Zebrafish_head_development
... Vertebrates develop a precise network of musculoskeletal connections. In the head, these are subdivided along the anteriorposterior (AP) axis into reiterated segments, the pharyngeal arches, and a dorsal neurocranium. In all vertebrates that have been examined the pharyngeal skeleton is derived embr ...
... Vertebrates develop a precise network of musculoskeletal connections. In the head, these are subdivided along the anteriorposterior (AP) axis into reiterated segments, the pharyngeal arches, and a dorsal neurocranium. In all vertebrates that have been examined the pharyngeal skeleton is derived embr ...
Marcus Gunn Jaw-Winking Phenomenon : A Review
... occulta, bilateral undescended testis and supernumerary incisors. ...
... occulta, bilateral undescended testis and supernumerary incisors. ...
Morphology of the Forelimb of the Mole
... other (fig. 3C). As a result of the torsion undergone by the humerus its proper lateral border faces antero-mediad and its medial border postero-laterad, while, as a result of extension and abduction, its proximal extremity is directed postero-mediad and its distal extremity antero-laterad. That the ...
... other (fig. 3C). As a result of the torsion undergone by the humerus its proper lateral border faces antero-mediad and its medial border postero-laterad, while, as a result of extension and abduction, its proximal extremity is directed postero-mediad and its distal extremity antero-laterad. That the ...
PDF
... conjugates increase in equatorial epithelial cell nuclei just prior to fiber cell differentiation, and localize to differentiating fiber cell nuclei (Shang et al., 1999). Second, zebrafish containing a mutation in the 26S proteasome gene Psmd6 experience abnormal retention of fiber cell nuclei, as w ...
... conjugates increase in equatorial epithelial cell nuclei just prior to fiber cell differentiation, and localize to differentiating fiber cell nuclei (Shang et al., 1999). Second, zebrafish containing a mutation in the 26S proteasome gene Psmd6 experience abnormal retention of fiber cell nuclei, as w ...
Print this article - International Journal of Research in Medical
... standing position. With each muscle contraction, blood is, therefore, propelled centrally. Hence the muscles serve as peripheral heart. ...
... standing position. With each muscle contraction, blood is, therefore, propelled centrally. Hence the muscles serve as peripheral heart. ...
The Role of Carnitine System in Maintaining Muscle Homeostasis
... Carnitine itself is not metabolized in humans. It is found in most cells at millimolar levels after uptake via carnitine transporters (Table 2). To exert its metabolic function it forms esters with a wide range of fatty acyl groups (i.e. acylcarnitines) [5] depending on an intracellular system of me ...
... Carnitine itself is not metabolized in humans. It is found in most cells at millimolar levels after uptake via carnitine transporters (Table 2). To exert its metabolic function it forms esters with a wide range of fatty acyl groups (i.e. acylcarnitines) [5] depending on an intracellular system of me ...
ARTICULAR SYSTEM
... The capsule is reinforced by the lateral ligament, lig. laterale, whose fibers run obliquely from the zygomatic process of the temporal bono to the neck of the mandible. Importantly, (ho following fasciae (ligaments) thicken in order to stabilize the mandible: 1) lig. stylomandibular, which runs fro ...
... The capsule is reinforced by the lateral ligament, lig. laterale, whose fibers run obliquely from the zygomatic process of the temporal bono to the neck of the mandible. Importantly, (ho following fasciae (ligaments) thicken in order to stabilize the mandible: 1) lig. stylomandibular, which runs fro ...
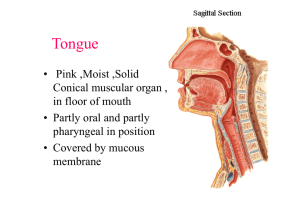
Tongue
... • Intermediate – pass deep to hyoglossus and are continuous with middle constrictor of pharynx • Upper – turn forward and upward from root to apex Action -Protrude tip of tongue and make dorsal ...
... • Intermediate – pass deep to hyoglossus and are continuous with middle constrictor of pharynx • Upper – turn forward and upward from root to apex Action -Protrude tip of tongue and make dorsal ...
Tongue
... • Intermediate – pass deep to hyoglossus and are continuous with middle constrictor of pharynx • Upper – turn forward and upward from root to apex Action -Protrude tip of tongue and make dorsal ...
... • Intermediate – pass deep to hyoglossus and are continuous with middle constrictor of pharynx • Upper – turn forward and upward from root to apex Action -Protrude tip of tongue and make dorsal ...
Clinico-anatomical considerations of unilateral bipartite abductor
... function of the heel. Defects in this region may be reliably covered by myocutaneous flaps. We present an interesting observation of an accessory belly of abductor digiti minimi (ADM) in the right foot of an adult male cadaver. The two bellies of ADM were placed in two planes - superficial and deep. ...
... function of the heel. Defects in this region may be reliably covered by myocutaneous flaps. We present an interesting observation of an accessory belly of abductor digiti minimi (ADM) in the right foot of an adult male cadaver. The two bellies of ADM were placed in two planes - superficial and deep. ...
Signaling Mechanisms That Regulate Smooth Muscle Cell
... A critical step in the activation of SMC-specific gene expression is SRF binding to CArG elements, and several mechanisms regulate this interaction. High SRF expression in all 3 muscle cell types likely promotes SRF binding to the relatively low affinity CArG elements present within the musclespecif ...
... A critical step in the activation of SMC-specific gene expression is SRF binding to CArG elements, and several mechanisms regulate this interaction. High SRF expression in all 3 muscle cell types likely promotes SRF binding to the relatively low affinity CArG elements present within the musclespecif ...
the axillary nerve giving motor branch to the long head
... The axillary nerve giving branch to the long head head of triceps muscle is rare. The posterior division of the axillary nerve is more variant in course and distribution than the anterior division [3]. In the present case the posterior branch of the axillary nerve gave the motor branch to the long h ...
... The axillary nerve giving branch to the long head head of triceps muscle is rare. The posterior division of the axillary nerve is more variant in course and distribution than the anterior division [3]. In the present case the posterior branch of the axillary nerve gave the motor branch to the long h ...
The Biceps Femoris Muscle Complex at the Knee
... angle to the sagittal plane of the femur and a 30° angle to the coronal plane of the femur when the knee was flexed to 90°. The first component of the short head of the biceps femoris muscle visualized was a proximal muscular attachment to the anterior and medial side of the tendon of the long head ...
... angle to the sagittal plane of the femur and a 30° angle to the coronal plane of the femur when the knee was flexed to 90°. The first component of the short head of the biceps femoris muscle visualized was a proximal muscular attachment to the anterior and medial side of the tendon of the long head ...
Biology 3B Laboratory Muscles of Vertebrate Animals: Shark
... The head has a mouth with lips. The upper lip is split by a groove, the philtrum. The nose has nares and the eyes bear upper and lower eyelids and a reduced nictitating membrane. The external ears or pinna direct sound into the auditory canal. The whiskers or vibrissae are sensory. The trunk has an ...
... The head has a mouth with lips. The upper lip is split by a groove, the philtrum. The nose has nares and the eyes bear upper and lower eyelids and a reduced nictitating membrane. The external ears or pinna direct sound into the auditory canal. The whiskers or vibrissae are sensory. The trunk has an ...
lower leg anatomy
... Deep peroneal n arises in PL and then passes to lie on interosseous membrane (Lat to vessels) Artery---initially lies on I/M between tib ant and EDL, then crossed by EHL so at ankle 2 muscles on each side Peroneus Longus Type IV muscle from peroneal—perforators through FHL (drains into short sapheno ...
... Deep peroneal n arises in PL and then passes to lie on interosseous membrane (Lat to vessels) Artery---initially lies on I/M between tib ant and EDL, then crossed by EHL so at ankle 2 muscles on each side Peroneus Longus Type IV muscle from peroneal—perforators through FHL (drains into short sapheno ...
Pdf - McMed International
... for chest-wall defects [7]. The axillary nerve may be injured in anterior-inferior dislocations of the shoulder joint, compression of the axilla with a crutch or fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus. Injury to the nerve results in the paralysis of the teres minor muscle and the deltoid muscl ...
... for chest-wall defects [7]. The axillary nerve may be injured in anterior-inferior dislocations of the shoulder joint, compression of the axilla with a crutch or fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus. Injury to the nerve results in the paralysis of the teres minor muscle and the deltoid muscl ...
FOREARM
... the brachial artery. The resulting ischaemia can cause Volkmann’s ischaemic contracture – uncontrolled flexion of the hand, as flexors muscles become fibrotic and short. --There also can be damage to the median or radial nerves. ...
... the brachial artery. The resulting ischaemia can cause Volkmann’s ischaemic contracture – uncontrolled flexion of the hand, as flexors muscles become fibrotic and short. --There also can be damage to the median or radial nerves. ...
Myology 肌学
... Insertion: mastoid process of temporal bone Action: contraction of one muscle draws head toward the same side, and turn face to opposite side; both muscles act together to draw head backward ...
... Insertion: mastoid process of temporal bone Action: contraction of one muscle draws head toward the same side, and turn face to opposite side; both muscles act together to draw head backward ...
The Axilla
... The Axilla The lower end, or base, is bounded in front by the anterior axillary fold (formed by the lower border of the pectoralis major muscle), behind by the posterior axillary fold (formed by the tendon of latissimus dorsi and the teres major muscle), and medially by the chest wall. ...
... The Axilla The lower end, or base, is bounded in front by the anterior axillary fold (formed by the lower border of the pectoralis major muscle), behind by the posterior axillary fold (formed by the tendon of latissimus dorsi and the teres major muscle), and medially by the chest wall. ...
Lumbar region - Lectures - gblnetto
... adipose capsule plays the main role. Parietal peritoneum getting from adjacent organs to kidneys from the ligaments. The ligaments of kidneys are composed of: hepatorenal ligament, duoÂdenorenal ligament and lienorenal ligament. We should also consider the pedicle of the kidney. It conÂsists of the ...
... adipose capsule plays the main role. Parietal peritoneum getting from adjacent organs to kidneys from the ligaments. The ligaments of kidneys are composed of: hepatorenal ligament, duoÂdenorenal ligament and lienorenal ligament. We should also consider the pedicle of the kidney. It conÂsists of the ...
Medical Gross Anatomy - University of Michigan
... In addition to parasympathetic and sympathetics, visceral afferent (sensory) fibers are often included during a discussion of autonomics because of their similar pathways of distribution. Visceral afferent (sensory) fibers also need to reach all organs within the pelvis. These fibers, originating wi ...
... In addition to parasympathetic and sympathetics, visceral afferent (sensory) fibers are often included during a discussion of autonomics because of their similar pathways of distribution. Visceral afferent (sensory) fibers also need to reach all organs within the pelvis. These fibers, originating wi ...
Cranial Nerves
... superior oblique, limiting inferolateral ocular movement; the affected eye rotates medially, producing DIPLOPIA. There is also some degree of extorsion, because the superior oblique, which normally produces intorsion, is not available. To compensate for this, the patient characteristically tilts the ...
... superior oblique, limiting inferolateral ocular movement; the affected eye rotates medially, producing DIPLOPIA. There is also some degree of extorsion, because the superior oblique, which normally produces intorsion, is not available. To compensate for this, the patient characteristically tilts the ...
Pdf - McMed International
... axillary nerve giving the motor branch to the long head of the triceps muscle. The axillary nerve winds backward, in company with the posterior humeral circumflex artery, through a quadrilateral space bounded above by the teres minor, below by the teres major, medially by the long head of the tricep ...
... axillary nerve giving the motor branch to the long head of the triceps muscle. The axillary nerve winds backward, in company with the posterior humeral circumflex artery, through a quadrilateral space bounded above by the teres minor, below by the teres major, medially by the long head of the tricep ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.