Chapter 22 Problem 66 † Given V (x)=3x - 2x 2
... Factor the potential function as much as possible. V (x) = x(3 − 2x − x2 ) V (x) = x(3 + x)(1 − x) The only places where the potential is equal to zero is when one of its factors is equal to zero. Therefore, Either x = 0, 3 + x = 0, or 1 − x = 0 From these 3 equations we get x = −3 m, 0 m, 1 m ...
... Factor the potential function as much as possible. V (x) = x(3 − 2x − x2 ) V (x) = x(3 + x)(1 − x) The only places where the potential is equal to zero is when one of its factors is equal to zero. Therefore, Either x = 0, 3 + x = 0, or 1 − x = 0 From these 3 equations we get x = −3 m, 0 m, 1 m ...
Cyclotron Motion - The Physics of Bruce Harvey
... will have a great enough magnetic moment to form its own magnetic field with n Φ0 quanta of magnetic flux threading the orbit. If the radius and velocity are comparable with an electron orbiting within an atom, we can assume that magnetic field contains half of the kinetic energy of the charges and ...
... will have a great enough magnetic moment to form its own magnetic field with n Φ0 quanta of magnetic flux threading the orbit. If the radius and velocity are comparable with an electron orbiting within an atom, we can assume that magnetic field contains half of the kinetic energy of the charges and ...
Charged particles and magnetic fields
... 1898), the then Chancellor of the Exchequer and subsequently four-time Prime Minister of Great Britain, challenged Faraday on the practical worth of this new discovery – electricity. Faraday’s response was ‘Why, sir, there is every probability that you will soon be able to tax it! ’ In fact it was m ...
... 1898), the then Chancellor of the Exchequer and subsequently four-time Prime Minister of Great Britain, challenged Faraday on the practical worth of this new discovery – electricity. Faraday’s response was ‘Why, sir, there is every probability that you will soon be able to tax it! ’ In fact it was m ...
PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #3
... gave a nonzero result for l = 0 states if we blindly let an l = 0 in the numerator cancel an ...
... gave a nonzero result for l = 0 states if we blindly let an l = 0 in the numerator cancel an ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 04. How are the bound and free charges related to each other in linear media? 05. State the Faraday’s law both in integral and differential form. 06. What is motional e.m.f 07. Define acceleration field? 08. What is anomalous dispersion? 09. Define the term skin depth? 10. Show that the power radiat ...
... 04. How are the bound and free charges related to each other in linear media? 05. State the Faraday’s law both in integral and differential form. 06. What is motional e.m.f 07. Define acceleration field? 08. What is anomalous dispersion? 09. Define the term skin depth? 10. Show that the power radiat ...
2017 AP Physics C Electricity and Magnetism Free Response Answers
... A given current will always produce a weaker-than-expected magnetic field because the solenoid is not an ideal solenoid. There will always be an “edge effect” unless the solenoid is infinitely long. 3d.ii. The absence of a resistor leads quickly to a very high current which would likely burn-out the ...
... A given current will always produce a weaker-than-expected magnetic field because the solenoid is not an ideal solenoid. There will always be an “edge effect” unless the solenoid is infinitely long. 3d.ii. The absence of a resistor leads quickly to a very high current which would likely burn-out the ...
hw08_assingnment
... 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
... 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
Magnetic monopoles
... B = ∇ × A for some vector potential A. This seems to imply the flux of through the sphere must vanish. Using Stokes’ theorem, show that the flux though the northern hemisphere is equal to the line integral of A around the equator one way, while the flux through the southern hemisphere is equal to th ...
... B = ∇ × A for some vector potential A. This seems to imply the flux of through the sphere must vanish. Using Stokes’ theorem, show that the flux though the northern hemisphere is equal to the line integral of A around the equator one way, while the flux through the southern hemisphere is equal to th ...
How does a Bohm particle localize?
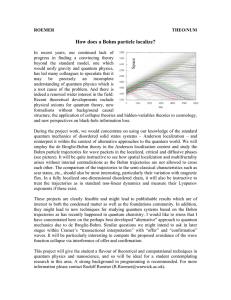
... scar states, etc., should also be most interesting, particularly their variation with magnetic flux. In a fully localized one-dimensional disordered chain, it will also be instructive to treat the trajectories as in standard non-linear dynamics and measure their Lyapunov exponents if these exist. Th ...
... scar states, etc., should also be most interesting, particularly their variation with magnetic flux. In a fully localized one-dimensional disordered chain, it will also be instructive to treat the trajectories as in standard non-linear dynamics and measure their Lyapunov exponents if these exist. Th ...
Name: Magnetic Field and Lorentz Force
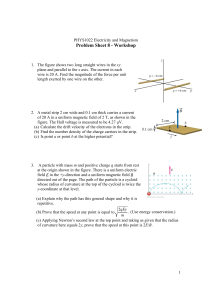
... 3. An electron accelerated from rest through potential difference V1 = 1.00 kV enters the gap between two parallel plates having separation d = 20.0 mm and potential difference V2 = 100 V. The lower plate is at the lower potential. Neglect fringing and assume that the electron's velocity vector is p ...
... 3. An electron accelerated from rest through potential difference V1 = 1.00 kV enters the gap between two parallel plates having separation d = 20.0 mm and potential difference V2 = 100 V. The lower plate is at the lower potential. Neglect fringing and assume that the electron's velocity vector is p ...