The Roots of Astronomy
... • Unfortunately, there are no written documents about the significance of stone and bronze age monuments. • First preserved written documents about ancient astronomy are from ancient Greek philosophy. ...
... • Unfortunately, there are no written documents about the significance of stone and bronze age monuments. • First preserved written documents about ancient astronomy are from ancient Greek philosophy. ...
Ancient Astronomy - Mrs. Petersen`s Earth Science
... important for the planners to keep the communications time lag, caused by the speed of light, in mind. For example, a probe designed to land on Mars must be smart enough to handle problems in the flight on it's own without instructions from Earth. If a course change is needed during landing the prob ...
... important for the planners to keep the communications time lag, caused by the speed of light, in mind. For example, a probe designed to land on Mars must be smart enough to handle problems in the flight on it's own without instructions from Earth. If a course change is needed during landing the prob ...
Stars
... For 2000 years, geocentric model for the universe was widely assumed. Stars affixed to celestial sphere Moon, Sun, planets, between Earth & stars Spherical Earth at center of universe ...
... For 2000 years, geocentric model for the universe was widely assumed. Stars affixed to celestial sphere Moon, Sun, planets, between Earth & stars Spherical Earth at center of universe ...
Powers of ten notation
... If we were at the North pole, how far above the horizon (in degrees) would the North celestial pole be? ...
... If we were at the North pole, how far above the horizon (in degrees) would the North celestial pole be? ...
Chapter 2 Knowing the Heavens
... meridian transits of the Sun IF it moved at a constant rate (exactly 24 hrs). • Sidereal time: the interval of time between two successive meridian transits of a star (23 hrs 56 min). ...
... meridian transits of the Sun IF it moved at a constant rate (exactly 24 hrs). • Sidereal time: the interval of time between two successive meridian transits of a star (23 hrs 56 min). ...
Discovering The Universe for Yourself
... • There are two periods each year when the nodes of the Moon’s orbit are nearly aligned with the Sun. • These are called Eclipse Seasons. • The combined effect of the changing dates of eclipse seasons and the 29.5 day lunar cycle, ...
... • There are two periods each year when the nodes of the Moon’s orbit are nearly aligned with the Sun. • These are called Eclipse Seasons. • The combined effect of the changing dates of eclipse seasons and the 29.5 day lunar cycle, ...
Chapter 3
... • Al-Mamun’s House of Wisdom in Baghdad was a great center of learning around A.D. 800 • With the fall of Constantinople (Istanbul) in 1453, Eastern scholars headed west to Europe, carrying knowledge that helped ignite the European Renaissance. ...
... • Al-Mamun’s House of Wisdom in Baghdad was a great center of learning around A.D. 800 • With the fall of Constantinople (Istanbul) in 1453, Eastern scholars headed west to Europe, carrying knowledge that helped ignite the European Renaissance. ...
history of astro outline 2014
... Ancient Babylonians develop number system based on 60 (led to time-keeping and angular measurements) and 12month calendar. Ancient Egyptians separated a day-night period into 24 separate hours and the year into 365 days ...
... Ancient Babylonians develop number system based on 60 (led to time-keeping and angular measurements) and 12month calendar. Ancient Egyptians separated a day-night period into 24 separate hours and the year into 365 days ...
Renaissance Astronomy - Faculty Web Sites at the University of
... Prior to the Renaissance The Greek astronomer Ptolemy (85-165 A.D.) successfully created a model that explained the complex observed planetary motion in the context of the dogmatic restrictions of the time. ...
... Prior to the Renaissance The Greek astronomer Ptolemy (85-165 A.D.) successfully created a model that explained the complex observed planetary motion in the context of the dogmatic restrictions of the time. ...
Homework #2 Solutions Astronomy 10, Section 2 due: Monday
... 3) Do planets orbiting other stars have ecliptics? Could they have seasons? All of the planets are orbiting the Sun. Therefore, the path of the SUn across the sky over the course of the year can be defined. This is the definition of an ecliptic. Every planet has one, and they are all slightly differ ...
... 3) Do planets orbiting other stars have ecliptics? Could they have seasons? All of the planets are orbiting the Sun. Therefore, the path of the SUn across the sky over the course of the year can be defined. This is the definition of an ecliptic. Every planet has one, and they are all slightly differ ...
lecture5 - UMass Astronomy
... Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s plac ...
... Earth. You can now imagine how Earth, the moon, and the sun move through space and how that produces the sights you see in the sky. But how did humanity first realize that we live on a planet moving through space? That required revolutionary overthrow of an ancient and honored theory of Earth’s plac ...
Apparent Motions of Celestial Objects
... In the Northern Hemisphere: The Sun rises north of east and sets north of west in the summer. The sun’s altitude at noon is highest during the year. The sun’s “apparent path” across the sky is at its longest (greater than 12 hours). ...
... In the Northern Hemisphere: The Sun rises north of east and sets north of west in the summer. The sun’s altitude at noon is highest during the year. The sun’s “apparent path” across the sky is at its longest (greater than 12 hours). ...
Star - Danielle`s science9 weebly
... retrograde motion (reversal of direction) of Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. To account for this Ptolemy developed a model that gave Aristotle’s planets another level of circular motion called epicycles. ...
... retrograde motion (reversal of direction) of Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. To account for this Ptolemy developed a model that gave Aristotle’s planets another level of circular motion called epicycles. ...
Earth Science Library wk 2 (WP)
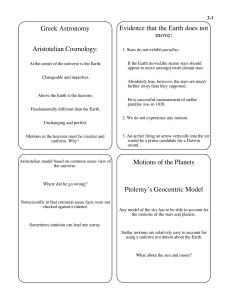
... If the Earth moved,the nearer stars should appear to move amongst more distant stars Absolutely true, however, the stars are much further away than they supposed. First successful measurement of stellar parallax was in 1838. ...
... If the Earth moved,the nearer stars should appear to move amongst more distant stars Absolutely true, however, the stars are much further away than they supposed. First successful measurement of stellar parallax was in 1838. ...
Introduction to cosmology I
... Heroic age followed by decline (Should have been Aristarchus - Copernicus, Archimedes-Galileo) ...
... Heroic age followed by decline (Should have been Aristarchus - Copernicus, Archimedes-Galileo) ...
Day 1 - Ch 1
... is due to the rotation of the Earth. The Earth is rotating around an axis that goes from pole to pole through a center. Eventually, each day, the Sun sets in the west. If we suppose the Sun is the center of the solar system, it is fixed, so: Each point on the surface of the Earth is going east all t ...
... is due to the rotation of the Earth. The Earth is rotating around an axis that goes from pole to pole through a center. Eventually, each day, the Sun sets in the west. If we suppose the Sun is the center of the solar system, it is fixed, so: Each point on the surface of the Earth is going east all t ...
Planetarium Lab 1
... • Direct motion is ___eastward___________ against the background of fixed stars. • Retrograde motion is ___westward___________ against the background of fixed stars. 3. Outer planets spend most of their time in which motion, direct or retrograde? 4. Define opposition ____________direct______________ ...
... • Direct motion is ___eastward___________ against the background of fixed stars. • Retrograde motion is ___westward___________ against the background of fixed stars. 3. Outer planets spend most of their time in which motion, direct or retrograde? 4. Define opposition ____________direct______________ ...
document
... world. His book the Almagest was the most widely read astronomy text. Many leaders created tables of the stars and planets based on the Ptolemaic models. ...
... world. His book the Almagest was the most widely read astronomy text. Many leaders created tables of the stars and planets based on the Ptolemaic models. ...
Geo-centric astronomy from Pythagoras to Ptolemy File
... in which he advanced the heliocentric model as an alternative hypothesis. Archimedes wrote: You (King Gelon) are aware the 'universe' is the name given by most astronomers to the sphere the center of which is the center of the Earth, while its radius is equal to the straight line between the center ...
... in which he advanced the heliocentric model as an alternative hypothesis. Archimedes wrote: You (King Gelon) are aware the 'universe' is the name given by most astronomers to the sphere the center of which is the center of the Earth, while its radius is equal to the straight line between the center ...
Sun - Blackboard
... The previous chapter took you on a cosmic zoom through space and time. That quick preview only sets the stage for the drama to come. Now it is time to return to Earth and look closely at the sky and answer four essential questions: • How do astronomers refer to stars and compare their brightness? • ...
... The previous chapter took you on a cosmic zoom through space and time. That quick preview only sets the stage for the drama to come. Now it is time to return to Earth and look closely at the sky and answer four essential questions: • How do astronomers refer to stars and compare their brightness? • ...
Quiz # 1 - Oglethorpe University
... c. the Sun moved among the planets, and pulled them out of their circular orbits d. the planets moved on a small circle whose center in turn circled a point near the Earth e. you can't fool me, Ptolemy's system did not include ANY explanation of retrograde motion We now know that the orbit of a stab ...
... c. the Sun moved among the planets, and pulled them out of their circular orbits d. the planets moved on a small circle whose center in turn circled a point near the Earth e. you can't fool me, Ptolemy's system did not include ANY explanation of retrograde motion We now know that the orbit of a stab ...
Life in the Universe
... On a clear night, with 20/20 vision, one can see about 3,000 stars at a given time. Ancient astronomers traced out “pictures” using groups of these stars. “Group of Stars” in Latin constellations ...
... On a clear night, with 20/20 vision, one can see about 3,000 stars at a given time. Ancient astronomers traced out “pictures” using groups of these stars. “Group of Stars” in Latin constellations ...
Celestial Motions
... They depend on latitude because your position on Earth determines which constellations remain below the horizon. (They depend on time of year because Earth’s orbit changes the apparent location of the Sun among the stars.) ...
... They depend on latitude because your position on Earth determines which constellations remain below the horizon. (They depend on time of year because Earth’s orbit changes the apparent location of the Sun among the stars.) ...
dtu7ech01 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... sky can be located, called the CELESTIAL SPHERE. As viewed from Earth, the celestial sphere appears to rotate around two axis points, the north and south celestial poles, which are located directly above the Earth’s poles. Between these is the celestial equator, which divides the celestial sphere ...
... sky can be located, called the CELESTIAL SPHERE. As viewed from Earth, the celestial sphere appears to rotate around two axis points, the north and south celestial poles, which are located directly above the Earth’s poles. Between these is the celestial equator, which divides the celestial sphere ...
Celestial spheres

The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus and others. In these celestial models the apparent motions of the fixed stars and the planets are accounted for by treating them as embedded in rotating spheres made of an aetherial, transparent fifth element (quintessence), like jewels set in orbs. Since it was believed that the fixed stars did not change their positions relative to one another, it was argued that they must be on the surface of a single starry sphere.In modern thought, the orbits of the planets are viewed as the paths of those planets through mostly empty space. Ancient and medieval thinkers, however, considered the celestial orbs to be thick spheres of rarefied matter nested one within the other, each one in complete contact with the sphere above it and the sphere below. When scholars applied Ptolemy's epicycles, they presumed that each planetary sphere was exactly thick enough to accommodate them. By combining this nested sphere model with astronomical observations, scholars calculated what became generally accepted values at the time for the distances to the Sun (about 4 million miles), to the other planets, and to the edge of the universe (about 73 million miles). The nested sphere model's distances to the Sun and planets differ significantly from modern measurements of the distances, and the size of the universe is now known to be inconceivably large and possibly infinite.Albert Van Helden has suggested that from about 1250 until the 17th century, virtually all educated Europeans were familiar with the Ptolemaic model of ""nesting spheres and the cosmic dimensions derived from it"". Even following the adoption of Copernicus's heliocentric model of the universe, new versions of the celestial sphere model were introduced, with the planetary spheres following this sequence from the central Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth-Moon, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn.