1 - 嘉義大學
... 6. What mass of calcium chloride, CaCl2, is needed to prepare 500 mL of a 1.56 M solution? (Ca: 40.08, Cl: 35.45) (A) 86.6 g (B) 60.8 g (C) 111 g (D) 25.6 g 7. Consider two organic molecules, ethanol and benzene. One dissolves in water and the other does not. Why? (A) They have different molar masse ...
... 6. What mass of calcium chloride, CaCl2, is needed to prepare 500 mL of a 1.56 M solution? (Ca: 40.08, Cl: 35.45) (A) 86.6 g (B) 60.8 g (C) 111 g (D) 25.6 g 7. Consider two organic molecules, ethanol and benzene. One dissolves in water and the other does not. Why? (A) They have different molar masse ...
Equilibrium - District 196
... At equilibrium, the color of a beaker containing this system would be violet (light purple) What would you see if the following possible stressors were Introduced according to LeChatlier? •Addition of Co(H2O)6+2 •Removal of Cl-(aq) •Removal of H2O(l) •Addition of CoCl4-2(aq) •Addition of ∆H •Removal ...
... At equilibrium, the color of a beaker containing this system would be violet (light purple) What would you see if the following possible stressors were Introduced according to LeChatlier? •Addition of Co(H2O)6+2 •Removal of Cl-(aq) •Removal of H2O(l) •Addition of CoCl4-2(aq) •Addition of ∆H •Removal ...
Assignment 3
... concentrations of N2, O2, and TOTC(4), and the solution pH once the system equilibrates with respect to gas-liquid exchange? Assume that redox reactions are kinetically inhibited. ...
... concentrations of N2, O2, and TOTC(4), and the solution pH once the system equilibrates with respect to gas-liquid exchange? Assume that redox reactions are kinetically inhibited. ...
Wanganui High School
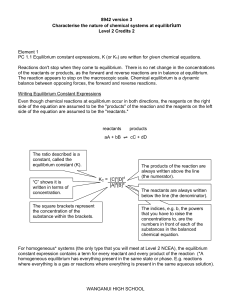
... For homogeneous* systems (the only type that you will meet at Level 2 NCEA), the equilibrium constant expression contains a term for every reactant and every product of the reaction (*A homogeneous equilibrium has everything present in the same state or phase. E.g. reactions where everything is a ga ...
... For homogeneous* systems (the only type that you will meet at Level 2 NCEA), the equilibrium constant expression contains a term for every reactant and every product of the reaction (*A homogeneous equilibrium has everything present in the same state or phase. E.g. reactions where everything is a ga ...
RTF
... All species must be present in the same concentration False. At equilibrium, the concentrations will not change, but they are not necessarily the same for all reaction participants. ...
... All species must be present in the same concentration False. At equilibrium, the concentrations will not change, but they are not necessarily the same for all reaction participants. ...
4. Which of the following describes how a Keq value is related to the
... What happens when O2 is added to the above system? Equilibrium ...
... What happens when O2 is added to the above system? Equilibrium ...
CHM 111: General Physical Chemistry 3 Units
... solids types of solids and their properties, ionic solids and lattice energy, crystalline solids. Chemical Energetic: definition of some thermodynamic terms, heat, work, internal energy, enthalpy, pressure-volume work. Relationship between internal energy and enthalpy. First law of thermodynamics an ...
... solids types of solids and their properties, ionic solids and lattice energy, crystalline solids. Chemical Energetic: definition of some thermodynamic terms, heat, work, internal energy, enthalpy, pressure-volume work. Relationship between internal energy and enthalpy. First law of thermodynamics an ...
Kc and Kp Conversions Hess`s Law in Equilibrium Constants
... The equilibrium constant of a reaction that has been multiplied by a number is the equilibrium constant raised to a power that is equal to that number. ...
... The equilibrium constant of a reaction that has been multiplied by a number is the equilibrium constant raised to a power that is equal to that number. ...
Balanced Equations And Equilibrium Constants
... Part 1: Balancing the Reaction. Step 1: Make a chart with the initial number of atoms on the reactants and products side for each element: Element #atoms as reactants #atoms as products ...
... Part 1: Balancing the Reaction. Step 1: Make a chart with the initial number of atoms on the reactants and products side for each element: Element #atoms as reactants #atoms as products ...
Notes on Chapter 12 Chemical Equilibrium
... 2. Reaction rates = speed of the reaction = change in concentration/change in time which can be measured in terms of formation of product or loss of reactants over time. Factors that affect the rate of reaction: a. temperature- increase in temperature increases reaction rates b. concentration- incre ...
... 2. Reaction rates = speed of the reaction = change in concentration/change in time which can be measured in terms of formation of product or loss of reactants over time. Factors that affect the rate of reaction: a. temperature- increase in temperature increases reaction rates b. concentration- incre ...
AP Chemistry
... 1. Ionic and molecular species present in chemical systems: net ionic equations 2. Balancing of equations, including those for redox reactions 3. Mass and volume relations with emphasis on the mole concept, including empirical formulas and limiting reactants C. Equilibrium 1. Concept of dynamic equi ...
... 1. Ionic and molecular species present in chemical systems: net ionic equations 2. Balancing of equations, including those for redox reactions 3. Mass and volume relations with emphasis on the mole concept, including empirical formulas and limiting reactants C. Equilibrium 1. Concept of dynamic equi ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY II QUIZ 5 November 10, 2009
... 0.600 mol of O2 are placed in a 2.00 L flask at 600 K, what are the equilibrium concentrations of all species? N2(g) + ...
... 0.600 mol of O2 are placed in a 2.00 L flask at 600 K, what are the equilibrium concentrations of all species? N2(g) + ...
lecture1
... the two opposing reactions occur simultaneously. At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products do not change with time. ...
... the two opposing reactions occur simultaneously. At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products do not change with time. ...
DOC
... unknown "x" -- usually one of the equilibrium concentrations or a change in a conc. Express all equilibrium concentrations in terms of "x" and initial values Insert these equilibrium values (in terms of "x") into the proper equation for K, and If possible, solve directly for "x" using simple math No ...
... unknown "x" -- usually one of the equilibrium concentrations or a change in a conc. Express all equilibrium concentrations in terms of "x" and initial values Insert these equilibrium values (in terms of "x") into the proper equation for K, and If possible, solve directly for "x" using simple math No ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... Increase in temperature shifts equilibrium to the _________________: More __________. Kc ____________________. Decrease in temperature shifts equilibrium to the ________________: More ___________. Kc ______________________. If ∆H < 0 (Exothermic): Increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to th ...
... Increase in temperature shifts equilibrium to the _________________: More __________. Kc ____________________. Decrease in temperature shifts equilibrium to the ________________: More ___________. Kc ______________________. If ∆H < 0 (Exothermic): Increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to th ...
General Equilibrium
... In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can be substituted for activities. (This assumption isn’t always good!) ...
... In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can be substituted for activities. (This assumption isn’t always good!) ...