Integrated Science Chapter 20 and 21 PRETEST
... 2. If the two charges represented in Figure 20-1 were brought near each other, they would a. attract each other. c. cause static discharge. b. repel each other. d. have no effect on each other. 3. What do electric forces between charges depend on? a. the quantity of charge involved c. both a. and b. ...
... 2. If the two charges represented in Figure 20-1 were brought near each other, they would a. attract each other. c. cause static discharge. b. repel each other. d. have no effect on each other. 3. What do electric forces between charges depend on? a. the quantity of charge involved c. both a. and b. ...
Nguyễn Văn Đồng1, Phạm Thị Lý Thu1, Phạm Thị Hương1,Trần
... tumefaciens mediated gene transfer in maize immature embryos was determined. The bacterial growth in log phase was strongest with intensity of magnetic field 0.14T at Southern as well as Northern pole. To estimate the effect of magnetic field, the explants in petri dishes were exposed to 0.085T and ...
... tumefaciens mediated gene transfer in maize immature embryos was determined. The bacterial growth in log phase was strongest with intensity of magnetic field 0.14T at Southern as well as Northern pole. To estimate the effect of magnetic field, the explants in petri dishes were exposed to 0.085T and ...
Magnetism and Electric Currents
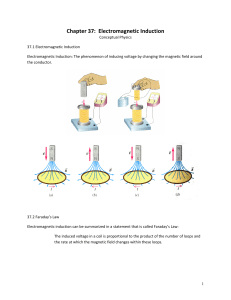
... it produces a strong magnetic field inside of the coil • This is referred to as an electromagnet because the magnetic field only exists when current flows through the wire ...
... it produces a strong magnetic field inside of the coil • This is referred to as an electromagnet because the magnetic field only exists when current flows through the wire ...
EXAM 3
... through all possible positions, the maximum torque on the coil by magnetic forces is 0.16 N m when the current in the coil is 4.0 mA. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... through all possible positions, the maximum torque on the coil by magnetic forces is 0.16 N m when the current in the coil is 4.0 mA. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field? a. b. c. d. e. ...
P14 - Electromagnetic effects
... Describe the effect of the magnetic field of changing the magnitude and direction of the current ...
... Describe the effect of the magnetic field of changing the magnitude and direction of the current ...
ece221h1s: electric and magnetic fields
... loop. This means that you only have to consider the applied magnetic field, so you can ignore the induced magnetic field if there is one (i.e., if the loop is closed such that an induced current can flow). This applies particularly to the questions with closed loops, 6.7, 6.11, 6.12, and 6.13) Chapt ...
... loop. This means that you only have to consider the applied magnetic field, so you can ignore the induced magnetic field if there is one (i.e., if the loop is closed such that an induced current can flow). This applies particularly to the questions with closed loops, 6.7, 6.11, 6.12, and 6.13) Chapt ...
Chapter 6 Part1: Multiple choices
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
Quiz 6
... into the sheet. The magnetic field has an intensity of 3.00 mT, lies in the sheet and is directed as shown. Find the direction (you can just draw an arrow) and magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron. Since the velocity is perpendicular to the sheet, it is also perpendicular to the magnetic ...
... into the sheet. The magnetic field has an intensity of 3.00 mT, lies in the sheet and is directed as shown. Find the direction (you can just draw an arrow) and magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron. Since the velocity is perpendicular to the sheet, it is also perpendicular to the magnetic ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.