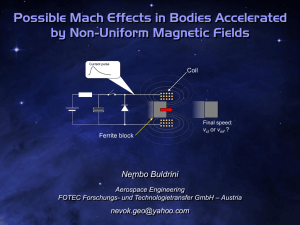
The fields of a current wire
... as we previously found on the basis of Lorentz transformations for the forces, charge and current densities and EM fields. It may be interesting to notice that there is already a subtle issue of charge conservation with the wire in S. In the material of which the wire is composed the charge densitie ...
... as we previously found on the basis of Lorentz transformations for the forces, charge and current densities and EM fields. It may be interesting to notice that there is already a subtle issue of charge conservation with the wire in S. In the material of which the wire is composed the charge densitie ...
INTO THE PAGE
... through two regions containing uniform magnetic fields of magnitudes B1 and B2. Its path in each region is a half-circle. The directions of the two fields are: A. Both B1 and B2 are directed into the page. B. Both B1 and B2 are directed out of the page. C. B1 is directed into the page and B2 is dire ...
... through two regions containing uniform magnetic fields of magnitudes B1 and B2. Its path in each region is a half-circle. The directions of the two fields are: A. Both B1 and B2 are directed into the page. B. Both B1 and B2 are directed out of the page. C. B1 is directed into the page and B2 is dire ...
magnetism - Sakshi Education
... Magnetism Pole strength (m) : i) Pole strength is a scalar. ii) S.I unit is ampere-metre. iii) Dimensional formula of m = [IL] iv) It (a) depends on nature of the material of the magnet (b) depends on level of magnetisation (c) is directly proportional to area of cross-section. v) Pole strength is ...
... Magnetism Pole strength (m) : i) Pole strength is a scalar. ii) S.I unit is ampere-metre. iii) Dimensional formula of m = [IL] iv) It (a) depends on nature of the material of the magnet (b) depends on level of magnetisation (c) is directly proportional to area of cross-section. v) Pole strength is ...
Magnetic Effects-2013
... directly over the wire. The compass needle shows no deflection when no current flows through the wire. When a current is passed through the wire, the needle shows deflection in one direction. When a current is passed through the wire in opposite direction, the needle shows deflection in opposite dir ...
... directly over the wire. The compass needle shows no deflection when no current flows through the wire. When a current is passed through the wire, the needle shows deflection in one direction. When a current is passed through the wire in opposite direction, the needle shows deflection in opposite dir ...
EXCITATION OF WAVEGUIDES
... exclusion of all other modes, by either an electric or magnetic current sheet of the appropriate form. In practice, however, such currents are very difficult to generate, and are usually only approximated with one or two probes or loops. In this case many modes may be excited, but usually most of th ...
... exclusion of all other modes, by either an electric or magnetic current sheet of the appropriate form. In practice, however, such currents are very difficult to generate, and are usually only approximated with one or two probes or loops. In this case many modes may be excited, but usually most of th ...
Physics: Waves, Sound/Light, Electromagnetic Waves, Magnetism
... 10. Complete the following paragraph to explain the motor effect using these words: flux, magnetic, force, length, conductor, current When a current carrying ________ is placed in a _______ field it experiences a _____. This force is called the motor effect. The motor effect is caused by the field c ...
... 10. Complete the following paragraph to explain the motor effect using these words: flux, magnetic, force, length, conductor, current When a current carrying ________ is placed in a _______ field it experiences a _____. This force is called the motor effect. The motor effect is caused by the field c ...
Northern Light Show
... magnet. The nail is only temporarily magnetized; if you pull away the magnet, the nail’s magnetism disappears. The polarization induced in the nail is similar to the polarization induced in a conductor by a nearby charged object, which you learned about in Chapter 20. ...
... magnet. The nail is only temporarily magnetized; if you pull away the magnet, the nail’s magnetism disappears. The polarization induced in the nail is similar to the polarization induced in a conductor by a nearby charged object, which you learned about in Chapter 20. ...
Unit 4 - Revision material summary
... Moving in a Circle (Also seen in GCSE Physics 3) For an object to continue to move in a circle a force is needed that acts on the object towards the centre of the circle. This is called the centripetal force and is provided by a number of things: For a satellite orbiting the Earth it is provided by ...
... Moving in a Circle (Also seen in GCSE Physics 3) For an object to continue to move in a circle a force is needed that acts on the object towards the centre of the circle. This is called the centripetal force and is provided by a number of things: For a satellite orbiting the Earth it is provided by ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.