here - Physics at PMB
... In the previous section we studied kinematic which is the study of objects in motion disregarding the force that initiated the motion. However, in this section we pay our attention to the force that causes the motion. In particular, we will study the dynamics of an object, which is the study of moti ...
... In the previous section we studied kinematic which is the study of objects in motion disregarding the force that initiated the motion. However, in this section we pay our attention to the force that causes the motion. In particular, we will study the dynamics of an object, which is the study of moti ...
Document
... time later, its velocity is (7i + 3j) m/s. How much work was done by the resultant force during this time interval, assuming no energy is lost in the process? ...
... time later, its velocity is (7i + 3j) m/s. How much work was done by the resultant force during this time interval, assuming no energy is lost in the process? ...
Lecture 13 - UD Physics
... A block of mass m, when placed on a rough inclined plane (µ > 0) and given a brief push, keeps moving down the plane with constant speed. ÍIf a similar block (same µ) of mass 2m were placed on the same incline and given a brief push, it would: (a) stop (b) accelerate (c) move with constant speed m ...
... A block of mass m, when placed on a rough inclined plane (µ > 0) and given a brief push, keeps moving down the plane with constant speed. ÍIf a similar block (same µ) of mass 2m were placed on the same incline and given a brief push, it would: (a) stop (b) accelerate (c) move with constant speed m ...
motion
... How should they design the experiment? What is 1 constant? May give answer verbally. Design- Push objects of different masses up a ramp and measure the force exerted. Constants- Same ramp height/incline, same acceleration, same object, same position of release on the ramp ...
... How should they design the experiment? What is 1 constant? May give answer verbally. Design- Push objects of different masses up a ramp and measure the force exerted. Constants- Same ramp height/incline, same acceleration, same object, same position of release on the ramp ...
q - Worth County Schools
... The central force FC and the friction force fs are not two different forces that are equal. There is just one force on the car. The nature of this central force is static friction. ...
... The central force FC and the friction force fs are not two different forces that are equal. There is just one force on the car. The nature of this central force is static friction. ...
HW4 - Bryn Mawr College
... Find the radius of the orbit of a synchronous sate!lite that circles the Earth. (A synchronous satellite goes around the Earth once ev- ...
... Find the radius of the orbit of a synchronous sate!lite that circles the Earth. (A synchronous satellite goes around the Earth once ev- ...
Frames of Reference Apparent Forces
... uniform motion has no net forces acting on it. • A body at rest or in uniform motion relative to the rotating earth is not at rest or in uniform motion relative to a coordinate system fixed in space. • To reconcile Newton’s laws with the noninertial reference frame of the rotating earth, two apparen ...
... uniform motion has no net forces acting on it. • A body at rest or in uniform motion relative to the rotating earth is not at rest or in uniform motion relative to a coordinate system fixed in space. • To reconcile Newton’s laws with the noninertial reference frame of the rotating earth, two apparen ...
Jeopardy
... Which of Newton’s Laws states: Acceleration is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass, the greater the amount of force that is needed (to accelerate the object). ...
... Which of Newton’s Laws states: Acceleration is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass, the greater the amount of force that is needed (to accelerate the object). ...
Forces - Physics
... • Two people are pushing on a stalled car. • The mass of the car is 1850 kg. • One person applies a force of 275 N to the car, while the other person pushes with a force of 395 N. • Both forces act in the positive x direction. • A third force due to friction from the cars tires and the road opposes ...
... • Two people are pushing on a stalled car. • The mass of the car is 1850 kg. • One person applies a force of 275 N to the car, while the other person pushes with a force of 395 N. • Both forces act in the positive x direction. • A third force due to friction from the cars tires and the road opposes ...
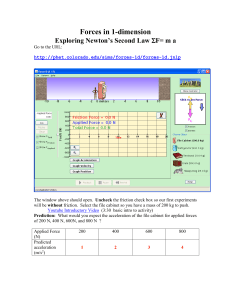
Forces in 1
... What is the maximum magnitude (ignore +/-) of the static friction force? (include units) Static Friction (maximum applied force before sliding begins) =about 600N___ What is the magnitude of the kinetic friction force? Kinetic friction force (friction while sliding) =_____392 N____________ ...
... What is the maximum magnitude (ignore +/-) of the static friction force? (include units) Static Friction (maximum applied force before sliding begins) =about 600N___ What is the magnitude of the kinetic friction force? Kinetic friction force (friction while sliding) =_____392 N____________ ...
Fourth Six Weeks TEST Study Guide 2015 What can you tell about
... What was Mary’s speed between seconds 2 and 3? What was John’s speed between seconds 2 and 3? ...
... What was Mary’s speed between seconds 2 and 3? What was John’s speed between seconds 2 and 3? ...
Section 4.1 Force and Motion
... the moving ball and the stationary object continues as it was. Newton’s First Law of Motion – also called the Law of Inertia. The law states the following: “An object at rest will stay at rest, an object in motion will stay in motion, unless acted on by an outside force.” Or the old book version is ...
... the moving ball and the stationary object continues as it was. Newton’s First Law of Motion – also called the Law of Inertia. The law states the following: “An object at rest will stay at rest, an object in motion will stay in motion, unless acted on by an outside force.” Or the old book version is ...
Conceptual Physics Semester 1 Review
... • Know that all objects on the Earth (or any other planet) accelerate downward under the influence of gravity • Know that objects that fall without significant air resistance and under the influence of only gravity are said to be in free fall ...
... • Know that all objects on the Earth (or any other planet) accelerate downward under the influence of gravity • Know that objects that fall without significant air resistance and under the influence of only gravity are said to be in free fall ...
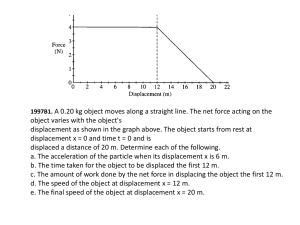
1997B1. A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line.
... 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through an angle of 60° with the vertical and held by a horizontal string as shown in the diagram above. This string is burned so that the pendulu ...
... 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through an angle of 60° with the vertical and held by a horizontal string as shown in the diagram above. This string is burned so that the pendulu ...