why do we have seasons?
... The Reasons for the Seasons on Earth • The seasons on Earth are caused by the 23.5º tilt of its rotation axis, and its revolution around the Sun. • Although the distance of the Earth to the Sun changes slightly as it orbits around the Sun, its effect is not big enough to cause the four seasons. • T ...
... The Reasons for the Seasons on Earth • The seasons on Earth are caused by the 23.5º tilt of its rotation axis, and its revolution around the Sun. • Although the distance of the Earth to the Sun changes slightly as it orbits around the Sun, its effect is not big enough to cause the four seasons. • T ...
astron_ch_7b
... It was detected by satellites launched in the late 1950’s. It contains two doughnutshaped zones of high energy particles (one about 3000 and the other 20 000 km above the Earth’s surface), called the Van Allen Belts. The radiation here is lethal. ...
... It was detected by satellites launched in the late 1950’s. It contains two doughnutshaped zones of high energy particles (one about 3000 and the other 20 000 km above the Earth’s surface), called the Van Allen Belts. The radiation here is lethal. ...
Ch. 23: “Touring Our Solar System”
... of the necessary timescales. a) There are rocks on the surface of the Earth which are at least 3.8 billion years old. b) There are lunar rock samples 4.4 billion years old. ...
... of the necessary timescales. a) There are rocks on the surface of the Earth which are at least 3.8 billion years old. b) There are lunar rock samples 4.4 billion years old. ...
The Melbourne Solar System Trail
... planets sim ply by following the bike and walking trail on the foreshore of the City of Port Phillip. In 2008 artists and scientists constructed a m odel of our Solar System to a scale of one to one billion between St Kilda and Port Melbourne. So instead of navigating 5.9 billion kilom etres from th ...
... planets sim ply by following the bike and walking trail on the foreshore of the City of Port Phillip. In 2008 artists and scientists constructed a m odel of our Solar System to a scale of one to one billion between St Kilda and Port Melbourne. So instead of navigating 5.9 billion kilom etres from th ...
SolarDermatology
... Coronal Mass Ejection: A huge eruption of material from the Sun’s corona into interplanetary space. CMEs are the most energetic of solar explosions and eject up to100 billion kilograms of multi-million-degree plasma at speeds ranging from 10 to 2,000 km/s. They often look like bubbles. CMEs originat ...
... Coronal Mass Ejection: A huge eruption of material from the Sun’s corona into interplanetary space. CMEs are the most energetic of solar explosions and eject up to100 billion kilograms of multi-million-degree plasma at speeds ranging from 10 to 2,000 km/s. They often look like bubbles. CMEs originat ...
Ay 101 - The Physics of Stars – fall 2015 -... Homework 1, due Friday Oct 9 at class (2 pm)
... g1 = 1, g2 = 2, g3 = 8. The ionization energy from the fundamental level for ion 1 is 30 eV, and it is 55 eV for ion 2. Calculate ne and T . 2. (10 points) Calculate (approximately) for the Sun the gravitational potential energy, the thermal energy, the rotational energy (assume solid body rotation) ...
... g1 = 1, g2 = 2, g3 = 8. The ionization energy from the fundamental level for ion 1 is 30 eV, and it is 55 eV for ion 2. Calculate ne and T . 2. (10 points) Calculate (approximately) for the Sun the gravitational potential energy, the thermal energy, the rotational energy (assume solid body rotation) ...
Planetary research at IRF
... evolution, and dynamics of solar system objects with focus on the inner planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and dust. Development of scientific instrumentation for satellite-based measurements in support of space ...
... evolution, and dynamics of solar system objects with focus on the inner planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and dust. Development of scientific instrumentation for satellite-based measurements in support of space ...
Lecture 02a: Setting a context for us in the Universe
... …but, they use it sparingly Tiny stars live very, very long times Tiny stars produce low energy radiation ...
... …but, they use it sparingly Tiny stars live very, very long times Tiny stars produce low energy radiation ...
Heliosphere

The heliosphere is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun, which extends far beyond the orbit of Pluto. Plasma ""blown"" out from the Sun, known as the solar wind, creates and maintains this bubble against the outside pressure of the interstellar medium, the hydrogen and helium gas that permeates the Milky Way Galaxy. The solar wind flows outward from the Sun until encountering the termination shock, where motion slows abruptly. The Voyager spacecraft have actively explored the outer reaches of the heliosphere, passing through the shock and entering the heliosheath, a transitional region which is in turn bounded by the outermost edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause. The overall shape of the heliosphere is controlled by the interstellar medium, through which it is traveling, as well as the Sun, and does not appear to be perfectly spherical. The limited data available and unexplored nature of these structures have resulted in many theories.On September 12, 2013, NASA announced that Voyager 1 had exited the heliosphere on August 25, 2012, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times. Because the heliopause marks one boundary between the Sun's solar wind and the rest of the galaxy, a spacecraft such as Voyager 1 which has departed the heliosphere can be said to have reached interstellar space.























