Monday, September 20, 2004
... Free-body diagram: A diagram of vector forces acting on an object A great tool to solve a problem using forces or using dynamics Select a point on an object in the problem Identify all the forces acting only on the selected object Define a reference frame with positive and negative axes specified Dr ...
... Free-body diagram: A diagram of vector forces acting on an object A great tool to solve a problem using forces or using dynamics Select a point on an object in the problem Identify all the forces acting only on the selected object Define a reference frame with positive and negative axes specified Dr ...
Force and Motion Unit Test
... 5. The amount of matter in an object is called its a. inertia. c. balance. b. force. d. mass. 6. The force that one surface exerts on another when the two rub against each other is called a. gravity. c. inertia. b. friction. d. acceleration. 7. An object that travels around another object in space i ...
... 5. The amount of matter in an object is called its a. inertia. c. balance. b. force. d. mass. 6. The force that one surface exerts on another when the two rub against each other is called a. gravity. c. inertia. b. friction. d. acceleration. 7. An object that travels around another object in space i ...
Preview of Period 3: Motion and Forces
... motion is indicated) 3.2:A change in velocity occurs when a net force acts on a moving object. ♦ A force is any push or pull on an object. ♦ The net force of all forces acting in the same direction is the sum of the forces. ♦ The net force of forces acting in opposite directions is the difference of ...
... motion is indicated) 3.2:A change in velocity occurs when a net force acts on a moving object. ♦ A force is any push or pull on an object. ♦ The net force of all forces acting in the same direction is the sum of the forces. ♦ The net force of forces acting in opposite directions is the difference of ...
Name
... 18. Is the following sentence true or false? When two surfaces rub, the irregularities of one surface get caught on those of the other surface. ___________ 19. What is friction? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
... 18. Is the following sentence true or false? When two surfaces rub, the irregularities of one surface get caught on those of the other surface. ___________ 19. What is friction? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
orbital motion in an inverse-square-law force field
... that mass, traditionally defined as the amount of matter contained in a given object, appears in physics in two different aspects: (1) as the coefficient of inertia in Newton’s second law - the more massive an object, the larger a force is required to produce a specified amount of acceleration; and ...
... that mass, traditionally defined as the amount of matter contained in a given object, appears in physics in two different aspects: (1) as the coefficient of inertia in Newton’s second law - the more massive an object, the larger a force is required to produce a specified amount of acceleration; and ...
Units, Metric System and Conversions - bba-npreiser
... Obviously, a case of Newton's third law of motion. The bug hit the windshield and the windshield hit the bug. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the bug or the force on the windshield? Explain. 2) A gun recoils when it is fired. The recoil is the result of action-reaction force pairs. ...
... Obviously, a case of Newton's third law of motion. The bug hit the windshield and the windshield hit the bug. Which of the two forces is greater: the force on the bug or the force on the windshield? Explain. 2) A gun recoils when it is fired. The recoil is the result of action-reaction force pairs. ...
02 Effeciency and AMA
... principle of applying force over a longer distance, and also the tension in the rope or cable, to reduce the magnitude of the necessary force. Complex systems of ____________ can be used to greatly reduce the force that must be applied initially to move an object. A ____________ is a doubleinc ...
... principle of applying force over a longer distance, and also the tension in the rope or cable, to reduce the magnitude of the necessary force. Complex systems of ____________ can be used to greatly reduce the force that must be applied initially to move an object. A ____________ is a doubleinc ...
Exam 2
... D) Yes, since it takes energy to turn an object. 40) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides head-on with a 6.0-kg object moving to the left at 2.0 m/s. Which statement is correct? A) The total momentum both before and after the collision is zero. B) The total momentum both before ...
... D) Yes, since it takes energy to turn an object. 40) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides head-on with a 6.0-kg object moving to the left at 2.0 m/s. Which statement is correct? A) The total momentum both before and after the collision is zero. B) The total momentum both before ...
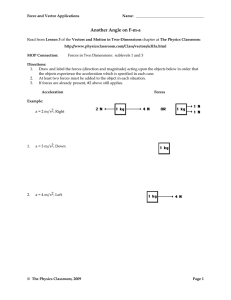
Another Angle on F-m-a
... The following statements were made about an object. In which case could you conclude that the object is at equilibrium? a. The object is at rest. b. The object has a constant velocity. c. The object is moving. d. The object has a constant speed. e. The object is stationary. f. The acceleration of th ...
... The following statements were made about an object. In which case could you conclude that the object is at equilibrium? a. The object is at rest. b. The object has a constant velocity. c. The object is moving. d. The object has a constant speed. e. The object is stationary. f. The acceleration of th ...
PowerPoint-Force and Motion
... over time. The acceleration of an object affected by gravity is 9.8 m/s. • Change in velocity of falling objects can be measured by the following equation: ∆v = g x t OR 9.8 m/s times the number of seconds an object falls… ...
... over time. The acceleration of an object affected by gravity is 9.8 m/s. • Change in velocity of falling objects can be measured by the following equation: ∆v = g x t OR 9.8 m/s times the number of seconds an object falls… ...
Force
... Practice force problem: (chp.10, p.337) You exert a force of 120N on a desk. Your friend exerts a force of 150N in the same direction. What is the net force you and your friend put on the desk? The net force is 270N ...
... Practice force problem: (chp.10, p.337) You exert a force of 120N on a desk. Your friend exerts a force of 150N in the same direction. What is the net force you and your friend put on the desk? The net force is 270N ...
During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and
... The drawing shows an object attached to an ideal spring, which is hanging from the ceiling. The unstrained length of the spring is indicated. For purposes of measuring the height h that determines the gravitational potential energy, the floor is taken as the position where h = 0 m. The equilibrium p ...
... The drawing shows an object attached to an ideal spring, which is hanging from the ceiling. The unstrained length of the spring is indicated. For purposes of measuring the height h that determines the gravitational potential energy, the floor is taken as the position where h = 0 m. The equilibrium p ...
The Geometry of Forces Along Equidistant Particle Paths
... a distance d/2 from the central inertial path is inward and is given by Fc = −2mv 2 k tanh(kd/2). We note that this force is essentially a result of the geometry of the manifold. This appears to be rather obvious although the authors are not aware that such an observation has been made in a mathemat ...
... a distance d/2 from the central inertial path is inward and is given by Fc = −2mv 2 k tanh(kd/2). We note that this force is essentially a result of the geometry of the manifold. This appears to be rather obvious although the authors are not aware that such an observation has been made in a mathemat ...