Magnetism - MWMS HW Wiki
... Pole. A magnet is the strongest at the poles. Like poles repel each other. Opposite poles attract each other. ...
... Pole. A magnet is the strongest at the poles. Like poles repel each other. Opposite poles attract each other. ...
Some More Slides on Magnetism
... The drawing shows a thin, uniform rod that has a length of 0.35 m and a mass of 0.080 kg. This rod lies in the plane of the screen and is attached to the floor by a hinge at point P. A uniform magnetic field of 0.27 T is directed perpendicularly into the plane of the screen. There is a current I = ...
... The drawing shows a thin, uniform rod that has a length of 0.35 m and a mass of 0.080 kg. This rod lies in the plane of the screen and is attached to the floor by a hinge at point P. A uniform magnetic field of 0.27 T is directed perpendicularly into the plane of the screen. There is a current I = ...
magnetic fields
... Any magnet, no matter what its shape, has two ends called poles. A pole is the area of a magnet where the magnetic effect is strongest. One pole of a magnet points towards magnetic north of the earth and is labeled north. The other pole is labeled south. Although magnetic forces are strongest at the ...
... Any magnet, no matter what its shape, has two ends called poles. A pole is the area of a magnet where the magnetic effect is strongest. One pole of a magnet points towards magnetic north of the earth and is labeled north. The other pole is labeled south. Although magnetic forces are strongest at the ...
Electromagnets Answers - Cockeysville Middle School
... It has been found that the overall strength of the field could be further amplified by inserting a ferrous (iron containing) core into the center of the wire loops. This increased field strength occurs because the domains inside the metal core temporarily align with the magnetic field produced by th ...
... It has been found that the overall strength of the field could be further amplified by inserting a ferrous (iron containing) core into the center of the wire loops. This increased field strength occurs because the domains inside the metal core temporarily align with the magnetic field produced by th ...
Magnetism
... credited for the discovery of the electron (Physics Nobel Prize in 1906), and the invention of the mass spectrometer. ...
... credited for the discovery of the electron (Physics Nobel Prize in 1906), and the invention of the mass spectrometer. ...
Answers
... 4.5) Magnetic Forces 1) For a current carrying wire you use F = L I x B. For a free charge you use F = Q v x B. Use the An electron is moving through a uniform magnetic field that is down. What will happen to it if it is moving: west? up? up and west? In the first case it will feel a force to the no ...
... 4.5) Magnetic Forces 1) For a current carrying wire you use F = L I x B. For a free charge you use F = Q v x B. Use the An electron is moving through a uniform magnetic field that is down. What will happen to it if it is moving: west? up? up and west? In the first case it will feel a force to the no ...
Magnetic Forces and Magnetic Fields Discussion Questions 1
... 7: What happens to the magnetic field strength inside a solenoid when you wrap the wire into turns that have a larger radius, while keeping the number of turns per unit length constant? 8: An electrically charged particle is at rest in a region of space that has a uniform magnetic field. If the char ...
... 7: What happens to the magnetic field strength inside a solenoid when you wrap the wire into turns that have a larger radius, while keeping the number of turns per unit length constant? 8: An electrically charged particle is at rest in a region of space that has a uniform magnetic field. If the char ...
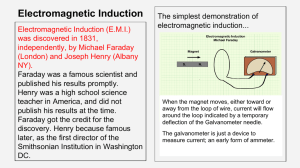
Electromagnetic Induction
... phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
... phenomenon, but Maxwell put it into mathematical terms. Consider a time-dependent magnetic field B(r,t); i.e., it changes in time t. The induced electric field E(r,t) circulates around the change of B. Picture: ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.