PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... • Gravity is always attractive, and acts between any two objects. • Electromagnetism causes repulsion and attraction between charged particles, such as the protons and electrons in matter. This gives rise to almost all of the forces we deal with in PHY131/132: Normal, Tension, etc. • Weak and Strong ...
... • Gravity is always attractive, and acts between any two objects. • Electromagnetism causes repulsion and attraction between charged particles, such as the protons and electrons in matter. This gives rise to almost all of the forces we deal with in PHY131/132: Normal, Tension, etc. • Weak and Strong ...
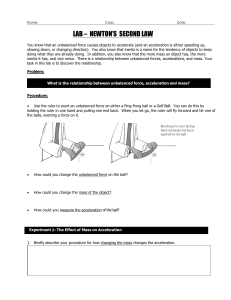
LAB – NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
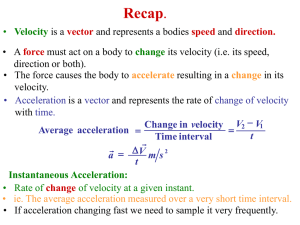
... is because acceleration and force change in the same way. The equation also shows that if you apply the same force to two objects, the one with the smaller mass will accelerate more. This is because acceleration and mass change in the opposite way. ...
... is because acceleration and force change in the same way. The equation also shows that if you apply the same force to two objects, the one with the smaller mass will accelerate more. This is because acceleration and mass change in the opposite way. ...
QUESTIONS MC Newton`s Laws
... The law of inertia applies to a. objects at rest. b. moving objects. c. both moving and nonmoving objects. ...
... The law of inertia applies to a. objects at rest. b. moving objects. c. both moving and nonmoving objects. ...
Chapter 4 Review
... 19. The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is _____. a. directly proportional the magnitude of the net force. b. in the same direction as the net force c. inversely proportional to the mass of the object d. all of the above e. none of the above 20. A heavy person and a light person pa ...
... 19. The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is _____. a. directly proportional the magnitude of the net force. b. in the same direction as the net force c. inversely proportional to the mass of the object d. all of the above e. none of the above 20. A heavy person and a light person pa ...
lectureslides09
... Electromagnetic Energy Nuclear Energy Energy can be transformed from one form to another ...
... Electromagnetic Energy Nuclear Energy Energy can be transformed from one form to another ...
V - USU Physics
... • But we now know that velocity changes are produced by an acceleration. • Thus when the car rounds the bend at a constant speed it is accelerating!! • Direction of acceleration is given by DV direction. ...
... • But we now know that velocity changes are produced by an acceleration. • Thus when the car rounds the bend at a constant speed it is accelerating!! • Direction of acceleration is given by DV direction. ...
centripetal force is the
... when the object is located at point A on the circle? 2. Which vector below represents the direction of the force vector when the object is located at point C on the circle? 3. Which vector below represents the direction of the velocity vector when the object is located at point B on the circle? 4. W ...
... when the object is located at point A on the circle? 2. Which vector below represents the direction of the force vector when the object is located at point C on the circle? 3. Which vector below represents the direction of the velocity vector when the object is located at point B on the circle? 4. W ...
Ch 4 Worksheet no Answers
... 4. A wooden plank is raised at one end until an angle of 30o is achieved. A 2.0 kg box is placed on the incline 1.0 m from the lower end and given a slight tap to overcome static friction. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and plank is 0.20. Determine the A. rate of acceleration o ...
... 4. A wooden plank is raised at one end until an angle of 30o is achieved. A 2.0 kg box is placed on the incline 1.0 m from the lower end and given a slight tap to overcome static friction. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and plank is 0.20. Determine the A. rate of acceleration o ...
Ch4 Sec1
... unbalanced force acts on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion describes how the forces exerted on an object, its mass, and its acceleration are related. ...
... unbalanced force acts on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion describes how the forces exerted on an object, its mass, and its acceleration are related. ...
Web Seminar—Force and Motion
... on something that's moving in a circle, such as a race car rounding a curve at constant speed. Should you do the following? Figure out all the forces of contact on the car, such as friction, and then add the centripetal force to these forces. ...
... on something that's moving in a circle, such as a race car rounding a curve at constant speed. Should you do the following? Figure out all the forces of contact on the car, such as friction, and then add the centripetal force to these forces. ...