Magnetism and electron configuration
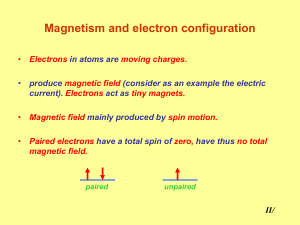
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
Ch. 28: Sources of Magnetic Fields
... magnetic dipoles are similar far from their sources, but differ close to the sources. ...
... magnetic dipoles are similar far from their sources, but differ close to the sources. ...
Exercise 9 - Magnetism-The Lorentz Force
... A cosmic ray proton (mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg) strikes the Earth near the equator with a vertical velocity of 2.8 x 10 7 m/s. Assume that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the equator is 30 mT. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic force on the proton to the gravitational force on ...
... A cosmic ray proton (mp = 1.67 x 10-27 kg) strikes the Earth near the equator with a vertical velocity of 2.8 x 10 7 m/s. Assume that the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the equator is 30 mT. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic force on the proton to the gravitational force on ...
Midterm Exam No. 03 (Spring 2015)
... 2. (20 points.) (Based on Griffiths 4th ed. problem 5.14.) A steady current I flows down a long cylindrical wire of radius a. Find the magnetic field, both inside and outside the wire, if the current is uniformly distributed over the outside surface of the wire. 3. (20 points.) (Based on Griffiths 4 ...
... 2. (20 points.) (Based on Griffiths 4th ed. problem 5.14.) A steady current I flows down a long cylindrical wire of radius a. Find the magnetic field, both inside and outside the wire, if the current is uniformly distributed over the outside surface of the wire. 3. (20 points.) (Based on Griffiths 4 ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.