Midterm 1
... force on the wagons is momentarily greater than the force exerted by the wagons on the locomotive. d. The locomotive’s force on the wagons is as strong as the force of the wagons on the locomotive, but the frictional force on the locomotive is forward and large, while the backward frictional force o ...
... force on the wagons is momentarily greater than the force exerted by the wagons on the locomotive. d. The locomotive’s force on the wagons is as strong as the force of the wagons on the locomotive, but the frictional force on the locomotive is forward and large, while the backward frictional force o ...
1443-501 Spring 2002 Lecture #3
... These forces are exerted on moving objects in opposite direction of the movement. These forces are proportional to such factors as speed. They almost always increase with increasing speed. Two different cases of proportionality: 1. Forces linearly proportional to speed: Slowly moving or very small o ...
... These forces are exerted on moving objects in opposite direction of the movement. These forces are proportional to such factors as speed. They almost always increase with increasing speed. Two different cases of proportionality: 1. Forces linearly proportional to speed: Slowly moving or very small o ...
Horizontal Motion
... curvature of the earth. This is called an orbit. A satellite is no more than a projectile moving fast enough to continually clear the horizon as it falls. ...
... curvature of the earth. This is called an orbit. A satellite is no more than a projectile moving fast enough to continually clear the horizon as it falls. ...
LINEAR KINETICS (Part 1)
... In other words, since acceleration (_) is the rate of change of velocity (_), (resultant) force (__) is the rate of change of momentum (__). If there is no _____________, then there is no change in ____________ IMPACTS AND THE PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ...
... In other words, since acceleration (_) is the rate of change of velocity (_), (resultant) force (__) is the rate of change of momentum (__). If there is no _____________, then there is no change in ____________ IMPACTS AND THE PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ...
Work done (J) - MrSimonPorter
... Ft = mv – mu The quantity Ft is called the impulse, and of course mv – mu is the change in momentum (v = final velocity and u = initial velocity) Impulse = Change in momentum ...
... Ft = mv – mu The quantity Ft is called the impulse, and of course mv – mu is the change in momentum (v = final velocity and u = initial velocity) Impulse = Change in momentum ...
Assignment 8 Solutions
... a height h = 5R above the base of a frictionless loop-the-loop track, as shown in the figure. The loop has a radius R = 30.0 cm. Use g = 10.0 m/s2 , to make the calculations easier (a) What is the speed of the block when it reaches position b, shown in the figure? We can use conservation of energy h ...
... a height h = 5R above the base of a frictionless loop-the-loop track, as shown in the figure. The loop has a radius R = 30.0 cm. Use g = 10.0 m/s2 , to make the calculations easier (a) What is the speed of the block when it reaches position b, shown in the figure? We can use conservation of energy h ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
Ph201_CH4_worksheet
... 9) A 2 kg block is supported by a flat wooden platform. The platform has an adjustable incline that can be raised from 0o to 90 o (with respect to the horizontal direction). The coefficient of static friction between the block and the platform surface is 0.5. a) As the platform is raised to some ang ...
... 9) A 2 kg block is supported by a flat wooden platform. The platform has an adjustable incline that can be raised from 0o to 90 o (with respect to the horizontal direction). The coefficient of static friction between the block and the platform surface is 0.5. a) As the platform is raised to some ang ...
Topic 4 Part 1 Review Questions student 2015
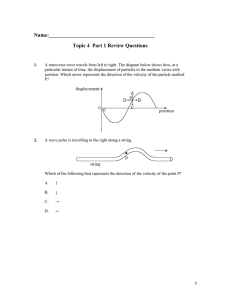
... A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the direction of the velocity of the particle marked P? ...
... A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the direction of the velocity of the particle marked P? ...
Gravity - Lauren - s3.amazonaws.com
... dropping a ball vertically, they will land motion at the same time. Why? The gravity is still forcing the horizontally thrown ball towards the ground. So it will land at the same time. • If you jump across a big gap( if its big enough) you will fall a little forward and straight down. You will event ...
... dropping a ball vertically, they will land motion at the same time. Why? The gravity is still forcing the horizontally thrown ball towards the ground. So it will land at the same time. • If you jump across a big gap( if its big enough) you will fall a little forward and straight down. You will event ...
Speed
... bottom of the hill with a velocity of 26m/s. What is the acceleration of the roller coaster? ...
... bottom of the hill with a velocity of 26m/s. What is the acceleration of the roller coaster? ...
Work and Kinetic Energy Script
... object, a force must be applied in the direction of the motion of the object. If there is no motion, no work is done on the object. If the motion is opposite to the direction of force, negative work is done on the object. In the equation, the angle is used to determine the component of the force tha ...
... object, a force must be applied in the direction of the motion of the object. If there is no motion, no work is done on the object. If the motion is opposite to the direction of force, negative work is done on the object. In the equation, the angle is used to determine the component of the force tha ...