Water Chemistry 3
... For equilibrium evaluations the [ ] of a pure liquid or solid is defined as 1 Depending on the type of reaction, K may be called acidity or dissociation constant for acid/base reactions complexation constant for complexation reactions solubility product for dissolution reaction adsorption constant f ...
... For equilibrium evaluations the [ ] of a pure liquid or solid is defined as 1 Depending on the type of reaction, K may be called acidity or dissociation constant for acid/base reactions complexation constant for complexation reactions solubility product for dissolution reaction adsorption constant f ...
GENERAL CHEMISTRY REVIEW
... and product concentrations, not necessarily those at equilibrium. The value of Q can be compared to that of K to predict which way an equilibrium will shift given a set of initial concentrations. For instance, if Q > K the reaction will shift to the left if Q < K the reaction will shift to the right ...
... and product concentrations, not necessarily those at equilibrium. The value of Q can be compared to that of K to predict which way an equilibrium will shift given a set of initial concentrations. For instance, if Q > K the reaction will shift to the left if Q < K the reaction will shift to the right ...
Introduction
... gas phase is measured with the chromatograph (Model TCD 580, Gow-mac) with a Porapak N column (Model VDP-DVB, Alltech). The concentration in liquid phase is analyzed by back-titration and also measured with a ammonia electrode (Model 9512 BN, Orion®). Isothermal measurements are performed as follows ...
... gas phase is measured with the chromatograph (Model TCD 580, Gow-mac) with a Porapak N column (Model VDP-DVB, Alltech). The concentration in liquid phase is analyzed by back-titration and also measured with a ammonia electrode (Model 9512 BN, Orion®). Isothermal measurements are performed as follows ...
IODINE, IODIDE, TRI-IODIDE EQUILIBRIUM (Rev`d 3/25
... Using volumetric pipets, transfer 2-7 mL of the iodide/iodine stock solution to 100 mL volumetric flasks and dilute to the marks1. Place these solutions in a constant temperature bath until thermal equilibrium has been reached. 5. Scan these diluted solutions to determine a spectral region where th ...
... Using volumetric pipets, transfer 2-7 mL of the iodide/iodine stock solution to 100 mL volumetric flasks and dilute to the marks1. Place these solutions in a constant temperature bath until thermal equilibrium has been reached. 5. Scan these diluted solutions to determine a spectral region where th ...
Subject:
... I will be able to interpret information from graphs that represent catalyzed and uncatalyzed endergonic and exergonic reactions. I can distinguish between a reversible reaction at equilibrium and one that is not at equilibrium. I can determine the direction a reaction will proceed in order to reach ...
... I will be able to interpret information from graphs that represent catalyzed and uncatalyzed endergonic and exergonic reactions. I can distinguish between a reversible reaction at equilibrium and one that is not at equilibrium. I can determine the direction a reaction will proceed in order to reach ...
Free energy and Equilibrium
... reversible and do not proceed to completion . Infact in all such cases, in the initial state, only the reactants are present but as the reaction proceeds, the concentration of reactants decreases and that of products increases. Finally a stage is reached when no further change in concentration of th ...
... reversible and do not proceed to completion . Infact in all such cases, in the initial state, only the reactants are present but as the reaction proceeds, the concentration of reactants decreases and that of products increases. Finally a stage is reached when no further change in concentration of th ...
CHEM121 Exam 4 ObjectivesW16
... Calculate equilibrium constants (given concentrations of reactants/products) Interpret equilibrium constants (large/small are products/reactants favored?) LeChatelier’s Principle -shift Left or Right in response to change in concentration, temperature, pressure Classifying Chemical Reactions by patt ...
... Calculate equilibrium constants (given concentrations of reactants/products) Interpret equilibrium constants (large/small are products/reactants favored?) LeChatelier’s Principle -shift Left or Right in response to change in concentration, temperature, pressure Classifying Chemical Reactions by patt ...
2012 Coaches Institute Presentation
... Percent ionization of a weak acid increases as its concentration decreases ...
... Percent ionization of a weak acid increases as its concentration decreases ...
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
... 1. Acid-base reactions; concepts of Arrhenius, BrønstedLowry, and Lewis; coordination complexes, amphoterism 2. Precipitation reactions 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidation-reduction c. Electrochemistry: electrolytic and galvanic cells; Farada ...
... 1. Acid-base reactions; concepts of Arrhenius, BrønstedLowry, and Lewis; coordination complexes, amphoterism 2. Precipitation reactions 3. Oxidation-reduction reactions a. Oxidation number b. The role of the electron in oxidation-reduction c. Electrochemistry: electrolytic and galvanic cells; Farada ...
Chemistry Name: LeChâtlier`s Principle Date: Chemical Equilibrium
... Dynamic Equilibrium: A forward reaction and reverse reaction will happen at the same rate, reaching equilibrium and no net change LeChâtlier’s Principle: When a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the reaction will shift to relieve the stress. What is meant by stress? For example: The conc ...
... Dynamic Equilibrium: A forward reaction and reverse reaction will happen at the same rate, reaching equilibrium and no net change LeChâtlier’s Principle: When a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the reaction will shift to relieve the stress. What is meant by stress? For example: The conc ...
AP CHEMISTRY Chang -Chemistry 9
... Chemical reactivity and products of chemical reactions Relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and the first series of transition elements Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional ...
... Chemical reactivity and products of chemical reactions Relationships in the periodic table: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal with examples from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and the first series of transition elements Introduction to organic chemistry: hydrocarbons and functional ...
Notes
... calculate Q, compare to K and predict direction of reaction represent the change in one concentration as x and use the mol relationships to define the changes in all other species in terms of x sum the initial concentration and the change represented by values of x to get expressions for the equilib ...
... calculate Q, compare to K and predict direction of reaction represent the change in one concentration as x and use the mol relationships to define the changes in all other species in terms of x sum the initial concentration and the change represented by values of x to get expressions for the equilib ...
solving equilibrium problems with the ti-92
... the correct answer. Remember the computer maxim, Garbage in, garbage out! The key to correctly solving equilibrium problems is in setting up the ICE table, or reaction stoichiometry matrix. This will be covered in detail by your instructor, and the textbook; here, we are only interested in solving t ...
... the correct answer. Remember the computer maxim, Garbage in, garbage out! The key to correctly solving equilibrium problems is in setting up the ICE table, or reaction stoichiometry matrix. This will be covered in detail by your instructor, and the textbook; here, we are only interested in solving t ...
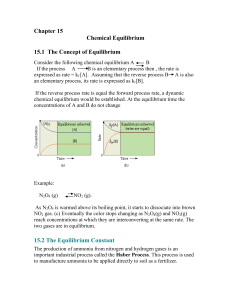
Consider the following chemical equilibrium A B
... Adding H2 will cause the system to shift as to reduce the concentration of H2 to its original value. This will caus the system to produce more of NH3 b. Effect of volume and pressure If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by decreasing the volume (increasing the total pressure), the system respond ...
... Adding H2 will cause the system to shift as to reduce the concentration of H2 to its original value. This will caus the system to produce more of NH3 b. Effect of volume and pressure If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by decreasing the volume (increasing the total pressure), the system respond ...
Chapter 13
... The decomposition of liquid water to gaseous hydrogen and oxygen, 2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g) K = [H2]2[O2] and Kp=(P2H2)(PO2) Water is not included in either equilibrium expression because it is a pure liquid. However, if water is a gas rather than a liquid, 2H2O(g) 2H2(g) + O2(g) ...
... The decomposition of liquid water to gaseous hydrogen and oxygen, 2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g) K = [H2]2[O2] and Kp=(P2H2)(PO2) Water is not included in either equilibrium expression because it is a pure liquid. However, if water is a gas rather than a liquid, 2H2O(g) 2H2(g) + O2(g) ...