Magnetic Force Guided Notes
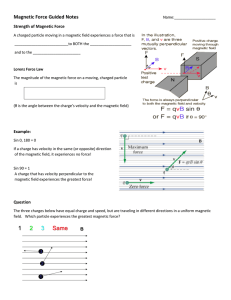
... A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a force that is __________________________to BOTH the ____________________ and to the _______________________ ...
... A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a force that is __________________________to BOTH the ____________________ and to the _______________________ ...
6. Magnetism
... Single poles cannot be isolated Magnetic monopoles do not exist in nature Break a magnet: ...
... Single poles cannot be isolated Magnetic monopoles do not exist in nature Break a magnet: ...
electromagnetic induction ppt
... Rotating a coil in a magnetic field will create alternating current As coil rotates, amount of magnetic field enclosed by loop changes, inducing a changing voltage Frequency of alternating current is the same as frequency of rotation of the coil Energy is converted from some mechanical form to elect ...
... Rotating a coil in a magnetic field will create alternating current As coil rotates, amount of magnetic field enclosed by loop changes, inducing a changing voltage Frequency of alternating current is the same as frequency of rotation of the coil Energy is converted from some mechanical form to elect ...
Magnet facts
... wire created a magnetic field that, while small because it was only from a D battery, was enough to pick up the paper clips or iron filings. To make the electromagnet stronger, you would wrap the wire more times around the nail. Using a different core will also make it stronger. The last thing is th ...
... wire created a magnetic field that, while small because it was only from a D battery, was enough to pick up the paper clips or iron filings. To make the electromagnet stronger, you would wrap the wire more times around the nail. Using a different core will also make it stronger. The last thing is th ...
Notes Sec 4.1
... PERMANENT MAGNET: materials that are able to stay magnetized for a long time. These magnets are able to lose their magnetism if the object is dropped or banged because this causes the domain to become disordered. 4.3 ELECTROMAGNETISM the magnetic field that is produced when an electric current is p ...
... PERMANENT MAGNET: materials that are able to stay magnetized for a long time. These magnets are able to lose their magnetism if the object is dropped or banged because this causes the domain to become disordered. 4.3 ELECTROMAGNETISM the magnetic field that is produced when an electric current is p ...
Electromagnetism - juan-roldan
... Ferromagnetic- A substance that is naturally and permanently magnetic like iron. Paramagnetic- which becomes magnetic under the influence of a magnetic field. Electromagnet- Becomes magnetic under the influence of an electric current. Is no longer magnetic when electricity flow is stopped. ...
... Ferromagnetic- A substance that is naturally and permanently magnetic like iron. Paramagnetic- which becomes magnetic under the influence of a magnetic field. Electromagnet- Becomes magnetic under the influence of an electric current. Is no longer magnetic when electricity flow is stopped. ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.