
Muscular Endurance Muscular endurance refers to the ability to
... cellular, and tissue level to better equip the muscles to cope with the demands placed on them. Not to be confused with muscular strength, muscular endurance is a measure of the ability to sustain muscular activity over time. While there is no clear distinction between cardiovascular endurance and m ...
... cellular, and tissue level to better equip the muscles to cope with the demands placed on them. Not to be confused with muscular strength, muscular endurance is a measure of the ability to sustain muscular activity over time. While there is no clear distinction between cardiovascular endurance and m ...
Abdomen (plate 249) - located between the thorax and the pelvis
... - in the inferior part of the AL Wall, down near the inguinal regions, the fascia is divided into two layers: 1- Superficial Layer – “camper’s fascia” - primarily fat tissue 2- Membranous Layer (deep to camper’s fascia) – “scarpas’ fascia” - only in inferior part Tranversalis Fascia - firm membranou ...
... - in the inferior part of the AL Wall, down near the inguinal regions, the fascia is divided into two layers: 1- Superficial Layer – “camper’s fascia” - primarily fat tissue 2- Membranous Layer (deep to camper’s fascia) – “scarpas’ fascia” - only in inferior part Tranversalis Fascia - firm membranou ...
Complete final sequence of Na V 1.4 from Ambystoma tigrinum
... These proteins are responsible for the initiation and propagation of actions potentials (APs) that form the basis of signal transmission in the neuromuscular system [1]. In vertebrates, these proteins are encoded by a multimember gene family with complex tissue-specific patterns of expression. One l ...
... These proteins are responsible for the initiation and propagation of actions potentials (APs) that form the basis of signal transmission in the neuromuscular system [1]. In vertebrates, these proteins are encoded by a multimember gene family with complex tissue-specific patterns of expression. One l ...
Full Article - Medical Ultrasonography
... within the tissues, represents the main way of lipid absorption within the intestinal tract, and, last but not least, it plays a major role in body immunity. The diffuse lymphatic tissue does not have a clear delineation, but it is represented by lymphocytes that are spread under mucosal membranes a ...
... within the tissues, represents the main way of lipid absorption within the intestinal tract, and, last but not least, it plays a major role in body immunity. The diffuse lymphatic tissue does not have a clear delineation, but it is represented by lymphocytes that are spread under mucosal membranes a ...
021~030.박경식
... brevis tendon, superior peroneal retinacula, calcaneofibular ligament, inferior extensor retinaculum, abductor digiti minimi, sheath of flexor tendon at outer layer, biceps femoris, semimembranosus, plantaris, soleus, posterior tibialis, fibularis brevis, extensor digitorum brevis, flexor digiti min ...
... brevis tendon, superior peroneal retinacula, calcaneofibular ligament, inferior extensor retinaculum, abductor digiti minimi, sheath of flexor tendon at outer layer, biceps femoris, semimembranosus, plantaris, soleus, posterior tibialis, fibularis brevis, extensor digitorum brevis, flexor digiti min ...
2 Pterygopalatine Fossa Lina Mansour Omar Saffar M.H.Almohtaseb
... preganglionic while after the synapse the nerve is post ganglionic. The sympathetic fibers tend to synapse right after its origin (near the cranium or the spines) >> this implies that any sympathetic fiber will be “postganglionic” while the parasympathetic tends to synapse near organs >> thus the ...
... preganglionic while after the synapse the nerve is post ganglionic. The sympathetic fibers tend to synapse right after its origin (near the cranium or the spines) >> this implies that any sympathetic fiber will be “postganglionic” while the parasympathetic tends to synapse near organs >> thus the ...
Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton Chapter 17
... Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton • Cells are not “bags of enzymes”, but rather organized in three dimensions. • This organization is carried out by the cytoskeleton, the “bones and muscles” (and more) of cells. • Cells are thousands of times larger than a typical molecule. Therefore the cytoskeleton must lo ...
... Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton • Cells are not “bags of enzymes”, but rather organized in three dimensions. • This organization is carried out by the cytoskeleton, the “bones and muscles” (and more) of cells. • Cells are thousands of times larger than a typical molecule. Therefore the cytoskeleton must lo ...
buccal
... the neck of the condyle, so it would be the artery damaged in this scenario. The buccal artery is a branch of the maxillary artery that travels in the cheek. It supplies blood to the cheek mucosa and skin. The external carotid artery is the source of the maxillary artery, but it is not the artery ly ...
... the neck of the condyle, so it would be the artery damaged in this scenario. The buccal artery is a branch of the maxillary artery that travels in the cheek. It supplies blood to the cheek mucosa and skin. The external carotid artery is the source of the maxillary artery, but it is not the artery ly ...
The autonomic nervous system
... sympathetic fibers synapse here. The parasympathetic fibers, however, pass through the plexus without synapsing and lead to the liver, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, kidney, ureter, and proximal half of the colon. The remaining parasympathetic fibers arise from levels S2 to S4 of the spinal cor ...
... sympathetic fibers synapse here. The parasympathetic fibers, however, pass through the plexus without synapsing and lead to the liver, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, kidney, ureter, and proximal half of the colon. The remaining parasympathetic fibers arise from levels S2 to S4 of the spinal cor ...
Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
... Muscles have different forms and fiber arrangements, depending on their function. Muscles in the limbs tend to be long. Because of this, they can contract more and are capable of producing greater movement. Muscles in the trunk tend to be broader and to form sheets that wrap around the body. Muscles ...
... Muscles have different forms and fiber arrangements, depending on their function. Muscles in the limbs tend to be long. Because of this, they can contract more and are capable of producing greater movement. Muscles in the trunk tend to be broader and to form sheets that wrap around the body. Muscles ...
PART ONE - WikiEducator
... This is longer but smaller. Why? Because the heart occupies much of the left side of the thorax and this accounts for the smaller left lung. An oblique fissure into superior and inferior lobes divides the left lung. It has no middle lobe. Each lung has an apex and a base. The base is broad and conca ...
... This is longer but smaller. Why? Because the heart occupies much of the left side of the thorax and this accounts for the smaller left lung. An oblique fissure into superior and inferior lobes divides the left lung. It has no middle lobe. Each lung has an apex and a base. The base is broad and conca ...
Variations in the anatomy of ansa cervicalis
... With the expanding use of the ansa cervicalis for reinnervation procedures and the fact that it is located in the vicinity of major nerves and vessels of the neck, knowledge of the topography and morphology of this loop is necessary in the modern era. Any variation in the course, contributing roots, ...
... With the expanding use of the ansa cervicalis for reinnervation procedures and the fact that it is located in the vicinity of major nerves and vessels of the neck, knowledge of the topography and morphology of this loop is necessary in the modern era. Any variation in the course, contributing roots, ...
THE PHARYNX
... whose pharyngeal branch reaches the nasopharynx via the palatovaginal canal. Most of the oropharynx receives its sensory supply from the glossopharyngeal nerve, but the vallecula is supplied by the internal laryngeal nerve, and all the rest of the pharyngeal mucosa is innervated by the internal an ...
... whose pharyngeal branch reaches the nasopharynx via the palatovaginal canal. Most of the oropharynx receives its sensory supply from the glossopharyngeal nerve, but the vallecula is supplied by the internal laryngeal nerve, and all the rest of the pharyngeal mucosa is innervated by the internal an ...
Chapter 31 Adductor Muscle Group (Medial Thigh
... inserted into the adductor hiatus to guide the cautery and protect the underlying vessels. (Courtesy of Martin M. Malawer.) ...
... inserted into the adductor hiatus to guide the cautery and protect the underlying vessels. (Courtesy of Martin M. Malawer.) ...
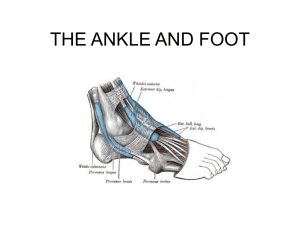
ankle_muscle
... – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral to the medial surface, thus aiding in support for the transverse arch. ...
... – Plantar flexion • The tendon goes under the foot from the lateral to the medial surface, thus aiding in support for the transverse arch. ...
ANATOMY 1. Metacarpophalangeal joint [MPJ] Flexion by long
... Each FDS tendon works independently while FDP tendons work as a unit. Lumbricals originate from one tendon [FDP] and inserts to the extensor expansion on the radial side. 4. ROM: PIP has the largest arc of motion (120º). This joint accounts for an es ...
... Each FDS tendon works independently while FDP tendons work as a unit. Lumbricals originate from one tendon [FDP] and inserts to the extensor expansion on the radial side. 4. ROM: PIP has the largest arc of motion (120º). This joint accounts for an es ...
07-lumbar plexus+lymphatics
... junction. 5-They have sphincter action on vagina by its anterior sphincter vaginae fibres. ...
... junction. 5-They have sphincter action on vagina by its anterior sphincter vaginae fibres. ...
Study of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) as
... May the reader take note that I have chosen to present this thesis in a manuscript-based format, where it has been included the text of two full papers. The first paper entitled: “Protein tyrosine nitration in the ventilatory muscles: Role of nitric oxide synthases” is presented in its galley proof ...
... May the reader take note that I have chosen to present this thesis in a manuscript-based format, where it has been included the text of two full papers. The first paper entitled: “Protein tyrosine nitration in the ventilatory muscles: Role of nitric oxide synthases” is presented in its galley proof ...
PDF + SI - Development - The Company of Biologists
... staining for β3-Tub, tupAME-moeGFP (see description below) and βPS integrin showed βPS accumulation both at the AM epidermal attachment site and at dorsal projections in contact with either the PSC or pericardial cells (supplementary material Fig. S2). Threedimensional reconstruction of embryos stai ...
... staining for β3-Tub, tupAME-moeGFP (see description below) and βPS integrin showed βPS accumulation both at the AM epidermal attachment site and at dorsal projections in contact with either the PSC or pericardial cells (supplementary material Fig. S2). Threedimensional reconstruction of embryos stai ...
15-Urogenital Traiangle2009-04-18 05:435.9 MB
... Erection of the Penis Erection in the male is gradually built up as a consequence of various sexual stimuli. Pleasurable sight, sound, smell, and other psychic stimuli, fortified later by direct touch sensory stimuli from the general body skin and genital skin, result in a bombardment of the centra ...
... Erection of the Penis Erection in the male is gradually built up as a consequence of various sexual stimuli. Pleasurable sight, sound, smell, and other psychic stimuli, fortified later by direct touch sensory stimuli from the general body skin and genital skin, result in a bombardment of the centra ...
15-Urogenital Traiangle2009-04-20 01:576.7 MB
... Erection of the Penis Erection in the male is gradually built up as a consequence of various sexual stimuli. Pleasurable sight, sound, smell, and other psychic stimuli, fortified later by direct touch sensory stimuli from the general body skin and genital skin, result in a bombardment of the centra ...
... Erection of the Penis Erection in the male is gradually built up as a consequence of various sexual stimuli. Pleasurable sight, sound, smell, and other psychic stimuli, fortified later by direct touch sensory stimuli from the general body skin and genital skin, result in a bombardment of the centra ...
The Histology of the Pulp
... Recognize, Capture Foreign Ag Non-Phagocytic Increased in Carious Teeth Class II MHC Positive ...
... Recognize, Capture Foreign Ag Non-Phagocytic Increased in Carious Teeth Class II MHC Positive ...
TMJ
... Danlos syndrome, etc. can be the predisposing factors. The use of antipsychotic drugs may cause extrapyramidal reactions and dislocation. Clinical picture o f acute dislocation Dislocation is a dramatic event. It maybe unilateral or bilateral. 1 listory of the patient may be diagnostic. Unilateral ...
... Danlos syndrome, etc. can be the predisposing factors. The use of antipsychotic drugs may cause extrapyramidal reactions and dislocation. Clinical picture o f acute dislocation Dislocation is a dramatic event. It maybe unilateral or bilateral. 1 listory of the patient may be diagnostic. Unilateral ...
Article - Archive ouverte UNIGE
... The finding that cultured rat vibrissa dermal papilla cells (Jahoda and Oliver, 1981) retain their capacity to stimulate hair growth (Jahoda et al. 1984; Home et al. 1986) distinguishes them as a culture system with particular relevance to known biological function. Other investigations have used cu ...
... The finding that cultured rat vibrissa dermal papilla cells (Jahoda and Oliver, 1981) retain their capacity to stimulate hair growth (Jahoda et al. 1984; Home et al. 1986) distinguishes them as a culture system with particular relevance to known biological function. Other investigations have used cu ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.














![ANATOMY 1. Metacarpophalangeal joint [MPJ] Flexion by long](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005376690_1-d5be1b48ed5480611ba50b35b5154162-300x300.png)







