powerpoint
... alternating dark and light stripes on a screen placed in front of these two slits. ...
... alternating dark and light stripes on a screen placed in front of these two slits. ...
Workshop in Computational Structural Biology
... – The representation of side chains as rotamers – Rotamer and off-rotamer sampling ...
... – The representation of side chains as rotamers – Rotamer and off-rotamer sampling ...
Raman Spectroscopy
... In fact, the difference between the successive translational energy levels is so small (~ 10-60 J mol-1) that it cannot be observed experimentally. For this reason, for practical purposes, translational energy is considered as continuous and we do not observe any translational spectrum. The differen ...
... In fact, the difference between the successive translational energy levels is so small (~ 10-60 J mol-1) that it cannot be observed experimentally. For this reason, for practical purposes, translational energy is considered as continuous and we do not observe any translational spectrum. The differen ...
Chapter 14 Proteins
... ◦ The polypeptide backbone is extended in a zigzag structure resembling a series of pleats. ◦ The six atoms of each peptide bond of a b-pleated sheet lie in the same plane. ◦ The C=O and N-H groups of the peptide bonds from adjacent chains point toward each other and are in the same plane so that hy ...
... ◦ The polypeptide backbone is extended in a zigzag structure resembling a series of pleats. ◦ The six atoms of each peptide bond of a b-pleated sheet lie in the same plane. ◦ The C=O and N-H groups of the peptide bonds from adjacent chains point toward each other and are in the same plane so that hy ...
Example 12. Find electric field a distance h above the center of a (i
... implying the previously stated result that ...
... implying the previously stated result that ...
File - Elko Science
... •folding of the polypeptide chain is stabilized by multiple weak, non-covalent interactions. These interactions include: + Hydrogen bonds - form when a Hydrogen atom is shared by two other atoms. + Electrostatic interactions - occur between charged amino acid side chains. + Hydrophobic interactions ...
... •folding of the polypeptide chain is stabilized by multiple weak, non-covalent interactions. These interactions include: + Hydrogen bonds - form when a Hydrogen atom is shared by two other atoms. + Electrostatic interactions - occur between charged amino acid side chains. + Hydrophobic interactions ...
HW11: Ch.31 Q 2,5,7,9,12 P 4,7,11,19, 23, 26
... V=V0 sin(2 π f t) is applied across the plates, where V0=150V and f=60Hz. (a) In the region between the plates, show that the magnitude of the induced magnetic field is given by B=B0(R) Cos(2 π f t) where R is the radial distance from the capacitor’s central axis. (b) Determine the expression for th ...
... V=V0 sin(2 π f t) is applied across the plates, where V0=150V and f=60Hz. (a) In the region between the plates, show that the magnitude of the induced magnetic field is given by B=B0(R) Cos(2 π f t) where R is the radial distance from the capacitor’s central axis. (b) Determine the expression for th ...
Proteins * Structure and Function
... • Fibrous protein molecules form long chains or fibres (they have primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure) • Their fibrous nature makes them insoluble in water... • ... this makes them useful for structure and support Collagen found in skin, teeth, bones, tendons, blood vessel ...
... • Fibrous protein molecules form long chains or fibres (they have primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure) • Their fibrous nature makes them insoluble in water... • ... this makes them useful for structure and support Collagen found in skin, teeth, bones, tendons, blood vessel ...
1 Biology - Organic Chemistry Notes Name Date Organic Chemistry
... broken down (digested to amino acids and simple sugars respectively), in order to enter cells. Once nutrients enter a cell, the cell will use them as building blocks in the synthesis of compounds necessary for life. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
... broken down (digested to amino acids and simple sugars respectively), in order to enter cells. Once nutrients enter a cell, the cell will use them as building blocks in the synthesis of compounds necessary for life. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
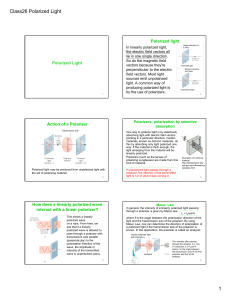
Class26 Polarized Light 1
... absorbing light with electric field vectors pointing in a particular direction. Certain materials, known as dichroic materials, do this by absorbing only light polarized one way. If the material is thick enough, the light emerging from the material will be linearly polarized. Polarizers (such as the ...
... absorbing light with electric field vectors pointing in a particular direction. Certain materials, known as dichroic materials, do this by absorbing only light polarized one way. If the material is thick enough, the light emerging from the material will be linearly polarized. Polarizers (such as the ...
Enzyme Biosinthess
... is bound during termination. Proteins called release factors participate in termination ...
... is bound during termination. Proteins called release factors participate in termination ...
Bioknowlodgy worksheet 2.4
... 2.4.A1 Rubisco, insulin, immunoglobulins, rhodopsin, collagen and spider silk as examples of the range of protein functions. 14. Take notes to outline each of the key examples of protein function. ...
... 2.4.A1 Rubisco, insulin, immunoglobulins, rhodopsin, collagen and spider silk as examples of the range of protein functions. 14. Take notes to outline each of the key examples of protein function. ...
EM Waves
... 4. Unlike mechanical waves, which need the oscillating particles of a medium such as water or air to be transmitted, electromagnetic waves require no medium. What’s “waving” in an electromagnetic wave are the electric and magnetic fields. ...
... 4. Unlike mechanical waves, which need the oscillating particles of a medium such as water or air to be transmitted, electromagnetic waves require no medium. What’s “waving” in an electromagnetic wave are the electric and magnetic fields. ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.