Do Now (2/5/14)
... 1. What must be true for a current to be induced in a wire as the wire moves through a magnetic field? 2. A uniform magnetic field B, with magnitude B = 1.2 x 10-3 T, points vertically upward throughout an enclosed space. A proton with a velocity v = 3.2 x 107 m/s enters the space moving horizontall ...
... 1. What must be true for a current to be induced in a wire as the wire moves through a magnetic field? 2. A uniform magnetic field B, with magnitude B = 1.2 x 10-3 T, points vertically upward throughout an enclosed space. A proton with a velocity v = 3.2 x 107 m/s enters the space moving horizontall ...
Study Guide - Chapter 29
... Though the net force on a loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field is always zero, a magnetic field can exert torque on a loop of wire. This is given by the equation: t t‚B 7t œ . t is called the magnetic moment. It is defined as follows.: The vector . t is ME, where M is the current, and E is the a ...
... Though the net force on a loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field is always zero, a magnetic field can exert torque on a loop of wire. This is given by the equation: t t‚B 7t œ . t is called the magnetic moment. It is defined as follows.: The vector . t is ME, where M is the current, and E is the a ...
Home Work Problem Set 9
... (b) Show that the inclination φi of the magnetic field is related to the magnetic latitudeλm by . (HRW 32-55) 9-2 A charge q is distributed uniformly around a thin ring of radius r. The ring is rotating about an axis through its center and perpendicular to its plane, at an angular speed ω. (a) Show ...
... (b) Show that the inclination φi of the magnetic field is related to the magnetic latitudeλm by . (HRW 32-55) 9-2 A charge q is distributed uniformly around a thin ring of radius r. The ring is rotating about an axis through its center and perpendicular to its plane, at an angular speed ω. (a) Show ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... Electron spinning • An electron spinning creates a magnetic field • A pair of electrons spinning in the same direction creates a stronger magnet • A pair of electrons spinning in the opposite direction work against each other ...
... Electron spinning • An electron spinning creates a magnetic field • A pair of electrons spinning in the same direction creates a stronger magnet • A pair of electrons spinning in the opposite direction work against each other ...
18_12_2012 - Physics.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Which one of the following actions produces attractive forces? ____ (a) bringing the north poles of two magnets together (b) ...
... Which one of the following actions produces attractive forces? ____ (a) bringing the north poles of two magnets together (b) ...
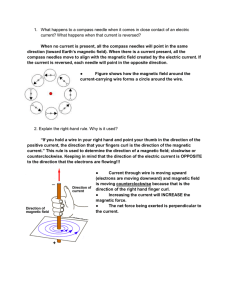
When no current is present, all the compass
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
Magnetism (Part 1)
... 5. Explain the differences between the magnetic field inside a solenoid and the field outside the solenoid. 6. A Solenoid with ends marked A and B is suspended by a thread so that the core can rotate in the horizontal plane. A current is maintained in the coil so that the electrons move clockwise wh ...
... 5. Explain the differences between the magnetic field inside a solenoid and the field outside the solenoid. 6. A Solenoid with ends marked A and B is suspended by a thread so that the core can rotate in the horizontal plane. A current is maintained in the coil so that the electrons move clockwise wh ...
SPH 3U(G) TEST
... a. the magnetic field around a magnet b. an atom that acts as a tiny magnet c. a group of atoms with their magnetic axes lined up in the same direction d. a metal that can be magnetized by induction e. the strength of a magnetic field ...
... a. the magnetic field around a magnet b. an atom that acts as a tiny magnet c. a group of atoms with their magnetic axes lined up in the same direction d. a metal that can be magnetized by induction e. the strength of a magnetic field ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.