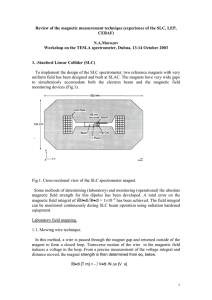
chapter27_1class
... wire at the same time (almost). These forces cause the electrons to move in the wire and create a current. So the current starts to flow anywhere in the circuit when the switch is closed. In the presence of an electric field, like the one set up by a battery, in spite of all the collisions, the char ...
... wire at the same time (almost). These forces cause the electrons to move in the wire and create a current. So the current starts to flow anywhere in the circuit when the switch is closed. In the presence of an electric field, like the one set up by a battery, in spite of all the collisions, the char ...
Magnetism – Part 3
... current of 1.20 A downward in a region between the poles of a large electromagnet where the field strength is 0.588 T and is horizontal. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a 1.00 cm section of this wire if the magnetic-field direction is (a) toward the east, (b) toward the ...
... current of 1.20 A downward in a region between the poles of a large electromagnet where the field strength is 0.588 T and is horizontal. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a 1.00 cm section of this wire if the magnetic-field direction is (a) toward the east, (b) toward the ...
11 - HCC Learning Web
... diameter of 6.20 cm and a length of 26.0 cm. Determine (a) the magnetic energy density in the field and (b) the energy stored in the magnetic field within the solenoid. 34. A flat coil of wire has an inductance of 40.0 mH and a resistance of 5.00 Ω. It is connected to a 22.0-V battery at the instant ...
... diameter of 6.20 cm and a length of 26.0 cm. Determine (a) the magnetic energy density in the field and (b) the energy stored in the magnetic field within the solenoid. 34. A flat coil of wire has an inductance of 40.0 mH and a resistance of 5.00 Ω. It is connected to a 22.0-V battery at the instant ...
for hard disk drives
... the magnetic flux density is essentially the same as that inside the magnetic poles on both sides of the gap, almost twice the fringing flux density. However, if the gap material is superconducting (this is a big ‘if’), the magnetic flux is repelled out of the gap and the field intensity in the reco ...
... the magnetic flux density is essentially the same as that inside the magnetic poles on both sides of the gap, almost twice the fringing flux density. However, if the gap material is superconducting (this is a big ‘if’), the magnetic flux is repelled out of the gap and the field intensity in the reco ...
CHAPTER- 1 : FUNDAMENTALS OF MAGETIC
... IN – H1 1 – H2 2 – H3 3 – Hg g = 0 In general, Mmf a closed magnetic circuit = 0 But this statement is similar to Kirchhoff's voltage law for a series electric circuit. Therefore, Kurchhoff's mmf law for a series magnetic circuit is as under Kirchhoff's mmf law (KML) states that algebraic su ...
... IN – H1 1 – H2 2 – H3 3 – Hg g = 0 In general, Mmf a closed magnetic circuit = 0 But this statement is similar to Kirchhoff's voltage law for a series electric circuit. Therefore, Kurchhoff's mmf law for a series magnetic circuit is as under Kirchhoff's mmf law (KML) states that algebraic su ...
Electric and Magnetic Fields Due to Massive Photons and Their
... Modern physics relies entirely on the intimate relations between electricity and magnetism. Maxwell had already formulated the theory of electricity and magnetism. This theory, however, does not reflect all symmetry properties existing between electricity and magnetism. For instance, while isolated ...
... Modern physics relies entirely on the intimate relations between electricity and magnetism. Maxwell had already formulated the theory of electricity and magnetism. This theory, however, does not reflect all symmetry properties existing between electricity and magnetism. For instance, while isolated ...
ISM_CH30
... 11. (a) It should be emphasized that the result, given in terms of sin(2 ft), could as easily be given in terms of cos(2 ft) or even cos(2 ft + ) where is a phase constant as discussed in Chapter 15. The angular position of the rotating coil is measured from some reference line (or plane), a ...
... 11. (a) It should be emphasized that the result, given in terms of sin(2 ft), could as easily be given in terms of cos(2 ft) or even cos(2 ft + ) where is a phase constant as discussed in Chapter 15. The angular position of the rotating coil is measured from some reference line (or plane), a ...
BA113 MCQ
... capacitors tend to maintain current through them at a constant value. current is used up after it leaves a junction. charge is neither created nor destroyed at a junction. ...
... capacitors tend to maintain current through them at a constant value. current is used up after it leaves a junction. charge is neither created nor destroyed at a junction. ...
Applied field Mössbauer study of shape anisotropy in Fe nanowire
... The effective hyperfine field with applied field parallel to the nanowire axis can be fitted in the formula of Heff = Hhf共Happ = 0兲 − Happ within the range of error. The fitting curve and the experimental dots are plotted in Fig. 3(b). Therefore, Hdm// = 0 can be deduced. This result is consistent w ...
... The effective hyperfine field with applied field parallel to the nanowire axis can be fitted in the formula of Heff = Hhf共Happ = 0兲 − Happ within the range of error. The fitting curve and the experimental dots are plotted in Fig. 3(b). Therefore, Hdm// = 0 can be deduced. This result is consistent w ...
Basis of Motor Action
... operation: applied voltage, torque, and angular velocity. It turns out that KT and Km are equal to one another but different motors have different K. So we finally get: VB = (R/K)T + K Suppose that the load and therefore the torque is constant. How does angular velocity change as applied voltage ch ...
... operation: applied voltage, torque, and angular velocity. It turns out that KT and Km are equal to one another but different motors have different K. So we finally get: VB = (R/K)T + K Suppose that the load and therefore the torque is constant. How does angular velocity change as applied voltage ch ...
Mass of the Electron Motivation for the Experiment
... Adjust the current creating the magnetic field until the electron beam forms a circular path. Adjust the bulb orientation in the magnetic field so that the electron path is circular and not spiral. Compute the actual magnetic field at each radius using Eq I-10 and I-9. Collect data for several diffe ...
... Adjust the current creating the magnetic field until the electron beam forms a circular path. Adjust the bulb orientation in the magnetic field so that the electron path is circular and not spiral. Compute the actual magnetic field at each radius using Eq I-10 and I-9. Collect data for several diffe ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.