Chapter 3 - Cloudfront.net
... Velocity: Speed and Direction • In physics, speed and velocity are NOT the same thing… • Speed refers to the distance covered by an object in a given time. • Velocity takes into account direction as well… • Velocity is a “vector” quantity…which means it includes magnitude and direction… ...
... Velocity: Speed and Direction • In physics, speed and velocity are NOT the same thing… • Speed refers to the distance covered by an object in a given time. • Velocity takes into account direction as well… • Velocity is a “vector” quantity…which means it includes magnitude and direction… ...
Chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... 11. The net force on the box is 10 N to the right. 12. The description of a vector quantity needs both magnitude and direction. 13. The force is tension. 14. Tension will be 20 N. ...
... 11. The net force on the box is 10 N to the right. 12. The description of a vector quantity needs both magnitude and direction. 13. The force is tension. 14. Tension will be 20 N. ...
Matching - Hauserphysics
... A) Change in position / Change in acceleration B) Change in velocity / Change in time C) Change in time / Change in position D) Change in position / Change in time 19. Which of the following quantities does not contain direction? A) Force B) Acceleration C) Displacement D) speed ...
... A) Change in position / Change in acceleration B) Change in velocity / Change in time C) Change in time / Change in position D) Change in position / Change in time 19. Which of the following quantities does not contain direction? A) Force B) Acceleration C) Displacement D) speed ...
Honors Physics Unit 5 Notes
... When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis in a given time interval, every portion on the object rotates through the same angle in a given time interval and has the same angular speed and the same angular acceleration ...
... When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis in a given time interval, every portion on the object rotates through the same angle in a given time interval and has the same angular speed and the same angular acceleration ...
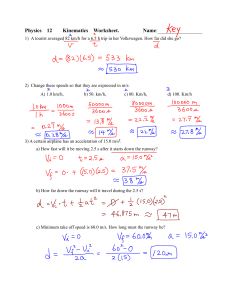
Newton`s 2nd Law and Momentum Problems
... 10. When a cannon is fired, Newton’s 3rd Law states that there will be an equal and opposite reaction, and momentum will be conserved. If a 20-Kg cannon ball is fired at a velocity of 980 m/s, what will the rearward velocity of a 1500-Kg cannon be if the cannon is mounted on wheels and allowed to ro ...
... 10. When a cannon is fired, Newton’s 3rd Law states that there will be an equal and opposite reaction, and momentum will be conserved. If a 20-Kg cannon ball is fired at a velocity of 980 m/s, what will the rearward velocity of a 1500-Kg cannon be if the cannon is mounted on wheels and allowed to ro ...
W3.13 Newton`s Law Quick Hitters 2
... 3. How much tension must a rope withstand if it is used to accelerate a 1200 kilogram crate vertically upwards at 0.80 m/s2? Ignore friction. 4. A 10-kilogram bucket is lowered by a rope in which there is 63 N of tension. What is the acceleration of the bucket? 5. The cable supporting a 2100-kilogra ...
... 3. How much tension must a rope withstand if it is used to accelerate a 1200 kilogram crate vertically upwards at 0.80 m/s2? Ignore friction. 4. A 10-kilogram bucket is lowered by a rope in which there is 63 N of tension. What is the acceleration of the bucket? 5. The cable supporting a 2100-kilogra ...
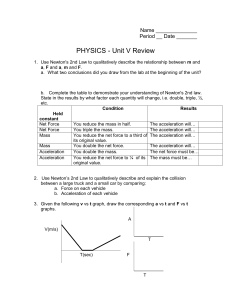
Unit V review
... 4. From dynamics information - If you are given forces, or the physical description of the system and surroundings, draw a force diagram. Ask yourself: "Can I tell if the system is accelerating?" If yes, then the forces do NOT add up to zero, then motionless, then the forces cancel out and ...
... 4. From dynamics information - If you are given forces, or the physical description of the system and surroundings, draw a force diagram. Ask yourself: "Can I tell if the system is accelerating?" If yes, then the forces do NOT add up to zero, then motionless, then the forces cancel out and ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - Mrs. Robbins Earth Science
... Part 2: Acceleration Depends on Force An object’s acceleration increases as the force on the object increases, and an object’s acceleration decreases as the force on the object decreases. The acceleration of an object is in the same direction as the force applied. ...
... Part 2: Acceleration Depends on Force An object’s acceleration increases as the force on the object increases, and an object’s acceleration decreases as the force on the object decreases. The acceleration of an object is in the same direction as the force applied. ...
Chapter 6 - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... The static frictional force keeps an object from starting to move when a force is applied. The static frictional force has a maximum value, but may take on any value from zero to the maximum, depending on what is needed to keep the sum of forces ...
... The static frictional force keeps an object from starting to move when a force is applied. The static frictional force has a maximum value, but may take on any value from zero to the maximum, depending on what is needed to keep the sum of forces ...