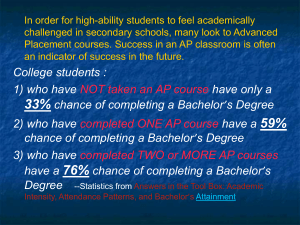
Fractional Composition
... • equilibrium constant, Henderson-Hasselbalch use approximations that fail if: – low concentrations – equilibrium constants too close • use fractional composition equations to calculate titration curves in spreadsheets • need to calculate mls of titrant (eg NaOH) • done by use of charge balance and ...
... • equilibrium constant, Henderson-Hasselbalch use approximations that fail if: – low concentrations – equilibrium constants too close • use fractional composition equations to calculate titration curves in spreadsheets • need to calculate mls of titrant (eg NaOH) • done by use of charge balance and ...
Exercises Chem Eqm
... energy when the partial pressure of the N2, H2, and NH3 (treated as perfect gases) are 3.0 bar, 1.0 bar, and 4.0 bar, respectively? What is the spontaneous direction of the reaction in this case? ...
... energy when the partial pressure of the N2, H2, and NH3 (treated as perfect gases) are 3.0 bar, 1.0 bar, and 4.0 bar, respectively? What is the spontaneous direction of the reaction in this case? ...
Equilibrium Constant- Keq
... mol/L. Find the concentration of the hydrogen chloride if the equilibrium constant is 1.6. 5. Methane and water vapor are reacted, in a 5.0L flask, to produce carbon monoxide and hydrogen. At equilibrium, the amounts of each material, respectively, are 4.8g, 4.3g, 8.62g and 2.60g. Calculate the Keq. ...
... mol/L. Find the concentration of the hydrogen chloride if the equilibrium constant is 1.6. 5. Methane and water vapor are reacted, in a 5.0L flask, to produce carbon monoxide and hydrogen. At equilibrium, the amounts of each material, respectively, are 4.8g, 4.3g, 8.62g and 2.60g. Calculate the Keq. ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... skeleton equation = formulas of the reactants & products only, no balancing of # of atoms due to the Law of Conservation of Mass, mass of reactants = mass of products o we cannot change the formulas therefore we must change the number of molecules o we do this by adding coefficients in front of th ...
... skeleton equation = formulas of the reactants & products only, no balancing of # of atoms due to the Law of Conservation of Mass, mass of reactants = mass of products o we cannot change the formulas therefore we must change the number of molecules o we do this by adding coefficients in front of th ...
Equilibrium
... if they are put them in but you are in the land of Q (more on that later) C = Change in concentration If the products are initially zero (0) then the reactants loose (−) and the products gain (+); if there are products present initially as well as reactants then you must enter the land of Q to deter ...
... if they are put them in but you are in the land of Q (more on that later) C = Change in concentration If the products are initially zero (0) then the reactants loose (−) and the products gain (+); if there are products present initially as well as reactants then you must enter the land of Q to deter ...
(General Equilibrium) Part 1
... 2. water- molar concentration is constant in aqueous solutions. (55.6M) (This is not true in gas phase reactions that produce water.) 3. Concentrations of pure solids or pure liquids are _________ (their activity is set to “1”.) when writing the equilibrium equation for any heterogeneous equilibriu ...
... 2. water- molar concentration is constant in aqueous solutions. (55.6M) (This is not true in gas phase reactions that produce water.) 3. Concentrations of pure solids or pure liquids are _________ (their activity is set to “1”.) when writing the equilibrium equation for any heterogeneous equilibriu ...
Le Chatelier`s Principle Quiz Answer Key
... 9. What factors alter the equilibrium position in chemical reactions? 10. Describe Le Chatelier's principle. 11. If more reactant is added to an equilibrium system, what happens to Keq (assume the temperature is not changed)? 12. How is changing the concentration of a reactant in a reaction related ...
... 9. What factors alter the equilibrium position in chemical reactions? 10. Describe Le Chatelier's principle. 11. If more reactant is added to an equilibrium system, what happens to Keq (assume the temperature is not changed)? 12. How is changing the concentration of a reactant in a reaction related ...
blood - SCH4U1-02-2010
... In the lungs where there is a high concentration of oxygen, by Le Chatelier's principle the equilibrium position shifts to the right resulting in the formation of oxyhaemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin). In tissues the concentration of oxygen is lower, so the equilibrium position shifts to the left, by Le Ch ...
... In the lungs where there is a high concentration of oxygen, by Le Chatelier's principle the equilibrium position shifts to the right resulting in the formation of oxyhaemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin). In tissues the concentration of oxygen is lower, so the equilibrium position shifts to the left, by Le Ch ...
CE3503 Expectations – Equilibrium Reactions that proceed to
... Reactions that proceed to equilibrium slowly (hours, e.g. BOD exertion, to decades, radioisotope decay) require a kinetic approach as introduced during our discussion of kinetics, reactors and mass balance. Those that proceed more rapidly (milliseconds, e.g. dissociation of strong acid, to minutes, ...
... Reactions that proceed to equilibrium slowly (hours, e.g. BOD exertion, to decades, radioisotope decay) require a kinetic approach as introduced during our discussion of kinetics, reactors and mass balance. Those that proceed more rapidly (milliseconds, e.g. dissociation of strong acid, to minutes, ...
printable version
... stopped, in fact the products are still being made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
... stopped, in fact the products are still being made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
Exercise 2 PARTITION COEFFICIENT OF SUCCINIC ACID
... Consider a system consisting of two liquid layers (phases) of two immiscible or partiallly miscible liquids. If a third substance, which is soluble in both liquids, is added into the system it is found to distribute, or divide, itself between the two layers in a definite manner. It has been shown ex ...
... Consider a system consisting of two liquid layers (phases) of two immiscible or partiallly miscible liquids. If a third substance, which is soluble in both liquids, is added into the system it is found to distribute, or divide, itself between the two layers in a definite manner. It has been shown ex ...
Equilibrium Reactions
... Write equilibrium expressions for these reactions: a) 2O3 (g) 3O2 (g) b) H2 (g) + F2 (g) 2HF(g) ...
... Write equilibrium expressions for these reactions: a) 2O3 (g) 3O2 (g) b) H2 (g) + F2 (g) 2HF(g) ...
equilibrium and activation energy
... What direction does the equilibrium shift if more oxygen is added? What direction does the equilibrium shift if water is removed? How does the concentration of methanol (CH3OH) change if more oxygen is added? How does the concentration of methanol change if more water is added? How does the concentr ...
... What direction does the equilibrium shift if more oxygen is added? What direction does the equilibrium shift if water is removed? How does the concentration of methanol (CH3OH) change if more oxygen is added? How does the concentration of methanol change if more water is added? How does the concentr ...
one way
... - the temperature: according to k = A exp(-Ea/RT) - the presence or the absence of a catalyst: a catalyst lowers the activation energy Ea The chemical equilibrium is reached when forward and backward reaction velocities are equal. In this case, an equilibrium constant Kc is given which is constant f ...
... - the temperature: according to k = A exp(-Ea/RT) - the presence or the absence of a catalyst: a catalyst lowers the activation energy Ea The chemical equilibrium is reached when forward and backward reaction velocities are equal. In this case, an equilibrium constant Kc is given which is constant f ...
u11_tqs
... 13. Adding a product to an equilibrium system pushes the reaction in the direction of… reactants. Removing a product from an equilibrium system pushes the reaction in the direction of… products. Adding a reactant to an equilibrium system pushes the reaction in the direction of… products. Removing a ...
... 13. Adding a product to an equilibrium system pushes the reaction in the direction of… reactants. Removing a product from an equilibrium system pushes the reaction in the direction of… products. Adding a reactant to an equilibrium system pushes the reaction in the direction of… products. Removing a ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... anion hydrolysis and results in a basic solution • If the cations react with water, the process is cation hydrolysis and results in an acidic solution ...
... anion hydrolysis and results in a basic solution • If the cations react with water, the process is cation hydrolysis and results in an acidic solution ...