Competency Goal 6: Students will conduct investigations
... b. height x length c. length /height d. length - height 2. M.A. of a lever a. length of effort arm/length of resistance arm b. length of resistance arm x length of effort arm c. length of resistance arm/length of effort arm d. length of effort arm x length of resistance arm 3. M.A. of wheel and axel ...
... b. height x length c. length /height d. length - height 2. M.A. of a lever a. length of effort arm/length of resistance arm b. length of resistance arm x length of effort arm c. length of resistance arm/length of effort arm d. length of effort arm x length of resistance arm 3. M.A. of wheel and axel ...
here - Physics
... 5. Two satellites, A and B, are in different circular orbits about the Earth. The orbital speed of the satellite A is three times that of satellite B. Find the ratio TA /TB . Solution: Since we are given the ratio of the orbital speeds and we are asked to find the ratio of the orbital periods, the e ...
... 5. Two satellites, A and B, are in different circular orbits about the Earth. The orbital speed of the satellite A is three times that of satellite B. Find the ratio TA /TB . Solution: Since we are given the ratio of the orbital speeds and we are asked to find the ratio of the orbital periods, the e ...
1 - Eickman
... B has the smallest mass because it has the biggest acceleration (smaller mass is easier to accelerate) C has the middle mass A has the largest mass because it has the least acceleration (larger mass is harder to accelerate) ...
... B has the smallest mass because it has the biggest acceleration (smaller mass is easier to accelerate) C has the middle mass A has the largest mass because it has the least acceleration (larger mass is harder to accelerate) ...
File - Mr. Brown`s Science Town
... If the object was sitting still, it will remain stationary. If it was moving at a constant velocity, it will keep moving. It takes force to change the motion of an object. ...
... If the object was sitting still, it will remain stationary. If it was moving at a constant velocity, it will keep moving. It takes force to change the motion of an object. ...
19.2 Gravity and the Moon
... Inertia and orbital motion Inertia: the tendency of any object to resist a change in motion. Planets, moons, are not going to stop their motion unless something (huge) gets in their path. Newton’s first law explains inertia: an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will rem ...
... Inertia and orbital motion Inertia: the tendency of any object to resist a change in motion. Planets, moons, are not going to stop their motion unless something (huge) gets in their path. Newton’s first law explains inertia: an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will rem ...
Ch. 8. Energy
... 16. What is the ground speed of a plane which is traveling at 80 km/h, if it encounters (a) tailwind of 10 km/h (b) headwind of 15 km/h (c) 60 km/h wind at right angles to it (a) 80 + 10 = 90 km/h (b) 80 – 15 = 65 km/h (c) (602 + 802)1/2 = 100 km/h 17. What are the horizontal and vertical forces act ...
... 16. What is the ground speed of a plane which is traveling at 80 km/h, if it encounters (a) tailwind of 10 km/h (b) headwind of 15 km/h (c) 60 km/h wind at right angles to it (a) 80 + 10 = 90 km/h (b) 80 – 15 = 65 km/h (c) (602 + 802)1/2 = 100 km/h 17. What are the horizontal and vertical forces act ...
Lecture 8 - Columbia Math Department
... purposes of this section and for this class, we will always assume that the mass of the relevant particle doesn’t change with time, i.e. that m(t) = m is a constant. Example 2.2. (Centripetal force) A test tube in a centrifuge of radius R has mass m. The centrifuge has angular speed ω radians per se ...
... purposes of this section and for this class, we will always assume that the mass of the relevant particle doesn’t change with time, i.e. that m(t) = m is a constant. Example 2.2. (Centripetal force) A test tube in a centrifuge of radius R has mass m. The centrifuge has angular speed ω radians per se ...
Free Body Diagram
... The length of the chain between the car and the tree is 15.0 m and the perpendicular force causes the chain to deflect 0.5 m from the dotted line in the diagram. If the perpendicular force is 100 N what is the force T on the car if the car doesn’t move? ...
... The length of the chain between the car and the tree is 15.0 m and the perpendicular force causes the chain to deflect 0.5 m from the dotted line in the diagram. If the perpendicular force is 100 N what is the force T on the car if the car doesn’t move? ...
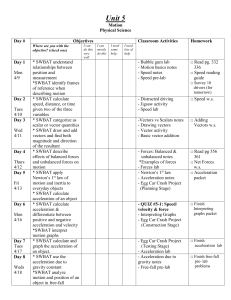
Unit 5 plan motion
... of reference when describing motion * SWBAT calculate speed, distance, or time given two of the three variables * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of balanced forces and unbala ...
... of reference when describing motion * SWBAT calculate speed, distance, or time given two of the three variables * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of balanced forces and unbala ...
Electromagnetic Induction Lab
... Force Table Vector Lab Introduction: Force is a vector quantity as is displacement, velocity and acceleration. When a body is in static equilibrium (not accelerating), the vector sum of all the forces acting on the body must be zero: F = 0. In this lab, you will analyze several forces that are bala ...
... Force Table Vector Lab Introduction: Force is a vector quantity as is displacement, velocity and acceleration. When a body is in static equilibrium (not accelerating), the vector sum of all the forces acting on the body must be zero: F = 0. In this lab, you will analyze several forces that are bala ...
Forces and Newton`s laws of motion
... Understand and use weight and motion in a straight line under gravity; gravitational acceleration, g, and its value in S.I. units to varying degrees of accuracy (The inverse square law for gravitation is not required and g may be assumed to be constant, but students should be aware that g is not a u ...
... Understand and use weight and motion in a straight line under gravity; gravitational acceleration, g, and its value in S.I. units to varying degrees of accuracy (The inverse square law for gravitation is not required and g may be assumed to be constant, but students should be aware that g is not a u ...
Newton's Laws of Motion
... Part 2: Acceleration Depends on Force An object’s acceleration increases as the force on the object increases, and an object’s acceleration decreases as the force on the object decreases. The acceleration of an object is in the same direction as the force applied. ...
... Part 2: Acceleration Depends on Force An object’s acceleration increases as the force on the object increases, and an object’s acceleration decreases as the force on the object decreases. The acceleration of an object is in the same direction as the force applied. ...
Force and Motion
... Lamont wants to move a 4,800 gram box from the floor to a shelf directly above the box. It takes Lamont 8 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 0.4 meters from the ground. It takes 12 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 1.2 meters off the ground. How much more work in joules is required ...
... Lamont wants to move a 4,800 gram box from the floor to a shelf directly above the box. It takes Lamont 8 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 0.4 meters from the ground. It takes 12 seconds to move the box to a shelf that is 1.2 meters off the ground. How much more work in joules is required ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... Laws of Motion Review Questions Name _________________________ Round all calculations. Given, formula, setup & solution is required. 1. State Newton’s 1st Law of Motion – An object maintains a constant velocity unless a net force acts on it 2. The tendency of an object to resist any change in motion ...
... Laws of Motion Review Questions Name _________________________ Round all calculations. Given, formula, setup & solution is required. 1. State Newton’s 1st Law of Motion – An object maintains a constant velocity unless a net force acts on it 2. The tendency of an object to resist any change in motion ...
Document
... acceleration and centripetal force to the solution of problems in circular motion. • Define and apply concepts of frequency and period, and relate them to linear speed. • Solve problems involving banking angles, the conical pendulum, and the vertical circle. ...
... acceleration and centripetal force to the solution of problems in circular motion. • Define and apply concepts of frequency and period, and relate them to linear speed. • Solve problems involving banking angles, the conical pendulum, and the vertical circle. ...
Unit C2: Scheme of Work
... is mostly introduced in subsequent sections. The particle model is introduced here: the body has no size but does have mass. So rotation is ignored, forces all act in one place. Return to questions above: simplifying assumptions could include: car is a particle; motion in a straight line; speed of c ...
... is mostly introduced in subsequent sections. The particle model is introduced here: the body has no size but does have mass. So rotation is ignored, forces all act in one place. Return to questions above: simplifying assumptions could include: car is a particle; motion in a straight line; speed of c ...
Ch 4 Review Worksheet
... 11) Two lifeguards pull on ropes attached to a raft. If they pull in the same direction, the raft experiences a net external force of 334N to the right. If they pull in opposite directions, the raft experiences a net external force of 105N to the left. a) Draw a free-body diagram representing the ra ...
... 11) Two lifeguards pull on ropes attached to a raft. If they pull in the same direction, the raft experiences a net external force of 334N to the right. If they pull in opposite directions, the raft experiences a net external force of 105N to the left. a) Draw a free-body diagram representing the ra ...