Section 5.1 Work
... If a man lifts a 20.0-kg bucket from a well and does 6.00 kJ of work, how deep is the well? Assume that the speed of the bucket remains constant as it is lifted. ...
... If a man lifts a 20.0-kg bucket from a well and does 6.00 kJ of work, how deep is the well? Assume that the speed of the bucket remains constant as it is lifted. ...
What do you want to know?
... Dude stands on the floor. His upper body weighs 438N and has a center of gravity 1.28m above the floor. His middle body has a weight of 144N and a center of gravity 0.76m above the floor. His lower body has a weight of 87N and a center of gravity 0.25m above the floor. Find the location of his cent ...
... Dude stands on the floor. His upper body weighs 438N and has a center of gravity 1.28m above the floor. His middle body has a weight of 144N and a center of gravity 0.76m above the floor. His lower body has a weight of 87N and a center of gravity 0.25m above the floor. Find the location of his cent ...
Physics CPA Unit 4 Conceptual Questions: Explain the concept of
... force of 30 N, the other suddenly pulls East with a force of 38 N and the toy flies away. What is the initial acceleration of the toy? 8. A 2.0 –kg rock falls against an instantaneous air resistance force of 11 N. a) Calculate the acceleration of the rock at this point in time. b) When the rock reac ...
... force of 30 N, the other suddenly pulls East with a force of 38 N and the toy flies away. What is the initial acceleration of the toy? 8. A 2.0 –kg rock falls against an instantaneous air resistance force of 11 N. a) Calculate the acceleration of the rock at this point in time. b) When the rock reac ...
Document
... Gravitational Force (Weight) The force exerted by the Earth on an object The gravitational force is some times expressed as: W mg Where: g = 9.81 m/s2 ...
... Gravitational Force (Weight) The force exerted by the Earth on an object The gravitational force is some times expressed as: W mg Where: g = 9.81 m/s2 ...
Speed and Velocity - The Physics Classroom
... a. the ride exerts an outward force on Darron that pushes him outward against the wall b. Darron has a natural tendency to move tangent to the circle but the wall pushes him inward c. air pressure is reduced by the barrel's motion that causes a suction action toward the wall d. the ride operator coa ...
... a. the ride exerts an outward force on Darron that pushes him outward against the wall b. Darron has a natural tendency to move tangent to the circle but the wall pushes him inward c. air pressure is reduced by the barrel's motion that causes a suction action toward the wall d. the ride operator coa ...
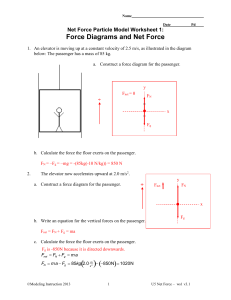
Force Diagrams and Net Force Key
... 6. a. Draw a force diagram for a 900 kg car that exerts 5000 N of traction force on a level road while being opposed by 1000 newtons of friction and drag forces combined. y Fnet FN Fg ...
... 6. a. Draw a force diagram for a 900 kg car that exerts 5000 N of traction force on a level road while being opposed by 1000 newtons of friction and drag forces combined. y Fnet FN Fg ...
Kendriyavidyalayasangathan 1 Multiple choice questions in Physics for class IX
... when it is acted upon by a. Uniform force c. Zero Force b. An Unbalanced force d. Balanced Force ...
... when it is acted upon by a. Uniform force c. Zero Force b. An Unbalanced force d. Balanced Force ...
1st Semester Review
... Explain difference between average and instantaneous velocities and speeds 2. Provide a scenario in which the average speed of a runner is greater than its instantaneous speed. Define in words, and equation: average and instantaneous, velocity and speed. Differentiate between them. 3. Explain the di ...
... Explain difference between average and instantaneous velocities and speeds 2. Provide a scenario in which the average speed of a runner is greater than its instantaneous speed. Define in words, and equation: average and instantaneous, velocity and speed. Differentiate between them. 3. Explain the di ...
Free Fall - Haiku Learning
... What do you notice about the motion of the object? – Initial speed is zero – The speed increases as it falls – The longer it falls the faster it travels – The object is accelerating. ...
... What do you notice about the motion of the object? – Initial speed is zero – The speed increases as it falls – The longer it falls the faster it travels – The object is accelerating. ...
Lecture 22 - LSU Physics
... a) What is the escape speed on a spherical asteroid whose radius is 500 km and whose gravitational acceleration at the surface is is 3 m/s2 ? b) How far from the surface will the particle go if it leaves the asteroid’s surface with a radial speed ...
... a) What is the escape speed on a spherical asteroid whose radius is 500 km and whose gravitational acceleration at the surface is is 3 m/s2 ? b) How far from the surface will the particle go if it leaves the asteroid’s surface with a radial speed ...
PY1052 Problem Set 2 – Autumn 2004 Solutions
... Because the acceleration is positive, it is in the +x direction – m 1 moves down the ramp. (b) We can now find the tension in the cord by plugging the acceleration from (a) back into either the second or the fourth equation above: −F2 + T = m2 a T = m 2 a + F2 = (3.00 kg)(1.06 m/s2 ) + 2.3 N T = 5.4 ...
... Because the acceleration is positive, it is in the +x direction – m 1 moves down the ramp. (b) We can now find the tension in the cord by plugging the acceleration from (a) back into either the second or the fourth equation above: −F2 + T = m2 a T = m 2 a + F2 = (3.00 kg)(1.06 m/s2 ) + 2.3 N T = 5.4 ...
Balancing Rotating Masses The balancing of rotating bodies is
... System of Co-Planar Concurrent Masses Rotating at 10 rev/min 3. Four masses A, B, C, and D, rotate together in a plane about a common axis O. The masses and radii of rotation are as follows: A, 2 kg, 0.6 m: B, 3 kg, 0.9 m; C, 4 kg, 1.2 m; D, 5kg, 1.5 m. The angles between the masses are : Angle AOB ...
... System of Co-Planar Concurrent Masses Rotating at 10 rev/min 3. Four masses A, B, C, and D, rotate together in a plane about a common axis O. The masses and radii of rotation are as follows: A, 2 kg, 0.6 m: B, 3 kg, 0.9 m; C, 4 kg, 1.2 m; D, 5kg, 1.5 m. The angles between the masses are : Angle AOB ...
Chapter 4-physics - Mrs. Krusa`s Wikispace
... First Law- an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force Sometimes called the Law of Inertia What is Inertia? Tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion If a net force on an object is zero, object is in equilibriumobject at ...
... First Law- an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force Sometimes called the Law of Inertia What is Inertia? Tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion If a net force on an object is zero, object is in equilibriumobject at ...