Magnets Notes
... Draw a picture modelling the behavior of magnetic poles when they are brought together. Like poles _______________ ...
... Draw a picture modelling the behavior of magnetic poles when they are brought together. Like poles _______________ ...
The Magnetic Field of Mars: Past, Present and Future
... volatiles. Ion pick-up becomes a significant atmospheric loss mechanism operating for billions of years, enhanced by the low gravity environment and corresponding large scale height that allow the solar wind to interact with exospheric neutrals over an extended volume of space. The MGS magnetic fiel ...
... volatiles. Ion pick-up becomes a significant atmospheric loss mechanism operating for billions of years, enhanced by the low gravity environment and corresponding large scale height that allow the solar wind to interact with exospheric neutrals over an extended volume of space. The MGS magnetic fiel ...
Mag Fields Pres New
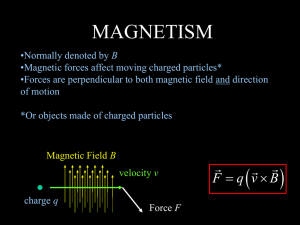
... The radius of curvature depends on the strength of the field, the mass of the particle, the charge of the particle and the velocity. ...
... The radius of curvature depends on the strength of the field, the mass of the particle, the charge of the particle and the velocity. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 16 a. Obtain the general expression for energy of a point charge distribution b. Find the energy of a uniformly charged shell of total charge q and radius R 17. Discuss the theory of multipole expansion of vector potential and derive an expression for the magnetic vector potential. 18. State and pro ...
... 16 a. Obtain the general expression for energy of a point charge distribution b. Find the energy of a uniformly charged shell of total charge q and radius R 17. Discuss the theory of multipole expansion of vector potential and derive an expression for the magnetic vector potential. 18. State and pro ...
Forces Study Guide: Magnets
... a. Natural magnets – found in nature (magnetite). Originally discovered 2000 years ago in China and Greece. b. Electromagnets – strong magnets that are created by combining magnets and electricity. c. Permanent magnets – retain their magnetism (harder to make) d. Temporary magnets – lose their magne ...
... a. Natural magnets – found in nature (magnetite). Originally discovered 2000 years ago in China and Greece. b. Electromagnets – strong magnets that are created by combining magnets and electricity. c. Permanent magnets – retain their magnetism (harder to make) d. Temporary magnets – lose their magne ...
Lecture18
... •All magnets have a north and south pole! No such thing as an isolated north or south pole. (have magnetic dipoles, not monopoles) •Different force laws! ...
... •All magnets have a north and south pole! No such thing as an isolated north or south pole. (have magnetic dipoles, not monopoles) •Different force laws! ...
TAP 411-2: Brush up on magnetism
... Use some permanent magnets and a current-carrying coil to review your knowledge of the nature and behaviour of magnetic fields. The purpose of this sheet is to help you to brush up your knowledge of magnets before you learn how magnetism is used with trains. ...
... Use some permanent magnets and a current-carrying coil to review your knowledge of the nature and behaviour of magnetic fields. The purpose of this sheet is to help you to brush up your knowledge of magnets before you learn how magnetism is used with trains. ...
Summary of lesson
... In this activity, you will explore some properties of magnetism by doing the following: (1) building an electromagnet; (2) gathering measurements of the electromagnet’s strength; and (3) analyzing the data. ...
... In this activity, you will explore some properties of magnetism by doing the following: (1) building an electromagnet; (2) gathering measurements of the electromagnet’s strength; and (3) analyzing the data. ...
Hans Christian Oersted
... the loop, therefore the B-field is stronger inside the loop. • Bend wire into another loop, the concentration of the B-field doubles, and so on. • The direction of the B-field depends on the direction of current flow in the wire. ...
... the loop, therefore the B-field is stronger inside the loop. • Bend wire into another loop, the concentration of the B-field doubles, and so on. • The direction of the B-field depends on the direction of current flow in the wire. ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.