* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gravitation - Siena College
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
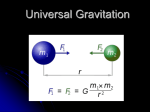
Gravitation Ch 9: Hasbun Ch 5: Thornton & Marion Introduction Newton, 1666 Published in Principia, 1687 (needed to develop calculus to prove his assumptions) Newton’s law of universal gravitation Each mass particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that varies directly as the product of the two masses and inversely as the square of the distance between them. Cavendish Experiment Henry Cavendish (1731-1810) verified law and measured G G=6.67 x 10-11 N m2 / kg2 video Extended Objects Gravitational Field Gravitational field = force per unit mass For point masses: For extended objects: White Boards Is gravity a conservative forces? Gravitational Potential Gravitational field vector can be written as the gradient of a scalar function: Φ is the gravitational potential Energy/mass We can obtain Φ by integrating: Potential from Continuous Mass Distributions Prime denotes integration element Gravitational Potential Once we know Φ, we can determine the gravitational force and the gravitational potential energy. Example What is the gravitational potential both inside and outside a spherical shell of inner radius b and outer radius a? Poisson’s Equation Gauss’s Law for the electric field Gauss’s Law for gravity Poisson’s Equation Lines of Force & Equipotential Surfaces Equipotential lines connect points of constant potential Force is always perpendicular to the equipotential lines Like a contour map, lines of equipotential show where an object can move while maintaining constant gravitational potential energy Using Potential Potential is a convenient way to calculate the force Force is physically meaningful In some cases, it might be easier to calculate the force directly Potential is a scalar Example Consider a thin uniform disk of mass M and radius a. Find the force on a mass m located along the axis of the disk. Solve this using both force and potential. Lagrange Points Solved by Euler & Lagrange Sun is M1 Earth-Moon is M2 Stable equilibrium L4 , L 5 WMAP satellite in L2 MATLAB Problem Start with the following code. Adjust the mass ratios and contour levels until you recreate the plot showing the Lagrange points. Name your file equipotential.m