5. Forces and Motion-I Newton's First Law:
... (b) Instead of starting from rest, at the moment the force was applied, the cart is already moving with a constant speed in the direction of the force. After exerting the same constant force for the same short time interval, the increase in the cart's speed is: 1. Two times its initial speed 2. The ...
... (b) Instead of starting from rest, at the moment the force was applied, the cart is already moving with a constant speed in the direction of the force. After exerting the same constant force for the same short time interval, the increase in the cart's speed is: 1. Two times its initial speed 2. The ...
Linear and angular concepts
... 7. Newton’s 1st Law - the law of 7. Newton’s 1st Law - the law of inertia inertia A body at rest remains at rest and a A body at rest remains at rest and a body in motion remains in motion in a body that is rotating remains rotating straight line unless acted upon by an unless acted upon by an outsi ...
... 7. Newton’s 1st Law - the law of 7. Newton’s 1st Law - the law of inertia inertia A body at rest remains at rest and a A body at rest remains at rest and a body in motion remains in motion in a body that is rotating remains rotating straight line unless acted upon by an unless acted upon by an outsi ...
Learning Outcomes
... 13. Can I predict what will happen to the acceleration of an object if only the force changes? 14. Can I use the equation F=ma when only one force is acting? 15. Can I use the equation F=ma when more than one force is acting? 16. Can I use Newton’s laws to explain: a) the motion of an object during ...
... 13. Can I predict what will happen to the acceleration of an object if only the force changes? 14. Can I use the equation F=ma when only one force is acting? 15. Can I use the equation F=ma when more than one force is acting? 16. Can I use Newton’s laws to explain: a) the motion of an object during ...
1 1. b (From Newton`s second law, the net torque is equal to the
... 1. b (From Newton’s second law, the net torque is equal to the rotational inertia times the angular acceleration; so, the correct choice must correspond to the situation where the torque is maximum. Since the torque is defined as the tangential force times the distance to the axis, the correct answer ...
... 1. b (From Newton’s second law, the net torque is equal to the rotational inertia times the angular acceleration; so, the correct choice must correspond to the situation where the torque is maximum. Since the torque is defined as the tangential force times the distance to the axis, the correct answer ...
Newton*s Second Law Examined
... • Anna is pushing a 7 kg box with 7 N of force to the left, but the box does not move. What is the force of static friction? • What is the max static frictional force if the coefficient of static friction for these materials is 0.31? ...
... • Anna is pushing a 7 kg box with 7 N of force to the left, but the box does not move. What is the force of static friction? • What is the max static frictional force if the coefficient of static friction for these materials is 0.31? ...
Assignment 9 (365178)
... is 0.20. Its velocity at point A is 7.8 m/s and at point B is 4.2 m/s. Use the impulse-momentum theorem to find how long the sled takes to travel from A to B. s A 7,000 kg railroad car is rolling at 3.5 m/s when a 4000 kg load of gravel is suddenly dropped in. What is the car's speed just after the ...
... is 0.20. Its velocity at point A is 7.8 m/s and at point B is 4.2 m/s. Use the impulse-momentum theorem to find how long the sled takes to travel from A to B. s A 7,000 kg railroad car is rolling at 3.5 m/s when a 4000 kg load of gravel is suddenly dropped in. What is the car's speed just after the ...
Air Resistance Force
... (gain speed) because there is no force big enough to balance the downward force of gravity. • As an object gains speed, it encounters an increasing amount of upward air resistance force. • objects will continue to accelerate (gain speed) until the air resistance force increases to a large enough val ...
... (gain speed) because there is no force big enough to balance the downward force of gravity. • As an object gains speed, it encounters an increasing amount of upward air resistance force. • objects will continue to accelerate (gain speed) until the air resistance force increases to a large enough val ...
Forces
... stronger as either or both objects increase in mass. Earth’s gravitational force is HUGE because the Earth is HUGE! ...
... stronger as either or both objects increase in mass. Earth’s gravitational force is HUGE because the Earth is HUGE! ...
Solution
... If we consider just the pulley above the painter’s head, there is a nonzero horizontal force to the left due to the tension in the rope. So the painter must actually pull the rope slightly to the left to balance this force. b) Find the acceleration of the platform. Solution: Let a1 denote the magnit ...
... If we consider just the pulley above the painter’s head, there is a nonzero horizontal force to the left due to the tension in the rope. So the painter must actually pull the rope slightly to the left to balance this force. b) Find the acceleration of the platform. Solution: Let a1 denote the magnit ...
Physics Web Search: Torque
... 6. From Newton’s second law, a force will cause an __________________________ 7. When considering angular motion, a torque will cause an ___________________ ____________________ (consider both torque equations) 8. What must be the centripetal force that keeps the lady bug moving in a circle? _______ ...
... 6. From Newton’s second law, a force will cause an __________________________ 7. When considering angular motion, a torque will cause an ___________________ ____________________ (consider both torque equations) 8. What must be the centripetal force that keeps the lady bug moving in a circle? _______ ...
Lab 6: Work-Energy Theorem
... force? Hint: it’s not equal to mhangingg. Predict the work WT done on the cart by the string using the fact that it traveled a distance d. b. Using a motion sensor (set Capstone to measure velocity to 3 significant figures) to measure the cart’s maximum velocity. Repeat ten times, determine vexpt an ...
... force? Hint: it’s not equal to mhangingg. Predict the work WT done on the cart by the string using the fact that it traveled a distance d. b. Using a motion sensor (set Capstone to measure velocity to 3 significant figures) to measure the cart’s maximum velocity. Repeat ten times, determine vexpt an ...
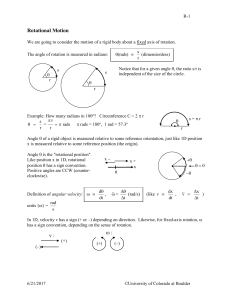
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... Definition of tangential acceleration atan = rate at which speed v along rim is changing d( r ) dv d a t an ...
... Definition of tangential acceleration atan = rate at which speed v along rim is changing d( r ) dv d a t an ...
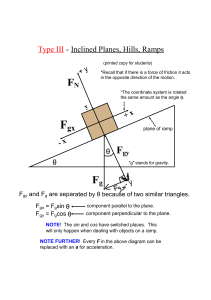
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... constant velocity by exerting a force of 211 N parallel to the inclined plane. a) What is the sum of your applied force, friction and the parallel component of the trunk's weight? Justify your ...
... constant velocity by exerting a force of 211 N parallel to the inclined plane. a) What is the sum of your applied force, friction and the parallel component of the trunk's weight? Justify your ...
Gravitation - Siena College
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Each mass particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that varies directly as the product of the two masses and inversely as the square of the distance between them. ...
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Each mass particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that varies directly as the product of the two masses and inversely as the square of the distance between them. ...
The work done on an object by an external force is given by the
... Work The work done on an object by an external force is given by the formula Wdone = force displacement Work is our first example of a scalar product or dot product. A dot product occurs when two vectors are multiplied together in such a way as to produce a scalar value. Technically, the above defin ...
... Work The work done on an object by an external force is given by the formula Wdone = force displacement Work is our first example of a scalar product or dot product. A dot product occurs when two vectors are multiplied together in such a way as to produce a scalar value. Technically, the above defin ...